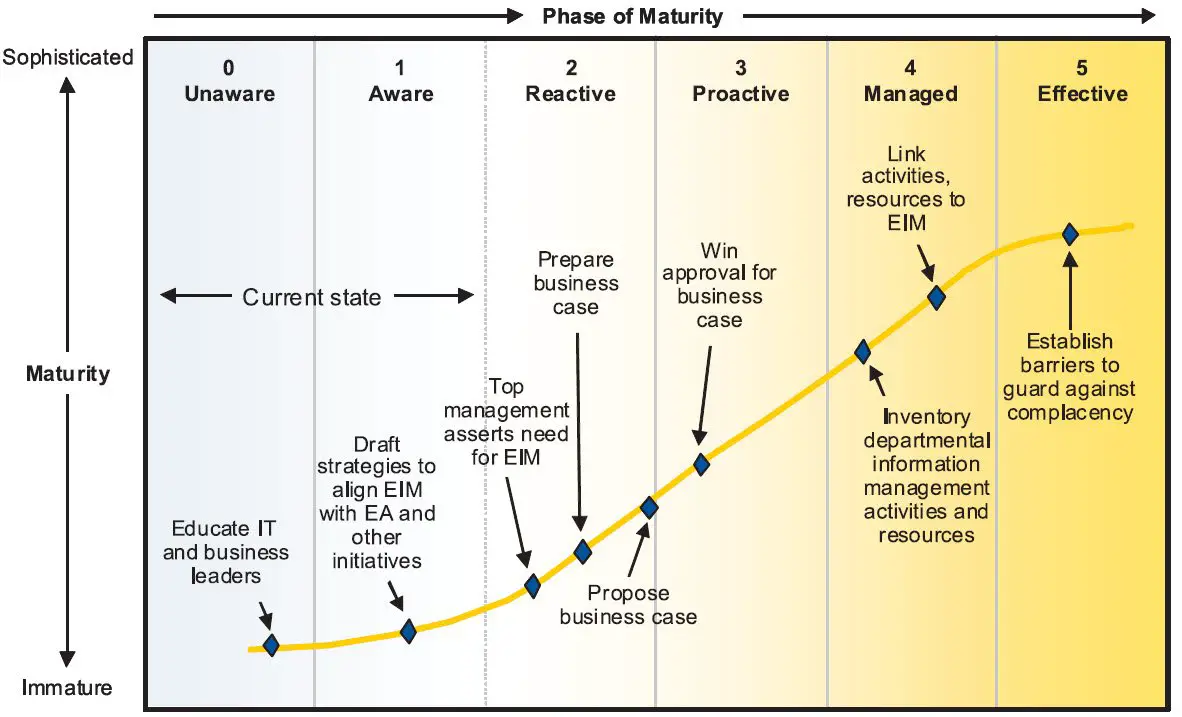
Stanford Data Governance Maturity Model
As an educator, speaker, and data governance professional I sometimes get asked,
How can you measure the effectiveness of your data governance program?
From my experience, there are two main ways to do so:
This series of articles is focusing on the second option by offering an introduction to some of the existing maturity models. So far Ive covered IBM data governance maturity model and it makes most sense to follow it with Stanfords as it follows the same maturity levels as IBMs.
Students Who Viewed This Also Studied
ISA 101 Mod 10 Measurement.docx
Defense Acquisition University
CSIA 310 Week 7 Discussion.docx
University of Maryland, University College
CSIA 310
ACQ 202 Module 3 Exam Part III.pdf
Defense Acquisition University
Defense Acquisition University ISA L10
ISA L10 Exam
Defense Acquisition University ISA 101
ISA 101 Mod 10 Measurement.docx
DEWA Islamabad Campus ACQ 1202
2 part 2
University of Maryland, University College CSIA 310
CSIA 310 Week 7 Discussion.docx
Defense Acquisition University ACQ 202 MODULE 3
ACQ 202 Module 3 Exam Part III.pdf
And What Is A Data Governance Maturity Model
A data governance maturity model is a tool and methodology used to measure your organization’s data governance initiatives and communicate them simply to your entire organization. In a mature organization, all the processes to manage, access, and innovate using data assets are in place. Less advanced organizations can use the maturity model to achieve this objective.
There are a handful of well-known data governance maturity models, including examples from IBM, Stanford, Gartner, and Oracle. These models provide a method by which a business can learn how to manage data effectively, provide user access, ensure that data is of high quality, and make it possible for everyone in an organization to benefit from these advances.
When a company achieves the highest level of data governance maturity, it will see palpable results. Company-wide, data will be used to innovate and collaborate and make better business decisions, while these same organizations will avoid the huge fines that arise when data protection regulations are not observed.
You May Like: Goverment Jobs In Las Vegas
The Ibm Data Governance Council Maturity Model: Building A Roadmap For Effective Data Governance
- Views:
Transcription
1 October 2007 The IBM Data Governance Council Maturity Model: Building a roadmap for effective data governance
2 Page 2 Introduction It s been said that IT is the engine for growth and business innovation in the 21st century, and data is the gasoline that fuels it. And while data is undeniably one of the greatest assets an organization has, it is increasingly difficult to manage and control. From structured to unstructured data including customer and employee data, metadata, trade secrets, , video and audio organizations must find a way to govern data in alignment with business requirements without obstructing the free flow of information and innovation. For many organizations today, data is spread across multiple, complex silos that are isolated from each other. There are scores of redundant copies of data, and the business processes that use the data are just as redundant and tangled. There is little cross-organizational collaboration, with few defined governance and stewardship structures, roles and responsibilities. Businesses want to leverage information for maximum performance and profit. They want to assess the value of data as a balance sheet asset, and they want to calculate risk in all aspects of their operations as a competitive advantage in decision-making. It is for these reasons that data governance has emerged as a strategic priority for companies of all sizes.
Data Governance Maturity Model: How Mature Is Your Approach To Data
Thereâs been a global shift toward data-driven business. But, in many cases, the data just under the surface is dirty, and itâs failing modern companies.
In their2020 Global data management research report, Experian estimated that many businesses aiming for agile, data-driven approaches believe almost a third of their data to be inaccurate.
âWhile the business wants to be agile and informed by data, this level of distrusted data often leads leaders to fall back on making decisions by gut instinct rather than by informed data insight.â Experian Global Managing Director of Data Quality Mike Kilander
That doesnât just mean a large chunk of the data the companies have isnât working for them. It means their data is working against themâcosting them money, frustrating their employees, and getting in the way of opportunities.
If you donât take an active role in your data governance, your dirty data will snowball, picking up crud as it rolls forward. If left uncleaned, it can tarnish up to 70% of your data after one year. This data erosion will directly impact your bottom line–as it does for 83% of companies–and cost you an average of 23% of your revenue.
Mature data governance is no longer a wish list item for modern companies. Itâs table stakes, so much so that, according to the 2019 State of Data Management Report, governance is one of the top five strategic initiatives for global companies.
Read Also: Polk Real Foreclosure
What Is The Role Of The Executive Steering Committee
A way of anchoring this kind data governance aim within an organisation is to establish and empower an Executive Steering Committee. This Committee typically consists of a relatively small number of executives and has the information and decision-making capacity to understand and implement not only new, organisation-wide data policies but the cultural change that is required to bring them successfully into practice.
It is important for this Committee to be truly cross-department and be able to assert decisions across different business areas. Failure to ensure that the necessary changes are applied totally and consistently would represent a failure of Data Governance.
An additional important role of the Executive Steering Committee is to establish the possible incentives and penalties that will be implemented in order to promote and maintain the necessary change. Any significant issues raised by Data Stewards, that are not resolvable within their teams will be escalated up to the Data Steward. Possessing the necessary information about the long-term strategic direction of the company, the executives will be able to determine where the balance between business requirements and the demands of a more rigorous data regimen.
You can read more about Data Governance Committees in our comprehensive exploration of Practical Data Governance.
Useful And Practical Data
Proper implementation and practice of improved data standards impacts the entire enterprise-wide data lifecycle. Data is made to be useful and fit-for-purpose without going through unnecessary and time-consuming rounds of processing. Proper use of metadata, badging and rating of assets and visualisations ensures that everyone is clear on the usefulness and limitations of any given element. This is a good way to build organisation-wide confidence in data, which is a major step in achieving good Data Governance.
Read Also: Las Vegas Government Jobs
Radcliffe Big Data Maturity Model
The Radcliffe big data maturity model, as other models, also consists of distinct maturity levels ranging from:
- 0 â “In the dark”
Current BDMMs have been evaluated under the following criteria:
- Completeness of the model structure
- The quality of model development and evaluation
- Ease of application
- Big data value creation
What Does It Mean To Have A Data Governance Framework
In the previous blog on Data Stewardship, we highlighted David Plotkins breakdown of the data management space in to the Three Ps, wherein Data Governance is concerned with the Policies and Processes and Data Stewardship refers to the effective implementation and maintenance of Procedures. The overall aim is to establish an organisation-wide web of responsibility and accountability. Data that exists in a void is useless. Data that accounts for the fact that it is produced and used by people, richly contextualised and fit-for-purpose, is the lifeblood of a successful enterprise.
Don’t Miss: Polk County Fl Forclosure
Data As A Business Asset
The path to effective organisational policy-driven data governance begins with recognising data as a valuable business asset and works towards building a framework that cultivates the value that it provides. It involves stepping back from the day-to-day decisions and processes in order to see the bigger picture and understand how poor data quality management leads directly or indirectly to lost revenue. An important aspect of this is to ensure that this outlook transcends departments and represents a truly organisation-wide change in attitude and processes, with responsibility and accountability effectively assigned.
Roles Around Data Governance
A few roles are key to the practice of data governance. Three roles ensure that standards are created and maintained over time, aiding in data compliance, security, data quality and automation goals.Chief data officer
Executive sponsors, such as chief data officers, signal the importance of a data governance program to the organization through its prioritization. These individuals are instrumental in the development of a cross-functional council, which usually sources members from various business units to represent the needs and concerns of different disciplines or product portfolios. This committee serves as a forum to communicate new data governance initiatives and assign responsibilities to achieve agreed upon timelines and outcomes.Data owners
These individuals are responsible for the state of the data. They are usually designated by the type of data that they manage, such as customer or financial data, and their role seeks to maintain data accuracy and usability. Common tasks include troubleshooting data issues, approving data definitions, and providing data recommendations, particularly as it relates to any regulatory requirements.Data stewards
Recommended Reading: Free Government Flip Phones
Level : There Is No Formal High
Level 2: Some lines of business have processes and standards for performing riskassessments. Risk assessment criteria are defined and documented for specificitems and the process is repeatable. There is limited context tovalidate that the risks identified are significant to the organization as a whole.
Which Data Governance Maturity Model Should You Use
Although there are several data governance maturity models out there, the best known were developed by OvalEdge, IBM and Gartner. As mentioned earlier in this blog, a maturity model is a tool for measuring the level of your data governance capabilities. So, you must ensure that when you adopt a maturity model, you also have in place a data governance framework and roadmap that follows the same methodology.
When you set out to decide on a data governance maturity model you need to consider many factors. These include key business drivers, the budget required to implement the model, the existing data management and governance framework, and the industry you operate in.
Also Check: Free Dental Implants Grants
Is There An Data Governance Australia Code Of Practice
Data Governance Australia are a not-for-profit industry association which aims to further:
principles-based self-regulatory regime that sets leading industry standards and benchmarks for responsible and ethical data-practices
For a number of years they have been accepting submissions from a range of data-involved organisations in order to put together a code which can be voluntarily adhered to by organisations. It has not been been published in its final form, but periodically released draft versions give us some idea of what it is going to look like.
In order to be compliant with the Code, a company has to make a determined effort to commit and abide to a list of 9 Principles, in addition to any other relevant legally binding obligations. These Principles are No-harm, Honesty & Transparency, Fairness, Choice, Accuracy, Stewardship, Security, Accountability and Enforcement.
The elaboration of these principles in the Code, show that they are essentially a combination of imperatives to abide with previously existing legislation, assertions that emphasise the importance of building accountability and responsibility into systems as well as an overarching call to act in good faith when dealing with data on a variety of different levels.
You can read more about the history of cloud data risks and evolving perceptions of data management and security in an Australian context here.
What Is Ibm Progress Maturity Model
IBMmaturity modelsmaturity modelmaturity assessment
. Also asked, what is data governance maturity model?
The Maturity Levels. Developed by the Software Engineering Institute in 1984, the Capability Maturity Model is a methodology used to develop and refine an organization’s software development process and it can be easily applied to an organization’s DG program and processes.
Subsequently, question is, why are maturity models important? A maturity model is a tool that helps people assess the current effectiveness of a person or group and supports figuring out what capabilities they need to acquire next in order to improve their performance. Maturity models are structured as a series of levels of effectiveness.
what is a process maturity model?
Maturity models are frameworks which help to assess the maturity level in a specific domain. Process maturity models aim at appraising an organisation’s level of process-centricity. They help to measure how effectively and efficiently the organisation is working, by means of its process management capabilities.
What does maturity level mean?
A maturity level is a well-defined evolutionary plateau toward achieving a mature software process. Each maturity level provides a layer in the foundation for continuous process improvement.
Read Also: Rtc Employment Las Vegas
Data Governance Maturity Model Gartner
First presented in 2008, this data maturity model looks at the enterprise information management system as one single unit. It has five primary goals, as follows:
This maturity model has a total of six stages of maturity. Each stage has its own attributes and action items. Lets take a look at each stage in detail:
Data Governance Maturity Models Explained
It is a good practice to assess the maturity of your organizations system periodically. Maturity is the quantification of an organizations ability and scope for improvement in a particular discipline.
A high level of maturity implies higher chances of improvement after the occurrence of an error or any incidence for that discipline.
These improvements could be either the quality or the use or implementation of the resources within the organization.
Data maturity models help companies understand their data capabilities, identify vulnerabilities, and know in which particular areas, employees need to be trained for improvement.
It also helps organizations compare their progress among their peers.
With maturity assessment, there is never a one model fits all situation. Although individual models for different organizations and vendors do exist, most follow the Capability Maturity Model method.
Here, we will go through two Data governance maturity models developed by two different vendors. Lets dive right in.
Read Also: Government Jobs Vegas
Make Better Decisions With Better Data
Your data governance is only as mature as the data underneath it is good. To become truly data-driven, you must ensure you have a single, high-quality source of truth to work with.
Avo helps you create this single source of truth and make the right data-driven decisions to move your business by allowing you to prioritize, inspect, analyze, and future-proof your tracking to create reliable data now and tomorrow.
The Ibm Data Governance Unified Process
- Author admin
The benefits of a commitment to a comprehensive enterprise Data Governance initiative are many and varied, and so are the challenges to achieving strong Data Governance.
Many enterprises have requested a process manual that lays out the steps to implement a Data Governance program. Obviously, every enterprise will implement Data Governance differently, mainly due to differing business objectives. Some enterprises might focus on data quality, others on customer-centricity, and still others on ensuring the privacy of sensitive customer data. Some organizations will embrace a formal Data Governance program, while others will want to implement something that is more lightweight and tactical.
Regardless of these details, every organization should perform certain steps to govern its data. The IBM Data Governance Unified Process shown in Figure 2.1 maps out these 14 major steps , along with the associated IBM software tools and best practices to support an effective Data Governance program.
The ten required steps are necessary to lay the foundations for an effective Data Governance program. An enterprise will then select one or more of the four optional tracks, namely Master Data Governance, Analytics Governance, Security and Privacy, and Information Lifecycle Governance. Finally, the Data Governance Unified Process needs to be measured, and the results conveyed to executive sponsors, on a regular basis.
Lets walk through the steps in the figure in further detail:
You May Like: Trucking Grants
Benefits Of Data Governance
Stakeholders can achieve cross-organization success with strong data governance practices that enable deeper insights while protecting data.Better data security and compliance
Different types of data may have different permissions or rules surrounding it, especially if that data contains personally identifiable information . Data governance practices can help promote security and compliance, assisting companies in reducing risks of breaches and fines, and protecting customer trust. Data governance practices help to know what PII exists and where, and through policy and metadata management can automate compliance.
Privacy regulations are only on the rise with global sweeping regulations like the European General Data Protection Regulation that provides data privacy to European citizens, particularly on the internet. Additionally, there are more industry-specific and regional regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act for protecting patients and their personal health information. Spurred by the rise in data-driven marketing and increasingly remote work, compliance regulations are only becoming more prevalent, as customers become more aware of their data rights and as companies address increasing reputational risks.Improved data quality
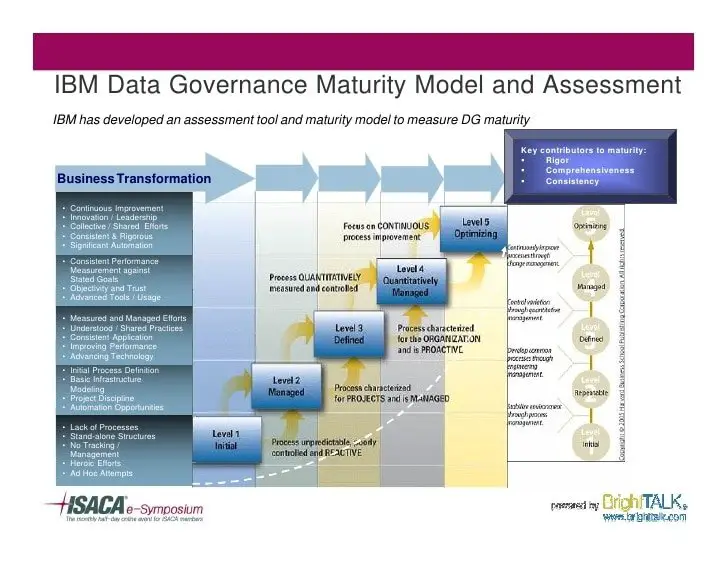
Data Governance Maturity Model Ibm

Introduced in 2007, this data governance model addresses a total of 11 domains mentioned below:
This model consists of a total of five levels. Lets take a quick look at the characteristics and the action items required for each level:
You May Like: Free Touch Screen Government Phones Georgia
What Exactly Is Data Governance Maturity
Data governance maturity refers to the stage an organization has reached in the implementation and adoption of data governance initiatives. An immature organization will have a great deal of unorganized data and will not be using this data to drive growth. Alternatively, a mature organization will be well-aware of the importance of data as a key business asset and governing and managing it accordingly.
