What Is The Filibuster
According to the Senate website which has its own glossary a filibuster is this: Informal term for any attempt to block or delay Senate action on a bill or other matter by debating it at length, by offering numerous procedural motions, or by any other delaying or obstructive actions.
These days, its shorthand for anytime senators demand a supermajority to cut off debate and move to an actual vote on just about anything.
Process For Limiting Or Eliminating The Filibuster
According to the Supreme Court‘s ruling in United States v. Ballin , Senate rules can be changed by a simple majority vote. Nevertheless, under current Senate rules, a rule change could itself be filibustered, requiring two-thirds of senators who are present and voting to end debate.
Despite the two-thirds requirement described above being written into the Senate rules, any Senator may attempt to nullify a Senate rule, starting by making a point of order that the rule is unconstitutional or just that the meaning of the rule should not be followed. The presiding officer is generally expected to rule in favor of the rules of the Senate, but under rule XX, “every appeal therefrom shall be decided at once, and without debate” and therefore by a simple majority as there is no need for a vote on cloture.
Procedure to invoke the nuclear option
Procedurally, the events described went as follows:
A new precedent was thus established allowing for cloture to be invoked by a simple majority on executive nominations, excluding those to the Supreme Court of the United States.
On April 6, 2017, that precedent was further changed by McConnell and the Republican majority, in a 48â52 vote against sustaining the decision of the chair, to include Supreme Court nominations.
More: Biden To Make ‘forceful’ Push For Voting Rights Filibuster Changes In Georgia Speech
In recent decades, a senator merely signaling his or her intent to filibuster a piece of legislation has been enough to stop action on a bill. Leaders, knowing the legislation lacks the support of 60 senators, might drop the issue from consideration and move on to other matters in the meantime.
How did the filibuster come about?
In 1806, then-Vice President Aaron Burr led the charge to eliminate a Senate rule, similar to one seen in the House, that could be used to cut off debate, inadvertently allowing lawmakers unlimited debate to delay proceedings.
In the 1840s, Democratic Sen. John Calhoun exploited this loophole by talking for hours on end to block bills he feared would diminish the power of Southern slave-holding states.
The Senate rule has changed several times since to make it easier for the minority to overcome a filibuster.
You May Like: Government Grants For Changing Careers
When Did The Senate Adopt The Filibuster Rule
Although the U.S. Constitution makes no mention of filibusters, long-winded Senate speeches became an increasingly common tactic in the 19th century.
But getting two-thirds of the Senate was hard, so filibusters continued. Notoriously, they were used by southern senators who sought to block civil rights laws.
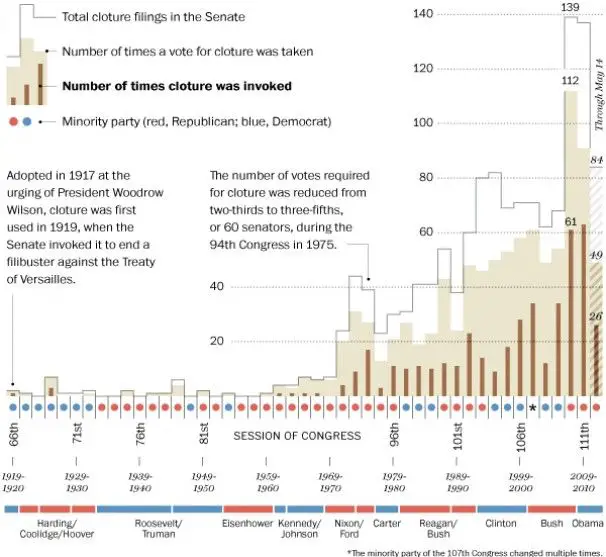
In 1975, the Senate reduced the requirement for limiting debate to three-fifths of the Senate – currently 60 senators.
In that decade, the Senate leadership began agreeing to allow measures that were facing a filibuster to be put aside while the chamber acted on other bills.
The move was intended to prevent opposition to a single bill bringing all work in the chamber to halt, but it also meant that the filibuster changed from an energy-draining maneuver involving lengthy speeches to a mere objection, or threat to object.
Over time the number of filibusters skyrocketed. There is no sure-fire way of counting how many bills are filibustered in a year because of the nebulous nature of the threats. But a count of votes to try to overcome a filibuster, the nearest reliable proxy, shows 298 such votes in the 2019-2020 legislative session. That’s up from 168 such votes in the previous two years. In 1969-1970 there were six.
Whats The History Of The Filibuster And Its Supermajority Requirement

Under original Senate rules, cutting off debate required a motion that passed with a simple majority. But in 1806, after Vice President Aaron Burr argued that the rule was redundant, the Senate stopped using the motion.
This change inadvertently gave senators the right to unlimited debate, meaning that they could indefinitely delay a bill without supermajority support from ever getting to a vote. This tactic is what we now know as a filibuster.
In 1917, the Senate passed Rule XXII, or the cloture rule, which made it possible to break a filibuster with a two-thirds majority. In 1975, the Senate reduced the requirement to 60 votes, which has effectively become the minimum needed to pass a law.
There are, however, exceptions to the filibuster rule. Perhaps the most notable recent example pertains to presidential appointments. In 2013, Democrats changed the Senate rules to enable the confirmation of executive branch positions including the cabinet and of nonSupreme Court judicial nominees with a simple majority. Four years later, Senate Republicans expanded the change to include Supreme Court appointments. Both changes invoked what is known as the nuclear option, or an override of a rule to overcome obstruction by the minority.
You May Like: Government Assistance Paying Utility Bills
Where Did The Filibuster Come From
While our understanding of the Senate as a slower-moving, more deliberative body than the House of Representatives dates to the Constitutional Convention, the filibuster was not part of the founders original vision of the Senate. Rather, its emergence was made possible in 1806 when the Senateat the advice of Vice President Aaron Burrremoved from its rules a provision allowing a simple majority to force a vote on the underlying question being debated. This decision was not a strategic or political oneit was a simple housekeeping matter, as the Senate was using the motion infrequently and had other motions available to it that did the same thing.
Consequently, for many matters in the Senate, debate can only be cut off if at least 60 senators support doing so. While Senate rules still require just a simple majority to actually pass a bill, several procedural steps along the way require a supermajority of 60 votes to end debate on bills.
Is Aaron Burr Really The Father Of The Filibuster
How did the Senate get the filibuster? The unique procedure may have been created thanks to some comments made by Aaron Burr.
The filibuster in its original American form dates back to the Burr era and it allows a Senator to delay a vote on procedures, under certain circumstances. After two recent rules changes, the filibuster can only be used to stall votes about legislation.
The old-school talking filibuster is rare today. Like actor Jimmy Stewart in the film Mr. Smith Goes To Washington, a Senator can speak continuouslysometimes off-the-cuff, other times, reading from a phone bookin a public protest about a vote. The modern version is called a silent filibuster. This happens when a Senator tells his or her floor leader that they wish to filibuster a vote. At that point, at least 60 senators have to agree to override the filibuster in what is called a cloture vote.
These kind of delaying tactics arent exactly new. One of the first recorded masters of the filibuster was the ancient Roman politician Cato the Younger. In Romes senate, Cato would speak until sunset, which was the official ending of a Senate session. One of his last filibusters was to oppose Julius Caesars return to Rome in 60 B.C. Caesar found a political way around Catos filibuster and was able to grab power in Rome anyway.
It still took three decades for the Senate to realize it could actually filibuster a motion, but it was Burrs comments that made it possible.
You May Like: Do I Qualify For A Government Grant
The Emergence Of Cloture
The Philadelphia InquirerUnited States Senate
In 1917, during World War I, at the urging of President Woodrow Wilson, the Senate adopted a rule by a vote of 76â3 to permit an end to debate on a measure in the form of cloture. This took place after a group of 12 anti-war senators managed to kill a bill that would have allowed Wilson to arm merchant vessels in the face of unrestricted German submarine warfare. At any time, a senator could present a cloture motion signed by 16 senators while a measure was pending. One hour after the Senate convened on the second calendar day of session following the filing of the cloture motion, the business then pending would be set aside, and the presiding officer would put to the Senate the question, “Is it the sense of the Senate that the debate shall be brought to a close?” If two-thirds of senators present and voting voted in favor of cloture, the measure would be the unfinished business to the exclusion of all other business no dilatory motions or amendments would be allowed all amendments must have been submitted prior to the cloture vote, and each senator would be limited to 1 hour of debate .
In 1949, in response to filibusters of motions to amend the Journal and motions to proceed to the consideration of bills, the cloture rule was amended to allow cloture to be filed on ‘any measure, motion, or other matter pending before the Senate, or the unfinished business’.
So How Many Votes Are Cloture Votes Today
Senators voted 720 times in 2019 and 2020, according to Senate records. If 298 of those votes were cloture votes, that means about 41% of all the votes senators took in the last Congress were cloture votes.
How would this process be changed?
There are two ways:
This second way of ending filibusters is known as the nuclear option because the idea is it would blow up the Senate system.
You May Like: Canadian Government Grants For Small Business
What Is A Filibuster And Why Reform Is Good
The filibuster has had two forms.
TALKING FILIBUSTER
The original filibusterknown as the talking filibusterrequired Senators to stand up for their principles through real debate and ensured the minority had their voices heard.
SECRET FILIBUSTER
The secret filibuster, which emerged later on, is a “pocket veto” for the Senate minorityallowing them to block legislation without ever engaging in open debate.
Originally, the filibuster existed as a mechanism for those whose conscience demanded they take a stand literally for their principles.
For most of our history, a filibuster required commitment. Senators had to keep speaking all day and night. It required a real belief in a cause, and often would end with one side giving up or a compromise.
But in recent years, the rules were changed so that Senators could filibuster without needing to hold the floor or even defend their position. Rather than being a tool to ensure debate and standing on principle, the filibuster became a way for popular legislation to be blocked from the shadows, for reasons that had nothing to do with conviction.
The movie,Mr. Smith Goes to Washington, depicts an idealistic Senator’s filibuster that allows the People’s interests to overcome special interests.
What is a Filibuster?
The filibuster was created to give the minority a chance to draw attention to its priorities, and it helped ensure important bills would be fully and openly debated.
Filibuster Goes Out of Control
Less Drama More Limits
Changes in senate practice would eventually curb the drama of the filibuster. In the early 1970s, Senate leaders adopted changes that allowed more than one bill or matter to be pending on the floor at once. Before, with only one bill under consideration at a time, a filibuster could stop all other matters in the Senateas long as a senator kept talking.
Now, with multiple measures moving at once, leadership can simply set aside a controversial bill as theoretical debate continues, and move onto other matters in the meantime.
As partisan clashing came to a head in the 1990s and 2000s, senators turned to the filibuster more frequently in an effort to thwart the majority party. According to research by UCLA political scientist Barbara Sinclair, there was an average of one filibuster per Congress during the 1950s.
That number grew steadily since and spiked in 2007 and 2008 , when there were 52 filibusters. By the time the 111th Congress adjourned in 2010, the number of filibusters had risen to 137 for the entire two-year term.
Read Also: Freedom Of Information Act Request Form For Local Government
Examples Of Filibuster In A Sentence
- The senators filibuster of the bill has lasted for over ten hours, with no end in sight.
- The filibuster is a tactic used by members of the Senate to block or delay legislation by continuously speaking for extended periods of time.
- The Senate recently changed its rules to make it more difficult for senators to launch a filibuster, requiring them to actually hold the floor and speak continuously rather than simply threatening to do so.
History And Use Of Reconciliation
Budget reconciliation was created by the Congressional Budget Act of 1974. Under the act, reconciliation can be used on legislation that changes the federal debt limit, revenue, or spending. As it relates to spending, reconciliation can be used to consider changes in spending on entitlement programs with the exception of Social Security. Because appropriations under mandatory spending are typically codified, amendments to those laws are often required. Reconciliation has not been used to change ‘discretionary’ spending because the process to modify discretionary spending is typically addressed through the annual budgetary process.
Process
For reconciliation measures to be considered by the Congress, both chambers must agree on a budget resolution. This resolution must include resolution instructions. Resolution instructions contain four elements:
- 1. the relevant committee to which the instruction is directed,
- 2. the deadline by which committee compliance must be achieved,
- 3. the specific change to either revenues, spending, or the debt , and
- 4. the time period over which those budgetary changes must be achieved.
The Byrd Rule
Advantages of reconciliation over filibusters
Though senators are limited at the number of bills that can be passed via budget reconciliation for any given Congress, scholars Tonja Jacobi and Jeff VanDam note a political advantage for a partisan majority in the Senate to using reconciliation. They write,
Recommended Reading: What Does Data Governance Team Do
Strategy Born Through A Loophole
Throughout history, senators have debated the merits of the filibuster. Some argue its an important tactic empowering a minority party that otherwise would have little sway in the Senate. Others contend it plays too much of a role and is undemocratic in the way it can paralyze the ability of the majority to act.
There is no filibuster in the because rules adopted in that larger legislative body strictly limit the amount of time each representative may speak on the House floor.
The loophole that permits a senators right to speak endlessly on the senate floor dates to Vice President Aaron Burr, who declared in 1805 that the Senate need not be burdened by too many procedural rules. Back then a process to end debate on legislation, known as the previous question motion, was rarely used, so upon Burrs recommendation, the senate dropped it in 1806.
Minority party senators soon figured out that talking endlessly on the Senate floor could prolong debate indefinitely and gum up progress on a bill or nomination. The first successful filibuster was recorded in 1837, when a group of Whig senators who opposed President Andrew Jackson filibustered to prevent Jacksons allies from expunging a resolution of censure against him.
What Is A Filibuster
In the Senate, a filibuster is an attempt to delay or block a vote on a piece of legislation or a confirmation. To understand the filibuster, its necessary first to consider how the Senate passes a bill. When a senator or a group of senators introduces a new bill, it goes to the appropriate committee for discussion, hearings, and amendments. If a majority of that committee votes in favor, the bill moves to the Senate floor for debate.
Once a bill gets to a vote on the Senate floor, it requires a simple majority of 51 votes to pass after debate has ended. But theres a catch: before it can get to a vote, it actually takes 60 votes to cut off debate, which is why a 60-vote supermajority is now considered the de facto minimum for passing legislation in the Senate.
Don’t Miss: Flex Modification Is A Free Government Program
Explainer: What Is The Filibuster And Why Do Some Democrats Want To Get Rid Of It
Abolishing the filibuster could allow Senate Democrats to pass Joe Bidens agenda, but there are risks
While the US Senate has temporarily averted a showdown over its so-called filibuster rule, the issue appears likely to resurface, as the wafer-thin Democratic majority endeavors to pass Joe Bidens legislative agenda into law and Republicans try to stop them. Heres what you need to know:
Whats The Difference Between Talking And Silent Filibusters
Filibusters traditionally involved long speeches in which a senator attempted to block a vote from proceeding by refusing to yield the floor. To stage such a talking filibuster, a senator would hold the floor by standing and talking for as long as they could, sometimes overnight. This was popularized in the 1939 film Mr. Smith Goes to Washington. The longest filibuster ever recorded, by South Carolina Sen. Strom Thurmond in opposition to the Civil Rights Act of 1957, lasted for more than 24 hours.
But since the early 1970s, senators have been able to use a silent filibuster. Anytime a group of 41 or more senators simply threatens a filibuster, the Senate majority leader can refuse to call a vote.
Read Also: Free Government Cyber Security Training
