What Is Data Security Governance
Gartner defines data security governance as a subset of information governance that deals specifically with protecting corporate data through defined data policies and processes.
You define the policies. You define the processes. There is no one-size-fits-all solution to DSG. Furthermore, there is no single product that meets all of the needs of DSG. You must look at your data and weigh which areas have the greatest need and the most importance to your company. You take data governance into your own hands to avert disaster. Remember that your information is your responsibility.
While there are multiple pathways to safeguarding data logical, physical, and human three primary software methods that IRI customers successfully employ are the classification, discovery, and de-identification of PII and other data considered sensitive.
Figure : Segregation Of Activities
Data governance is responsible for ensuring data assets are of sufficient quality, and that access is managed appropriately to reduce the risk of misuse, theft, or loss. Data governance is also responsible for defining guidelines, policies, and standards for data acquisition, architecture, operations, and retention among other design topics. In the next blog post, we will discuss further the segregation of duties shown in figure 1 however, at this point, it is important to note that modern data governance programs need to take a holistic view to guide the organization to bake quality and privacy controls into the design of products and services.
Privacy by design is an important concept to understand and a requirement of modern privacy regulations. At the simplest level, it means that processes and products that collect and or process personal information must be architected and managed in a way that provides appropriate protection so that individuals are not harmed by the processing of their information nor by a privacy breach.
Detecting and responding to a data breach requires strong organizational alignment, communication, and collaboration. Having data management resources aligned to support privacy management through data governance can improve our ability to know when a breach has happened and respond appropriately without delay. Insufficient alignment will result in undetected breaches, confused response plans, and delays.
You Might Also Like
Data Privacy Is Not Data Security
Security can exist without privacy principles, but privacy needs security in fact, there is no privacy without security.
Implementing a full suite of privacy policies data collection, data processing, data portability, data retention, and data deletion is meaningless if someone can gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. Data privacy and data security professionals must work together to ensure that sensitive data is both private and secure.
Security applies to all types of information, whether it’s PII or not. The question of whether information is personally identifying simply determines the level of security necessary. PII requires the highest security standard. However, privacy encompasses a wider set of obligations than security, including:
- Data lifecycle: The data lifecycle for PII must begin with a clear purpose for collecting user data. It also maps how PII is managed, from collection to deletion.
- Data ethics: Ethics extend beyond lawfulness and compliance with data privacy regulations. Ethical behavior towards personal data includes transparency, openness, and fairness regarding how that data is handled.
- Data quality: While ensuring the accuracy of user data isn’t solely the responsibility of data privacy professionals, it is vital to maintaining data privacy. For example, if patient records aren’t up to date, test results could go to the wrong person.
Don’t Miss: Cio Sp3 Fbo
Data Governance: A Business Strategy
If data management is the logistics of data, data governance is the strategy of data. Data governance should feel bigger and more holistic than data management because it is: as an important business program, governance requires policy, best reached by consensus across the company.
The purpose of data governance is to provide tangible answers to how a company can determine and prioritize the financial benefits of data while mitigating the business risks of poor data. Data governance requires determining what data can be used in what scenarios which requires determining exactly what acceptable data is:
- What constitutes data?
- Where is it collected and used?
- How accurate must it be?
- Which rules must data follow?
- Who is involved in the various stages in a data lifecycle?
Importantly, data governance must go beyond IT and include stakeholders from across the enterprise. In order to ensure the safety, reliability, and trustworthiness of all data, governance requires that stakeholders from all business areas be involved. Consider the alternative: if each business silo approaches their data strategy differently, the end result is chaotic and not comprehensive enough to be useful.
The ultimate goal is to determine a holistic way to control data assets, so that the company can get the absolute most value from the data.
How Is Data Governance Essential To Cybersecurity
Data governance plays an essential role in cybersecurity because data is attackers number one target. Keeping data private and protected prevents hackers from exploiting it. At the same time, categorizing and mapping data helps you understand the types of attackers it appeals to, as well as what methods they may try to get it.
Read Also: City Jobs In Las Vegas Nv
How Does Data Governance Help Cybersecurity
In order to protect against threats, organizations need to know what data to protect and how to help keep it protected.. Information protection is at the core of security, but how can you protect it if you do not know what data you have, where your data is, how it is used, who it is shared with ? Businesses can no longer have perimeter protections in place and call it a day.the perimeter has expanded to suppliers, cloud vendors, partners, and so on. So managing your data in a structured, responsible, and law-abiding way will make it more efficient for security professionals to protect it.
What Is A Data Governance Framework
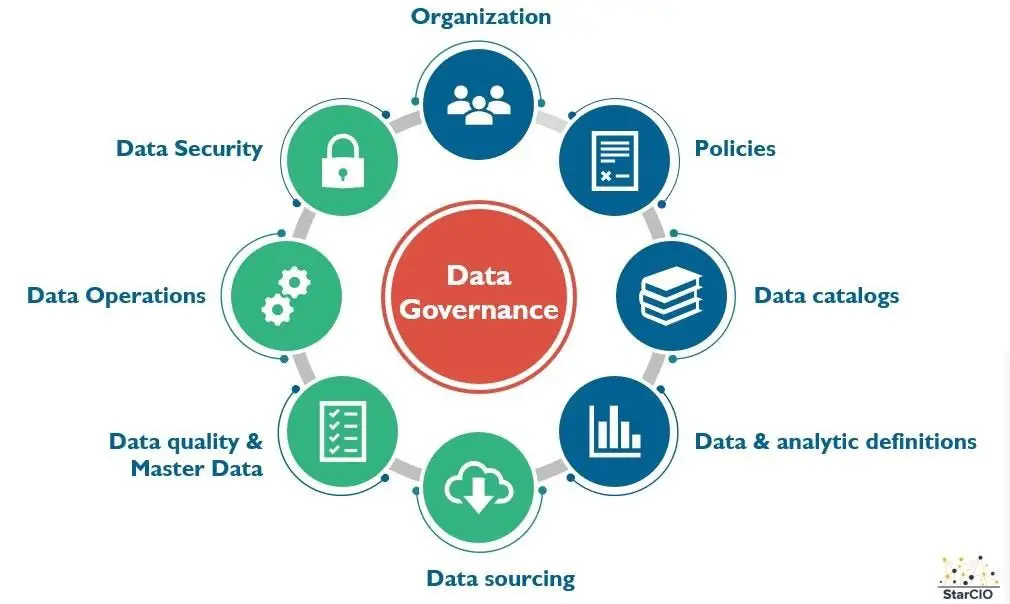
A data governance framework is a set of specific policies and guidance by which your data governance strategy should operate. This framework ensures that policies are consistent and appropriate given your organizations needs, and it allows the business to establish roles and responsibilities around how to treat data.
A data governance framework includes information about the policies and standards on the following issues:
- The overall objectives of data governance in the organization, including any special concerns around security and privacy
- How the enterprise creates data, including approved methods and technologies
- Acceptable methodologies for managing, transferring and removing data from the enterprise
- Metrics for monitoring how successful all of the above activities progress over time
The overarching goal of a data governance framework is to give an organizations data stewards business intelligence and other tools to understand the value of its data and data assets while establishing the rules to manage that data. Adhering to this framework will help your organization improve the overall quality of its data and, over time, improve your businesss ability to make strategic decisions.
You May Like: Las Vegas Government Jobs
What Is It Governance
IT governance ensures that the organizations IT investments support the business objectives, manage the risks, and meet compliance regulations.
Examples of organizations IT investments: physical and technical security, encryption, servers, software, computer and network devices, database schemas, and backups.
Its often argued that these investments are considered a cost center rather than a money generator. Heres some tough talk: organizations wouldnt be able to operate, optimize or even generate revenue without IT.
In short: no IT, no data, and no business.
But good IT operations require dedicated leadership to ensure that tech investments are maximized.
Stakeholders involved in the success of IT governance include the board of directors, executives in finance, operations, marketing, sales, HR, vendors and, of course, the chief information officer as well as other IT management.
The key individual whos responsible for aligning IT governance to the organizations business goals is the CIO.
To accomplish their goals, CIOs will often use existing data governance frameworks, created by industry experts. These frameworks also provide implementation guides, case studies and assessments. Here are some frameworks you may have heard of:
When it comes to frameworks, youll have to decide which one works with your company culture and often times, organizations will find that a hybrid approach works the best.
How Effective Is It
Managing identities is crucial. If done well, youll be able to simultaneously protect your employees and put them at ease, making it easier for them to be as productive as possible. Be it password management, access requests, or any other governance type, theyre all worth investing in.
Automating some facets of identity governance can be especially helpful and save IT administrators time to put towards business needs of higher importance than fielding service requests all day. The Microsoft Authenticator app, for instance, streamlines two-factor authentication by sending a notification directly to an employees phone to confirm their access permissions. For more on passwordless authentication .
While there are obvious benefits to staying up-to-date with identity governance, it also has its ramifications and challenges, including the various mistakes admins are bound to make. Many are still struggling to fine-tune their access lifecycles amidst the constant traffic of users joining and leaving their companies. Is your company prepared to navigate such constant change?
Recommended Reading: Peachtree City Job Seekers
Data Governance Vs Data Protection Vs Information Security: Understanding The Difference
4minute read
The inventor of the World Wide Web, Tim Berners-Lee says, Data is a precious thing and will last longer than the systems themselves.
Is your organization protecting its data and every crucial information? What governs your data?
Well, your data is centered around three terms Data Governance, Data Protection, and Information Security.
Although these terminologies are interrelated, they are all very different from each other.
With this blog post, lets dive deeper into understanding what these three components are and how they differentiate from each other.
Here we go!
Key Differences Among Information Security, Data Governance, and Data Protection
Data Governance
It refers to the procedures organizations follow to govern their data, which can be in the form of digital or hard copy assets.
The Data Governance Institute defines Data Governance as, a system of decision rights and accountabilities for info-related processes, executed according to agreed-upon models which describe who can take what actions with what information, and when, under what circumstances, using what methods.
Data governance is important for businesses because:
a. It protects them against cyber attacks and security breaches.b. It reduces data management costs.c. It increases the ROI of your data analytics.d. It is easier to maintain compliance standards.e. It allows better decision-making.
1. Decentralized Execution for Sole Proprietorship
2. Decentralized Execution for Team
Example #: Regulatory Compliance
Organizations need data governance and data management to extract real value from their data while ensuring regulatory compliance.
For instance, while the GDPR doesnt specify the duration for which organizations must retain their data, a good practice is to maintain records for at least seven years from the end of their tax year/accounting period.
Here, the data governance framework must identify the data to be retained for seven years and the format in which it must be stored and audited according to GDPR. Data management would then be responsible for retrieving the necessary data and cataloging it in the right format within an organizations storage systems.
Don’t Miss: Congress Mortgage Stimulus Program For Middle Class 2021
Create A Catalog For Faster Access
It is also preferable to build a singular source of truth as the initial step to creating a long-lasting advantage. Even though the data is in a simplified landscape, one requires knowing where to find it. Data repositories should be considered as well-organized libraries. They could be stocked with thousands of varied pieces of information. Automated systems and users would never know where to look for them without thousands of individual components. So, setting up a cataloging system allows professionals to easily track down the hunting information.
Gdpr And Other Data Regulations
Data privacy laws specify how data should be collected, stored, and shared with third parties. The most widely discussed data privacy laws include:
GDPR: The European Unions General Data Protection Regulation is the most comprehensive data privacy law in effect. It applies to European Union citizens and all companies that do business with them, including countries not based in Europe. GDPR gives individuals the right to determine what data organizations store, request that organizations delete their data, and receive notifications of data breaches. Noncompliance may result in hefty fines and legal action.
CCPA: The California Consumer Privacy Act is a state-level regulation in the United States. It enables California residents to ask organizations what personal data exists about them, delete it on request, and find out what data has been given to third parties. These measures apply to consumer data gathered within the state.
Read Also: Government Jobs For History Majors
What Is Data Governance And Why Is It Important
Data governance refers to a system that makes sure only authorized people can interact with specific datawhile controlling what they can do, in which situation, and the methods they can use. Organizations need to govern data for the same reasons they need to govern their money. Like money, data is valuable. It can be stolen, but when governed properly, data can play a key role in improving core systems.
Data Mapping And Classification
Although data mapping and classification are intricately linked, they involve different principles and action steps. Data mapping refers to how you connect one data field that exists in one source to a different data field that lives in another source.
How Data Mapping Works
Suppose you have a vendor charged with setting up an e-commerce portal that will process transactions for customers purchasing through your website. To create your system, the vendors team needs to gain access to the following customer data:
The mapping process involves answering two core questions:
The answers to these questions are only the beginning. You also have to determine:
How Data Classification Works
Data classification is typically more straightforward. Classifying data can be done using a few different classification categories, as well as a combination of several. For example, you have to classify data according to:
You May Like: Grants For Teeth Implants
Data Governance Is Not Data Stewardship
Data governance ensures that the right people are assigned the right data responsibilities. Data stewardship refers to the activities necessary to make sure that the data is accurate, in control, and easy to discover and process by the appropriate parties. Data governance is mostly about strategy, roles, organization, and policies, while data stewardship is all about execution and operationalization.
Data stewards take care of data assets, making certain that the actual data is consistent with the data governance plan, linked with other data assets, and in control in terms of data quality, compliance, or security.
Check out our Definitive Guide to Data Governance today
What Are The Similarities Between Data Privacy And Data Security
While they have several significant differences, the fact that data security is fundamental to data privacy also means that they have many similarities. In fact, most privacy laws include data security protections and best practices. If you do business in a region or industry, or manage a particular type of data, then you must comply with those laws.
Also Check: Entry Level Government Jobs For College Graduates
Data Governance Manager And Team
Data governance managers may be covered by the chief data officer role or may be separate staff. This role is responsible for managing your data governance team and having a more direct role in the distribution and management of tasks. This person helps coordinate governance processes, leads training sessions and meetings, evaluates performance metrics, and manages internal communications.
Big Data Privacy Vs Traditional Data Privacy Standards
Of course, data privacy is not a new topic. By the 1970s, it was a recognized concern for issues such as medical records or financial information. In those early days, the first data privacy principles adopted what were often called Fair Information Practices .The FIP efforts in organizations followed five tenants.
- Openness. There should be no systems for collecting personal data that are kept secret.
- Disclosure. Organizations should provide a way for individuals to learn what information is available and how it is used.
- Secondary usage. Information collected for one purpose should not be used for another purpose without the consent of the individual. .
- Correction. Individuals should have the ability to correct or amend erroneous information.
- Security. Any organization creating, maintaining, using or disseminating identifiable personal data must assure the data is being used correctly and must take precautions to prevent misuse.
Don’t Miss: Government Dental Grants For Seniors
What Are The Differences Between Data Privacy And Data Security
Despite their differences, data privacy and data security are interlinked. IT leaders generally view data privacy as a sub-component of data security. And more recently, data governance leaders are making data security a central focus of their responsibilities.
To illustrate the subtle differences between data privacy and data security, consider a bank vault. A bank vault has both security and privacy measures in place to protect the contents within.
Security features thwarts external threats. Guards, an alarm system, and the vaults lock represent security features.
Privacy measures prevent internal threats. Those may include protocols that limit employees access to the vault or knowledge of its contents. Privacy measures can also mitigate external threats, so if personal information is stolen, its value is restricted by anonymization.
Taking a wider view, the primary differences between data privacy and data security are:
