Where Does Government Debt Go
Public Debt. . The public holds over $21 trillion, or almost 78%, of the national debt. 1 Foreign governments hold about a third of the public debt, while the rest is owned by U.S. banks and investors, the Federal Reserve, state and local governments, mutual funds, pensions funds, insurance companies, and savings bonds.
Maintaining Canadas Low Debt Advantage
Entering into the crisis, Canada had the lowest net debt-to-GDP ratio among the Group of Seven countries, reflecting significant holdings of financial assets. Due to temporary COVID-19 related spending, the federal debt-to-GDP ratio is expected to rise from 31 per cent in 2019-20 to 49 per cent in 2020-21. Even with this adjustment, Canada is expected to maintain its low-debt advantage.
G7 General Government Net Debt, 2019 and 2020
- Text version
154 15
In addition, Canada has a diversified investor base that promotes more certainty of access to funding markets over time, contributes to lower and less volatile yields for government securities, and provides flexibility to meet changing financial requirements. Canadian investors, such as insurance companies, pension funds and financial institutions, hold more than two-thirds of outstanding Government of Canada securities, which helps provide a buffer against potential fluctuations in foreign demand. In addition, Canada has a balanced portfolio of debt instruments with a wide range of maturities. This helps meet the needs of many different types of investors and provides the government more funding options.
Chart A3.3
-
144% 95%
How Is The Covid
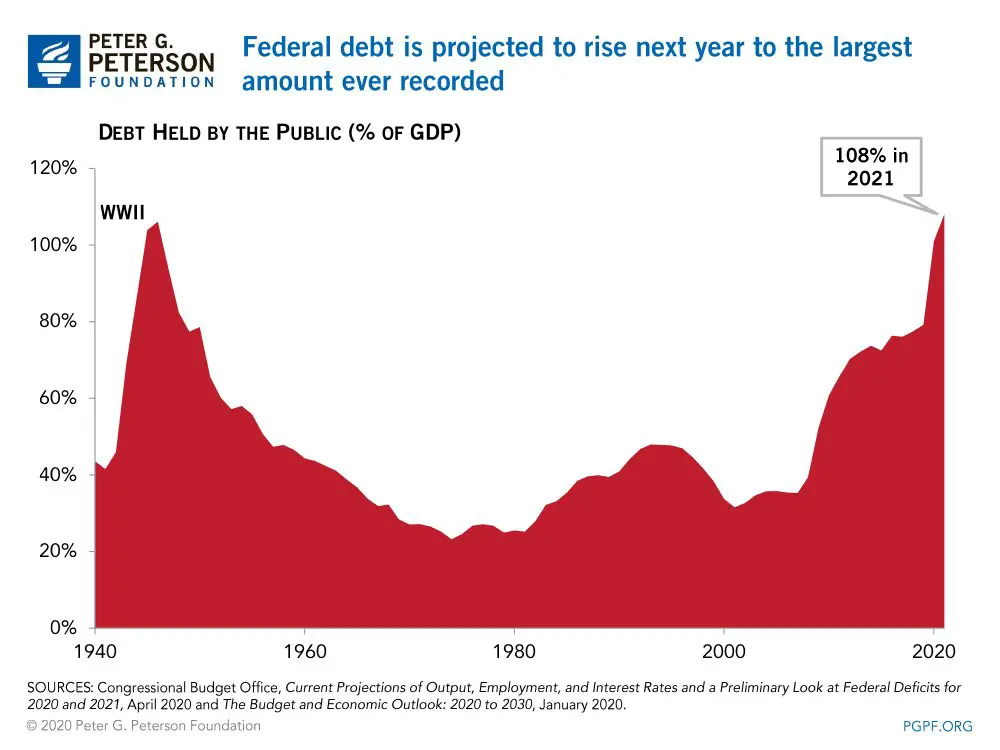
In response to the pandemic, the federal government has spent trillions of dollars to boost the economy, including on stimulus checks for citizens and aid for businesses and state and local governments. According to the Congressional Budget Office , these measures swelled the federal deficit to $3.1 trillion in 2020, about 15 percent of GDP and the highest level since World War II. Even before the pandemic, the CBO projected that annual deficits would breach the $1 trillion mark in 2020 and remain above that level indefinitely.
More on:
Debt held by the publicthe measure of how much the government owes to outside investorswas $16.9 trillion in 2019. That was more than double the amount in 2007, an increase to almost 80 percent of GDP from 35 percent. Before accounting for spending to combat COVID-19, publicly held U.S. debt was set to nearly double to more than $29 trillion over the next decade. Now, it is about $22 trillion, and its projected to be double the size of the economy by 2051.
Also Check: How Are Governments Using Blockchain Technology
How Much Is The Us Debt Limit
The cap is now $28.4 trillion. During the Trump administration, the debt limit was suspended three times. The last suspension passed on a bipartisan basis in 2019, when the debt stood at $22 trillion ended in July.
Since then, the Treasury Department has been engaging in what it calls extraordinary measures to keep the government operating.
What’s Stopping The Us From Paying Down Its Debt
![U.S. National Debt Is Growing Rapidly [Infographic] U.S. National Debt Is Growing Rapidly [Infographic]](https://www.knowyourgovernment.net/wp-content/uploads/u-s-national-debt-is-growing-rapidly-infographic.jpeg)
Most creditors dont worry about a nation’s debt until it’s more than 77% of gross domestic product that’s the point at which added debt cuts into annual economic growth, according to the World Bank. At the end of the second quarter of 2021, the U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio was 125%. That’s much higher than the tipping point and is a concern for many.
Over $22 trillion of that national debt is public debt, which is what the government owes investors and taxpayers.
So what’s stopping the U.S. from eliminating its debt and paying people back? There are a few main reasons why:
- U.S. economic growth has historically outpaced its debt: For example, the U.S. debt was $258.68 billion in August 1945 but the economy outgrew that in less than a few years. By 1960, GDP more than doubled. Congress believes that today’s debt will be dwarfed by tomorrow’s economic growth.
- Congressional representatives have a lot to lose by cutting spending: If elected officials cut Social Security or Medicare benefits, they could lose their next election, for example.
- Raising taxes can be politically unpopular: Experts believe President George H.W. Bush lost re-election because he raised taxes after promising he wouldn’t at the 1988 Republican convention. He raised taxes in 1990 to reduce the deficit, and voters remembered.
Don’t Miss: Us Federal Government Registration Sam System For Award Management
How Bad Is National Debt
Economists and policy analysts disagree about the consequences of carrying federal debt. Certain aspects are agreed upon, however. Governments that run fiscal deficits have to make up the difference by borrowing money, which can crowd out capital investment in private markets. Debt securities issued by governments to service their debts have an effect on interest rates. This is one of the key relationships that is manipulated through the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy tools.
Proponents of the Modern Monetary Theory believe that not only is a long-term budget deficit sustainable, but it is also preferable to a government surplus however, this view is not held by the majority of economists.
Keynesian macroeconomists believe it can be beneficial to run a current account deficit in order to boost aggregate demand in the economy. Most neo-Keynesians support fiscal policy tools like government deficit spending only after the monetary policy has proven ineffective and nominal interest rates have hit zero.
Chicago and Austrian school economists argue that government deficits and debt hurt private investment, manipulate interest rates and the capital structure, suppress exports, and unfairly harm future generations either through higher taxes or inflation.
What Is Government Debt In Economics
Public debt, sometimes also referred to as government debt, represents the total outstanding debt of a countrys central government. Public debt as a percentage of GDP is usually used as an indicator of the ability of a government to meet its future obligations.
What Is The Meaning Of Government Debt In Economics? Public debt is the total amount, including total liabilities, borrowed by the government to meet its development budget. It has to be paid from the Consolidated Fund of India. The sources of public debt are dated government securities , treasury bills, external assistance, and short-term borrowings.
What Is A Government Debt Called? Government debt is also known as public debt, national debt or sovereign debt and is money owed by a central government to creditors within the country as well as to international creditors.
What Is Government Debt Used For? The public debt is the amount of money that a government owes to outside debtors. Public debt allows governments to raise funds to grow their economy or pay for services. Politicians prefer to raise public debt rather than raise taxes. When public debt reaches 77% of GDP or higher, the debt begins to slow growth.
You May Like: Keep Your Government Hands Off My Medicare
Canadas Debt In Context
The Government of Canada has increased its borrowing in order to make the necessary temporary investments to stabilize the Canadian economy amidst the extraordinary circumstances of the COVID-19 pandemic. The current environment provides a unique opportunity for the government to issue an unprecedented level of long-term bonds at historically low interest rates. This will ensure Canadas debt remains affordable and is less vulnerable to increases in interest rates for future generations. Despite an increased deficit for 2020-21, public debt charges are expected to decline, and the country is retaining its low-debt advantage . As noted in Annex 2, Canadas public debt charges are expected to be more than $4 billion lower this year compared to the forecast in the 2019 Economic and Fiscal Update.
Chart A3.1
Federal Debt and Public Debt Charges
- Text version
Public Debt Charges Federal Debt Public Debt Charges 1994 0.9
Increased Risk Of Government Default
As the national debt per capita increases, the likelihood of the government defaulting on its debt service obligation increases. The situation means that the Treasury Department will have to raise the yield on newly issued Treasury securities in order to attract new investors. This reduces the amount of tax revenue available to spend on other governmental services because more tax revenue will have to be paid out as interest on the national debt.
Over time, this shift in expenditures will cause people to experience a lower standard of living, as borrowing for economic enhancement projects becomes more difficult.
Recommended Reading: Government Loans For Small Business Startup
Why Does The Us Government Have Debt
The U.S. Government is just like a business. The Government has to provide services for the people of the United States such as military protection, education and health programs, the space program, and social services programs. It also needs money to buy supplies and equipment.
The Government’s main source of money is the taxes it collects from individuals and businesses. There are different kinds of taxes. Here are some examples:
- Income tax
- Sales and excise tax
- Corporate tax
However, the amount of money the Government spends to pay for the services it provides is often more than the taxes it collects. To make up the difference, the Government borrows money in other words, it goes into “debt.”
Why Is Raising The Debt Limit So Difficult
For many years, raising the debt ceiling was routine. But as the political environment has become more polarized, brinkmanship over the debt ceiling has increased. The House used to employ the Gephardt Rule, which required the debt limit to be raised when a budget resolution was passed, but that was for the most part phased out during the 1990s.
During the 2011 debt ceiling battle, some argued that President Barack Obama had the power to unilaterally lift the debt ceiling. Former President Bill Clinton said at the time that if he were still in office he would invoke the 14th Amendment, which says the validity of U.S. debt shall not be questioned, raise the debt ceiling on his own and force the courts to stop him.
Mr. Obama and his lawyers disagreed and opted against that approach. After leaving office, Mr. Obama acknowledged that he and Treasury officials considered several creative contingency plans, such as minting a $1 trillion coin to pay off some of the national debt. In a 2017 interview, he described the idea as wacky.
You May Like: Articles On Politics And Government
What Does The Rest Of The Budget Look Like
Emergency spending aside, most of the federal budget goes toward entitlement programs, such as Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid. Unlike discretionary spending, which Congress must authorize each year through the appropriations process, entitlements are mandatory spending, which is automatic unless Congress alters the underlying legislation. In 2019, only 30 percent of federal spending went toward discretionary programs, with defense spending taking up roughly half of that.
National Debt Vs Budget Deficit
First, it’s important to understand what the difference is between the federal government’s annual budget deficit and the outstanding federal debt, known in official accounting terminology as the national public debt. Simply explained, the federal government generates a budget deficit whenever it spends more money than it brings in through income-generating activities. These activities include individual, corporate, or excise taxes.
To operate in this manner of spending more than it earns, the U.S. Treasury Department must issue Treasury bills, notes, and bonds. These Treasury products finance the deficit by borrowing from the investors, both domestic and foreign. These Treasury securities also sell to corporations, financial institutions, and other governments around the world.
By issuing these types of securities, the federal government can acquire the cash that it needs to provide government services. The national debt is simply the net accumulation of the federal government’s annual budget deficits. It is the total amount of money that the U.S. federal government owes to its . To make an analogy, fiscal or budget deficits are the trees, and the national debt is the forest.
You May Like: Government Grants Anyone Can Get
Concerns Over Chinese Holdings Of Us Debt
According to a 2013 Forbes article, many American and other economic analysts have expressed concerns on account of the People’s Republic of China’s “extensive” holdings of United States government debt as part of their reserves. The National Defense Authorization Act of FY2012 included a provision requiring the Secretary of Defense to conduct a “national security risk assessment of U.S. federal debt held by China.” The department issued its report in July 2012, stating that “attempting to use U.S. Treasury securities as a coercive tool would have limited effect and likely would do more harm to China than to the United States. An August 19, 2013 Congressional Research Service report said that the threat is not credible and the effect would be limited even if carried out. The report said that the threat would not offer “China deterrence options, whether in the diplomatic, military, or economic realms, and this would remain true both in peacetime and in scenarios of crisis or war.”
When Will The Debt Limit Be Breached
Technically, the United States hit its debt limit at the end of July, following a two-year extension that Congress agreed to in 2019. Treasury Secretary Janet L. Yellen has been using extraordinary measures since then to delay a default. Those are essentially fiscal accounting tools that curb certain government investments so that the bills continue to be paid.
The Bipartisan Policy Center estimates that Treasury will really run out of cash sometime between Oct. 15 and Nov. 4. However, it is more difficult to project the so-called X-date because of all the pandemic relief money that the government is distributing and uncertainty surrounding how much tax revenue will be coming in this fall.
You May Like: Government Home Loans For First Time Buyers With Bad Credit
What Are The Primary Drivers Of Future Debt
The main drivers are still mandatory spending programs, namely Social Securitythe largest U.S. government programMedicare, and Medicaid. Their costs, which currently account for nearly half of all federal spending, are expected to surge as a percentage of GDP because of the aging U.S. population and resultant rising health expenses. Yet, corresponding tax revenues are projected to remain stagnant.
Meanwhile, interest payments on the debt, which now account for nearly 10 percent of the budget, are expected to rise, while discretionary spending, including programs such as defense and transportation, is expected to shrink as a proportion of the budget.
President Trump signed off on several pieces of legislation with implications for the debt. The most significant of these is the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. Signed into law in December 2017, it is the most comprehensive tax reform legislation in three decades. Trump and some Republican lawmakers said the bills tax cuts would boost economic growth enough to increase government revenues and balance the budget, but many economists were skeptical of this claim.
The CBO says the law will boost annual GDP by close to 1 percent over the next ten years, but also increase annual budget shortfalls and add another roughly $1.8 trillion to the debt over the same period. In addition, many of the provisions are set to expire by 2025, but if they are renewed, the debt would increase further.
President Andrew Jackson Cuts Debt To Zero
The War of 1812 more than doubled the nations debt. It increased from $45.2 million to $119.2 million by September 1815. The Treasury Department issued bonds to pay a portion of the debt, but it was not until Andrew Jackson became president and determined to master the debt that this national curse, as he deemed it, was addressed.
The time of prosperity was short-lived, as state banks began printing money and offering easy credit, and land value dropped.
Also Check: Government Help For Single Pregnant Mothers
Interest Rates On Government Debt
Looking at the total amount of debt as a percent of GDP provides insight into the relative financial situation of the government, but it does not provide the full story. Another thing to consider when looking at government debt is how much it costs to service that debt.
Similar to when a client is shopping for a mortgage, the government also has to be mindful of prevailing interest rates that will affect the total cost of borrowing. Looking at the total value of a mortgage is important, but the more meaningful number to assess the affordability of the mortgage or debt is the monthly payment which is impacted by the mortgage interest rate.
Though debt levels have increased over the past few decadeswith a recent large increase due to COVID-19 stimulus spendinginterest rates have also come down substantially and are currently sitting near zero. This means that the cost of servicing these large national debts remains manageable despite the size of the debt increasing.
In the below chart, we can see that U.S. national debt interest payments rose following WWII and the dot-com bubble of the late 1990s, where they were in fact higher than 2019. Though we do not yet have data for 2020, we can safely expect that debt expenses will have risen with the recent increase in the amount of total debt.
Increased Costs To Borrow Money
As the yield offered on Treasury securities increases, the cost of borrowing money to purchase a home will also increase because the cost of money in the mortgage lending market is directly tied to the short-term interest rates set by the Federal Reserve and the yield offered on Treasury securities issued by the Treasury Department.
Given this established interrelationship, an increase in interest rates will push home prices down because prospective homebuyers will no longer qualify for as large a mortgage loan. The result will be more downward pressure on the value of homes, which in turn will reduce the net worth of all homeowners.
Also Check: Government Assistance Cell Phone Programs
