Skills For Quality & Data Governance Specialist Resume
- Work experience with health care data and health care process / operations
- Progressive health insurance experience with a Blue Cross Blue Shield Plan
- One to two years of experience in data governance activities
- Experience with data quality concepts, data quality metrics and governance processes is required
- Extensive experience in working in a Data Governance and/or Quality delivery function
Identify And Recruit The Early Adopters
The next step is to survey the list of intersecting priorities identified in step 2, note the accountable leaders for each and identify which of these leaders are likely early adopters of data governance. Energetic leaders who truly understand the importance of data governance should be top of mind. Once each group establishes its governance objectives, these leaders often naturally become the champions of the organizations new data governance program.
Creating a list of desired characteristics for a data governance leader launches the search for early adopters. Geoffrey
Moores book Crossing the Chasm offers valuable insights into important characteristics of effective early adopters:
- Connections: Early adopters need to be connected to the right resources.
- Enthusiasm: Because early adopters motivate others to get on board, they must understand what needs to be done and why and be excited to get to work.
- A deep understanding of data governance: Early adopters should understand data governance on more than a casual level and be aware of the challenges and benefits. Such awareness fuels the drive necessary to break through the inertia early in the programs development.
As the list of candidates grows, some questions that probe each persons understanding of the benefits of data governance will help narrow down the list to those most likely to carry the data governance program across the finish line. Consider questions such as the following:
The Data Governance Committee Charter
From the outset, this committee made it clear that its purpose wasnt to own data, but to facilitate its use for effective decision-making. To that end, the committee pursues four primary goals for data:
Information governance. This involves bringing clinical, administrative, and technology partners together to jointly design and optimize information assets in alignment with the organizations strategies and goals. It also includes the declaration of sources of truth, systems of record, roles and responsibilities, information delivery standards and certified enterprise reports/dashboards. Data security and access decisions are within the scope of this governance.
Quality. Successful decision making is enabled by data that is complete, timely, accurate and consistent. The Committee assures data quality through standardization, process engineering and the creation and monitoring of data quality metrics.
Usability. Usability includes easy-to-use applications that promote data interaction and informed decision making, as well as creating a common data language for understanding organizational performance. Tools to create such usability include data dictionaries, training, a metadata repository, and access to trusted data sets as close to real-time as possible.
Also Check: City Of Las Vegas Government Jobs
Data Quality Dimension #: Timeliness
Timeliness references whether information is available when it is expected and needed. Timeliness of data is very important. This is reflected in:
- Companies that are required to publish their quarterly results within a given frame of time
- Customer service providing up-to date information to the customers
The timeliness depends on user expectation. Online availability of data could be required for room allocation system in hospitality, but nightly data could be perfectly acceptable for a billing system.
As you can see, data quality is an important issue that should be considered starting with initial application design, all the way through implementation, maintenance and use. In future blog posts, we will discuss techniques for addressing these types of data quality issues.
S Toward Better Data Governance For Your Organization
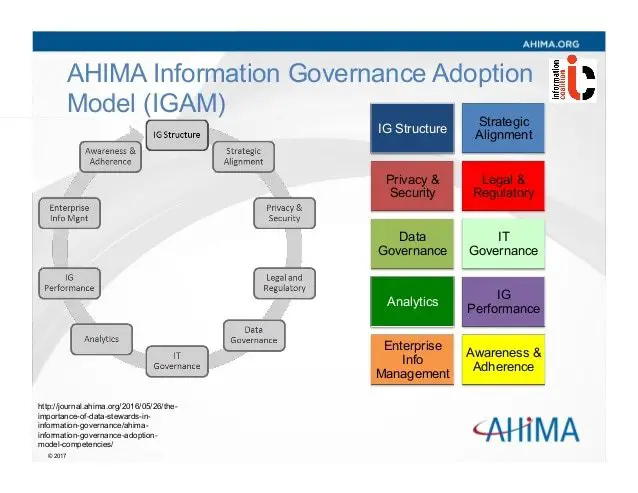
The above examples are illustrative and only a small part of building the right infrastructure for data governance within any organization, whether that be a health system, health information exchange or health plan. Higher quality data within electronic health records pays for itself through better patient care. It eases clinical workflow, improves decision support and enables accurate performance measurement. Moreover, it empowers cross-provider interoperability. Clinicians and analysts alike spend less time on data cleanup and more time on improving care quality and efficiency. The reality is that little or no resources are allotted to data cleanup, and the problems can persist and spread through growing data exchange.
There are many resources that can help, such as SAFER guidelines put out by ONC and various programs in health information management and informatics. Whatever you do to improve data quality and governance, it needs to be put in routine practice with real-world data. Doing a test, usually against test data samples, once every few years with sample data isnt effective data governanceits just box checking.
The software that enables better governance will come from many sectors. Some will be open-source and free. Those are great places to start, but require technical skill and caution when applied to protected health information. Others come from a framework of private and not-for-profit organizations.
Organizational Governance Resources
Recommended Reading: Government Jobs In Las Vegas Area
Electronic Health Record Data Governance And Data Quality In The Real World
John DAmore, MS, President & Informatics, Diameter Health and Sandra Mitchell, RPH, MSIS, FASHP, J P Systems HIMSS Members
Healthcare data grows daily by petabytes. With over a billion healthcare encounters a year in the United States alone, this wealth of data exceeds current structures for data governance and scope of secondary use. The past decade has successfully delivered data digitization and a reduction in paper records, but the next decade requires healthcare leaders to play catch upwe need to find the right tools to effectively govern clinical data in EHRs. Ultimately this will pay rich dividends in how we can improve both care quality and efficiency.
First, lets talk about a problem we believe is the largest challenge for this generations health IT and informatics professionals: data quality. Medicine and nursing historically started as craft industries, where students learned under mentors with myriad ways to document for effective diagnosis and treatment. Documentation wasnt consistent between institutions or even individual clinicians.
What is data governance?
This program brought electronic health records to well over 80% of ambulatory physicians and virtually every hospital in the United States.
Data included in the USCDI source: The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology
Data Governance Vs Data Management
First, lets clear up any confusion between data governance and data management. Both address questions of where data is stored, how it is accessed, and whether it can be trusted.
The key difference between data management and data compliance is their scope:
- Data management is an IT practice encompassing an organizations practices across the data life cycle
- Data governance policies are business practices pertaining that define how data is processed across the organization to ensure privacy and compliance
In simple terms, you can have data management without data governance policies , but you cant have data governance without data management.
Data governance addresses who has ownership of which data, and who can access the data. Data governance is also the discipline concerned with whether given data is subject to privacy laws or other regulatory requirements, and what its security requirements should be. The data retention and deletion policies defined by a data governance framework become part of the data life cycle.
Recommended Reading: Good Jobs For History Majors
Skills For Data Governance Specialist Resume
- Establish enterprise-wide training and mentoring for tools required for data governance practices
- Accountable for establishing and managing business processes for data governance
- Arrange training for all data governance personnel including Data Stewards, DQ Analyst, Metadata Analyst, etc
- Approve all labels and packaging that contains SKU data
- Plan and run a Proof of Concept and implement roll out and maintain a new Data Governance tool including its business data glossaries and workflows
- Assist with the implement of data management solutions using available data management tools
What Is Data Quality Management
Data quality management is a set of procedures and technologies for effectively integrating and validating data sources, securely collaborating between trusted parties, handling lifecycle systems such as aggregation and deduplication, and safely sharing the results while protecting sensitive customer information.
Effectively managing data quality is particularly important in the healthcare industry. Electronic healthcare records and reports are not only heavily governed by strict regulationssuch as HIPAAbut also affect physical treatments and policies. They have a very real and tangible impact on peoples lives.
Also Check: City Of Las Vegas Government Jobs
Build Your Team To Be Self
Once youve set up sufficiently strong data governance protocols and have a solid data governance strategy, data governance professionals often work best when allowed to make their own interior processes and design decisions. Allowing your team to self-organize will ensure that they can optimize their processes and do their job as efficiently as possible. Once the connection between the business offices data priorities and the data governance teams goals has been established, the team may function best with minimal outside interference and strong internal management. Depending on the size of your organization, you may need a team as small as one or two people, or you may need a larger team. Regardless of size, filling all of the essential data governance roles may save your organization many headaches down the road.
What Is Data Governance
Data governance defines the rules, influence, and regulations for data in order to set and oversee appropriate policy. These rules and policies establish decision rights, as well as the controls that ensure security, accountability, and trustworthiness. Governance is not active day-to-day oversight, but rather a strong foundation for a viable data management system. Like any governance structure, data governance is in place to foster good use of information through sound policy, clarity of controls, and consistent processes.
Data governance stems in part from the collapse of Enron, Adelphia, and other businesses in the early 2000s, which forced companies to take another look at their data and the U.S. government to pass laws ensuring that corporations post accurate financial reports. Data governance formed the core of this work to satisfy requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and other regulations. But data governance has evolved over its relatively short life, and today, even small businesses need available, accurate, and comprehensive information to lead their decision-making and growth.
Recommended Reading: Government Grants To Start Trucking Business
Challenges For Data Governance In Healthcare Organizations
- Data governance is a complex but increasingly important department for any modern healthcare organization to have. The associated challenges in healthcare include:
- Building and organizing a system that makes intuitive sense
- Ensuring efficient and intentional movement of data throughout an organization
- Reducing security breach risks
- Creating a foundation that can be built on as the healthcare organization grows
- While these are all issues, thoughtful and intentional planning in the first stages of the healthcare data governance process will help alleviate some of these potential challenges.
Getting Started With Data Quality Management In Healthcare
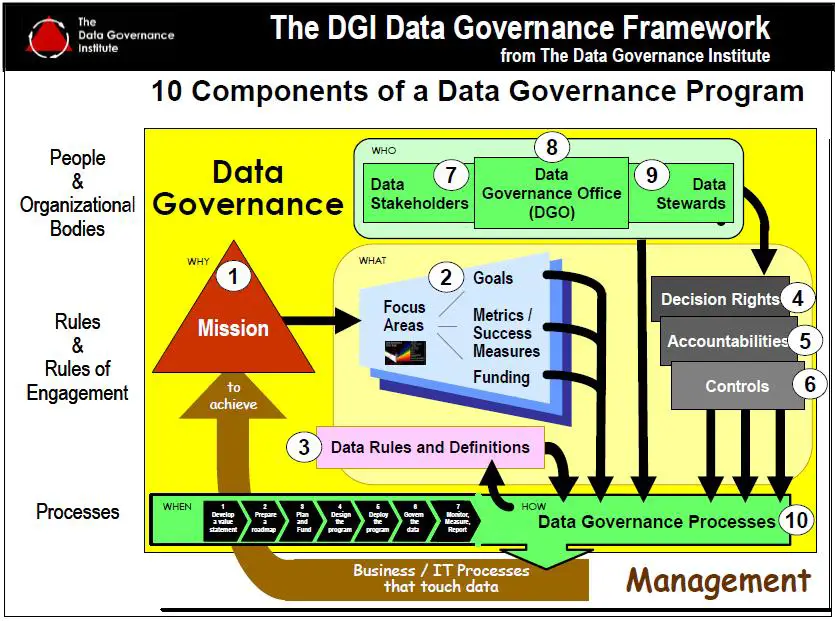
Data quality management has become an essential part of healthcare organizations of all forms. While data processing systems are becoming key components of operational decision making and individualized treatment processes, poor data quality and management is becoming a primary inhibitor of operational success and is causing significant strain on such processes.
Building a comprehensive and trusted data integration system that can deliver with speed is essential to resolving the strains that come from poor data management. Talend Data Fabric offers a suite of applications to help healthcare organizations properly manage their data in all environments multi-cloud and on-premises by providing a unified and collaborative system for securely collecting, processing, and governing large amounts of data.
To see how Talend can benefit your organization, try Talent Data Fabric to learn for yourself how data quality management can be used to create a more comprehensive and scalable data system for your entire organization.
You May Like: Trucking Business Grants
Standardizing Terms And Definitions Throughout The Industry
Having standardized clinical coding standards is crucial for the quality and safety of health service delivery. Currently, EMRs dont all use the same data domains. In many cases, they dont share the same business definitions, clinical terminology or metadata, which means that they refer to health symptoms, diseases, medications and procedures differently.
Its vital for patient care and healthcare research and development to share data across disparate systems, providers, networks and applications in a meaningful way.
Going Beyond An Edw With A Data Operating System
To be successful, the late-binding approach to data warehousing requires the right technology foundation. Organizations trying to implement a late-binding data warehouse with traditional ETL or data processing tools often find themselves overwhelmed with the volume of analytic requests. Their methodology scales, but their tools and people do not.
At the core of the Health Catalyst® Data Operating System platform is a metadata-driven data processing engine and toolset that allows organizations to scale their analytics efforts. It enables the building of a late-binding data warehouse with a significantly lower total cost of ownership than other solutions. Additionally, DOS allows you to take the analytic value contained in your data warehouse and use it in new and interesting ways to drive clinical and business improvements throughout your organization.
Recommended Reading: Polk County Fl Forclosure
Identify The Scope Of The Opportunity Appropriately
Many organizations tackling data governance try to do too much too soon and get bogged down. Its important to scope the opportunity narrowly enough to get traction with a small pilot team that is nimble enough to improvise and redesign processes on the fly. Focus on a specific data governance opportunity within a specific area to target the effort on a manageable subset of the organizations data governanceversus trying to fix all of it at once.
If the data governance team chooses one of the loftier organizational goals, such as increase patient engagement, it will need to refine this into something more precise, such as, increase usage of the patient portal by 10 percent of patients in the Tri-Cities region.
This is psychologically and physically pragmatic. It renders the problem more familiar by focusing on the teams immediate domain . It also lowers the amount of data, oversight, and approval that might otherwise be needed and could impede the teams progress
The Nuts And Bolts Of Data Governance: Tools And Frameworks
Data governance is not in and of itself a technology, but it can be aided by the use of technology tools. A governance committee sets the guidelines, policies, and focus, and this team should be a prime driver for deploying appropriate data governance tools. Tools that support security and compliance will work differently than those that value storage and retrieval. However, as with most initiatives that involve changing roles or processes, transparent and continual communication should be a high priority. The right tool can also foster this function.
When researching appropriate tools, look for one that strikes the appropriate balance between the role of governance and the functional framework that supports data management.
As with other software solutions and tools, your choice will depend on your organizations needs. Some tools may be labeled as data governance solutions, while others may be primarily used for different purposes, but are able to address governance needs.
The following are vendor tools for data governance:
- Collibra
For more information on these and other processes, read this article.
You May Like: Grants To Start A Trucking Business
How To Gain Data Governance Experience
How can HIM professionals hone their data governance skills to lead efforts within their organizations?
Pursuing aBachelor of Science in Health Information Management and Technology is a great place to start. An HIMT degree focuses on many of the ten important data governance core competencies:
Students in the four-course, HIMSS-approved UW HIMT technology track explore data governance competencies in depth. Examples of technology track course outcomes include:
HIMT 375 Database Structures and Management Systems: Analyze and design databases to support computer-based information systems. Develop and implement relational database management systems using SQL. Topics include: data-modeling techniques such as entity-relationship modeling, extended entity-relationship modeling, database constraints, database normalization techniques, and basic and advanced features of database query language SQL, etc.
HIMT 425 Data Warehousing and Mining: Examine the concept of the data warehouse and its effectiveness in supporting strategic decision making. Address the process of creating data warehouse/data-mart solutions from the identification of the enterprise informational and analytical needs to producing business intelligence by extracting information from the data warehouse by using data-mining methods and models.
Why Do Organizations Need Data Governance
More and more, in-house information is finding a new life as a valued asset across the entire organization rather than simply as the property of individual departments. In fact, many data governance initiatives originate as attempts to improve data as it becomes actionable across the organization. Data is now used to develop organizational efficiencies, identify profit opportunities, enhance customer experiences, and improve or develop new products.
However, two of the primary reasons for data governance are regulatory mandates and risk assessments that rely on high-quality data. In particular, many regulations focus on an organizations data to show proof of compliance, especially in the area of data security. According to the 2013 Rand Secure Archive Data Governance Survey, 82 percent of respondents know they face external regulatory requirements, but 44 percent of those respondents still dont have a defined data governance policy.
Areas that benefit from data governance include those that require regulatory reporting data to meet guidelines for Sarbanes-Oxley Basel I, II, and III COBIT Dodd-Frank cGMP ISO/IEC 38500 and elements of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act .
Read Also: Federal Government Jobs Las Vegas Nv
