How Are Medicare Supplement Plans Funded
Unlike other parts of Medicare, supplemental plans are entirely supported by beneficiary premiums and coinsurance costs. The plans do not receive money from the federal government.
Because Medicare Parts A and B cover only about 80% of medical costs, a supplemental plan is used to fill in the coverage gaps and reduce the amount that enrollees pay for medical care. Beneficiaries buy supplemental plans, which are also known as Medigap policies, from insurance companies such as Aetna, Cigna and UnitedHealthcare.
Medicare And Medicaid Costs
Medicare is administered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services , a component of the Department of Health and Human Services. CMS works alongside the Department of Labor and the U.S. Treasury to enact insurance reform. The Social Security Administration determines eligibility and coverage levels.
Medicaid, on the other hand, is administered at the state level. Although all states participate in the program, they aren’t required to do so. The Affordable Care Act increased the cost to taxpayersparticularly those in the top tax bracketsby extending medical coverage to more Americans.
According to the most recent data available from the CMS, national healthcare expenditure grew 9.7% to $4.1 trillion in 2020. That’s $12,530 per person. This figure accounted for 19.7% of gross domestic product that year. If we look at each program individually, Medicare spending grew 3.5% to $829.5 billion in 2020, which is 20% of total NHE, while Medicaid spending grew 9.2% to $671.2 billion in 2020, which is 16% of total NHE.
What If Youre Self
Employers are required to withhold FICA taxes from employee paychecks. Self-employed individuals paying the self-employment tax instead of FICA taxes. The SE tax is the same 15.3% as FICA taxes . Self-employed individuals have to pay the entire tax since they dont have an employer to pay half, but they can deduct the employer half of the taxes on their tax returns.
If youre self-employed, youll need to pay estimated taxes to cover the self-employment tax. Learn more about how to make estimated tax payments.
Also Check: United States Government Life Insurance
Medicare And The Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act reduced the disparity in drug costs by closing the Donut Hole between the authorizations for prescription benefits.
The ACA reduced some payments to beneficiaries while increasing services in the qualified health plan requirements. Original Medicare meets the standards for Obamacare coverage due to the addition of the below-described essential benefits, prevention services, and wellness reforms.
- Added prevention and wellness benefits at no costs to users
- Reduced the Donut Hole and help it disappear in future years
- Management improvement, costs reduction, and better patient outcomes
- Strengthened the Trust Fund for Hospital Insurance
Is Medicare State And Federally Funded
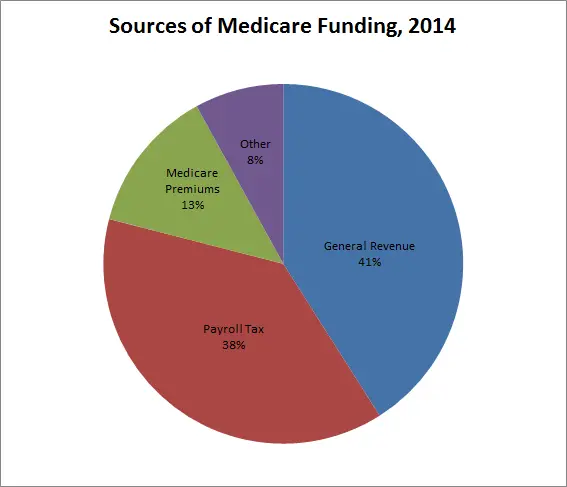
Medicare is federally administered and covers older or disabled Americans, while Medicaid operates at the state level and covers low-income families and some single adults. Funding for Medicare is done through payroll taxes and premiums paid by recipients. Medicaid is funded by the federal government and each state.
You May Like: Tyler Technologies County Government Records
Managing For Success And Savings
The Affordable Care Act has revised the fee for services approach to Medicare and particularly the Original Medicare. The law has moved Medicare to a value-based approach that has turned in some solid signs of improvement in payments, costs, and performance.
The system detects and discourages waste, inaccuracy, and overcharges by providers. Fee for service medicine emphasized the volume of patients seen and the number of services performed.
This approach put pressure on providers to see patients too frequently and perform tests, procedures, and activities with only marginal benefits. The value basis goes to results and efficiency.
Tell Me The Origin Of Medicare
Part A or Part B Medicare is commonly called Original Medicare. Original Medicare was created by the federal government and provides Medicare eligible individuals insurance coverage and specialized healthcare services that accept Medicare.
There are fee-for-service plans which means a Medicare user pays an annual fee for each service. Medicare pays its part of the approved sum in monetary terms, and Medicare pays the rest. The Congressional Budget and Administration Office manages Medicare. CMS is part of the Department of Health.
Recommended Reading: United States Government Watch List
What Are The Two Treasury Accounts Used To Pay For Medicare
The federal government relies on two trust funds to finance Medicare services provided through Medicare Part A and Medicare Parts B and D, respectively.
One trust fund, known as the Hospital Insurance Trust Fund, supplies money for Part A services. The other trust fund, known as the Supplemental Insurance Trust Fund, provides money for Parts B and D.In other words, Part A draws funding from the HI Trust Fund, while Medicare Parts B and D derive funding from the SMI Trust Fund.
The HI Trust Fund is funded through the following sources that finance Part A:
- Payroll taxes from employers and employees
- Part A premiums from people who dont qualify for premium-free Part A
- Income from taxes from Social Security benefits
- Interest from trust fund investments
The SMI Trust Fund is funded through sources that provide money for Parts B and D:
- Funds authorized by Congress
- Interest accrued from trust fund investments
How Are Costs Contained
Annual per capita health expenditures in the United States are the highest in the world , with health care costs growing between 4.2 percent and 5.8 percent annually over the past five years.43
Private insurers have introduced several demand-side levers to control costs, including tiered provider pricing and increased patient cost-sharing . Other levers include price negotiations, selective provider contracting, risk-sharing payments, and utilization controls.
The federal government controls costs by:
-
setting provider rates for Medicare and the Veterans Health Administration
-
capitating payments to Medicaid and Medicare managed care organizations
-
capping annual out-of-pocket fees for beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans and individuals enrolled in marketplace/exchange plans
-
negotiating drug prices for the Veterans Health Administration.
However, since most Americans have private health insurance, there are limited options available to the federal government. The ACA introduced cost-control levers for private insurers offering marketplace coverage, requiring that insurers planning to significantly increase plan premiums submit their prospective rates to either the state or the federal government for review.
Attempts to contain pharmaceutical spending are limited to a few mechanisms:
Also Check: Getting A Job With The Federal Government
Is Medicare Funding Going To Run Out
The government allocates funds to the SMI Trust Fund annually in the hope that this will reduce a potential funding deficit. Like other SMI trust funds, HI Trust Funds do not receive an annual funding from Congress, making them vulnerable to the economic conditions.
Medicare Part A expenditures have outpaced Medicare Part A revenue, which results in a slow and surely depleted funding stream. The federal government has predicted that by 2021 the HI Trust Fund will run out.
How Is Medicare Part D Funded
About 73% of the $105.8 billion in Medicare D spending is derived from general revenue. An additional 15% is generated by beneficiary premiums, while another 11% in funding comes from payments from the state for dual eligible beneficiaries who qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid because of having a low income.
Medicare Part D is an optional benefit that helps beneficiaries enrolled in Original Medicare pay for prescription drug coverage. Private insurance companies administer Part D prescription drug plans, charging beneficiaries premiums, deductibles and copays as part of the policies coverage of prescription drugs.
You May Like: Government Surplus Computers For Sale
The Solvency Of The Medicare Hi Trust Fund
This measure involves only Part A. The trust fund is considered insolvent when available revenue plus any existing balances will not cover 100 percent of annual projected costs. According to the latest estimate by the Medicare trustees , the trust fund is expected to become insolvent in 8 years , at which time available revenue will cover around 85 percent of annual projected costs for Part A services. Since Medicare began, this solvency projection has ranged from two to 28 years, with an average of 11.3 years. This and other projections in Medicare Trustees reports are based on what its actuaries call intermediate scenario but the reports also include worst-case and best-case projections that are quite different .
States Give Requirements For Medigap Variety
Although Medicare is a federal program, states help regulate Medigap by licensing companies that offer Medigap insurance companies. In other words, states require that private insurance carriers offer a wide variety of Medigap insurance options.
Law standardizes each type of Medigap policy to cover specific Medicare-approved services in specific amounts, meaning that all Medigap plans of the same type only differ in terms of premium charged by the private carrier.
States mandate the availability of different Medigap options to account for wide medical needs and cost preferences, regardless of a persons location.
The private companies that offer Medicare Supplements must offer an approved combination of plans. States require a combination of comprehensive plans along with any limited option plans.
Despite being subject to state rules for types of Medigap plans, the insurance companies offering the policies can assess a persons medical history to determine whether to accept or reject applications.
Medicare Supplement requires Medicare Parts A, and B. Acceptance is guaranteed during open enrollments and the initial enrollment period.
Also Check: Federal Government Jobs Tucson Az
What Is Being Done To Reduce Disparities
Several federal agencies are tasked with monitoring and reducing disparities. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality publishes an annual national report highlighting disparities in health care quality by race/ethnicity, age, and sex. According to the latest report, disparities related to income and race persist but grew smaller between 2000 and 2016.35 African Americans, American Indians, Alaska Natives, Native Hawaiians, and Pacific Islanders received worse care than whites according to about 40 percent of quality measures. Hispanics and Asian Americans received worse care per 35 percent and 28 percent of measures, respectively. Disparities for poor and uninsured populations are also persisting in major priority areas for quality.
Certain federal offices have specific responsibilities related to reducing disparities:
The ACA created a legal requirement for nonprofit hospitals, which are exempt from paying certain taxes because of their charitable status, to conduct community health needs assessments together with community stakeholders to identify and address unmet health needs in their communities. This requirement is enforced through the Internal Revenue Service, and reporting must be made available to the public.37
How Is Medicare Part B Funded
Nearly 75% of the $452.3 billion annual budget for Medicare Part B comes from general revenues, which are primarily raised through federal income taxes and other government taxes.
Another 25% of funding comes from the monthly premiums that Medicare Part B enrollees pay. Interest on Social Security payments accounts for a very small portion, less than 1%, of Part B funding.
The amount that Part B enrollees pay is adjusted annually. And in 2022, the standard monthly cost of Medicare Part B is $170.10, which is automatically deducted from Social Security payments. Enrollees with an income higher than $91,000 per year pay higher rates.
Read Also: Articles On Politics And Government
General Fund Revenue As A Share Of Total Medicare Spending
This measure, established under the Medicare Modernization Act , examines Medicare spending in the context of the federal budget. Each year, MMA requires the Medicare trustees to make a determination about whether general fund revenue is projected to exceed 45 percent of total program spending within a seven-year period. If the Medicare trustees make this determination in two consecutive years, a “funding warning” is issued. In response, the president must submit cost-saving legislation to Congress, which must consider this legislation on an expedited basis. This threshold was reached and a warning issued every year between 2006 and 2013 but it has not been reached since that time and is not expected to be reached in the 20162022 “window”. This is a reflection of the reduced spending growth mandated by the ACA according to the Trustees.
C: Medicare Advantage Plans
| Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
With the passage of the Balanced Budget Act of 1997, Medicare beneficiaries were formally given the option to receive their Original Medicare benefits through capitated health insurance Part C health plans, instead of through the Original fee for service Medicare payment system. Many had previously had that option via a series of demonstration projects that dated back to the early 1970s. These Part C plans were initially known in 1997 as “Medicare+Choice”. As of the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003, most “Medicare+Choice” plans were re-branded as “Medicare Advantage” plans . Other plan types, such as 1876 Cost plans, are also available in limited areas of the country. Cost plans are not Medicare Advantage plans and are not capitated. Instead, beneficiaries keep their Original Medicare benefits while their sponsor administers their Part A and Part B benefits. The sponsor of a Part C plan could be an integrated health delivery system or spin-out, a union, a religious organization, an insurance company or other type of organization.
The intention of both the 1997 and 2003 law was that the differences between fee for service and capitated fee beneficiaries would reach parity over time and that has mostly been achieved, given that it can never literally be achieved without a major reform of Medicare because the Part C capitated fee in one year is based on the fee for service spending the previous year.
Don’t Miss: Free Internet Through The Government
Trust Fund Versus Budget Perspectives
Medicare provides access to health insurance coverage for over 40 million people who qualify due to disability, permanent kidney failure, or age. The three components of Medicare are Parts A, B, and D.1 Part A, or hospital insurance , provides coverage for inpatient hospital services, skilled nursing facility services, hospice services, and post-institutional home health care. Covered services and items under Part Bone component of supplementary medical insurance include physician services, durable medical equipment, laboratory services, outpatient hospital services, physician-administered drugs, dialysis, and certain other home health care services. The other component of SMI, Part D, principally provides access to prescription drug coverage through private insurance plans beginning in 2006.
Medicare’s financial transactions consist of payments for health care services and administrative expenses, and receipt of taxes and other revenues. These operations are handled through the HI trust fund and the Parts B and D accounts in the SMI trust fund, and they can be considered from two different viewpoints: a trust fund perspective and a budget perspective.
Costs And Funding Challenges
Over the long-term, Medicare faces significant financial challenges because of rising overall health care costs, increasing enrollment as the population ages, and a decreasing ratio of workers to enrollees. Total Medicare spending is projected to increase from $523 billion in 2010 to around $900 billion by 2020. From 2010 to 2030, Medicare enrollment is projected to increase dramatically, from 47 million to 79 million, and the ratio of workers to enrollees is expected to decrease from 3.7 to 2.4. However, the ratio of workers to retirees has declined steadily for decades, and social insurance systems have remained sustainable due to rising worker productivity. There is some evidence that productivity gains will continue to offset demographic trends in the near future.
The Congressional Budget Office wrote in 2008 that “future growth in spending per beneficiary for Medicare and Medicaidthe federal government’s major health care programswill be the most important determinant of long-term trends in federal spending. Changing those programs in ways that reduce the growth of costswhich will be difficult, in part because of the complexity of health policy choicesis ultimately the nation’s central long-term challenge in setting federal fiscal policy.”
You May Like: Government Rebate For Hybrid Cars
Better Care Better Outcomes
The Affordable Care Act has moved Medicare to a value based system of management. This emphasizes the importance of initial care.
Thorough diagnostics and impactful treatment processes reduce the need for further and far more costly treatment in future years for these patients. This, in turn, reduces demands on Medicare and re-admissions.
The old system promoted higher demands with incentives based on the volume of care rather than the quality of care. The Act stabilized funding for the Medicare HI Trust through 2028.
Is Medicare Funded By Taxpayers
You might be wondering who pays for Medicare. Medicare is funded by taxpayers. Your FICA taxes are the primary source of funding for Medicare. Total Medicare costs are covered by income tax, employer payroll tax, interest from Medicare trust funds, premium payments, and some government subsidies. You and your employer both pay 1.45% of your income into the Medicare trust fund. If you are self-employed, then youll be required to cover the entire 2.9%. There is also no income cap on this tax, so youll pay it on every dollar you earn regardless of how much income you have.
Don’t Miss: Government Pandemic Extra Stimulus Bonus Program
What’s The Difference Between Medicaid And Medicare
Medicare is a federal program that provides health coverage if you are 65+ or under 65 and have a disability, no matter your income. Medicaid is a state and federal program that provides health coverage if you have a very low income. … They will work together to provide you with health coverage and lower your costs.
How Are Medicare Supplements Funded
The federal government doesnt contribute financially to Medigap premiums.
If youd like more information on Medicare plans near you, complete an online rate comparison form to have an agent get in contact with you. Also, you can call the number above and speak with a Medicare expert today!
- Was this article helpful ?
Recommended Reading: Is Planned Parenthood Government Funded
