Buying The Minimal Risk Asset
Because of the costs involved in trading bonds, most investors in short-term bonds have to accept that in most cases the bonds in their portfolios will not be super short term6, and that you will be taking a little bit of interest rate risk as a result.
The most liquid short-term bond products like ETFs or index funds have average maturities of 13 years. The slight interest rate risk that comes from holding such bonds is a reasonable compromise between the theoretical minimal risk product and one we can actually buy in the real world.
For most investors with longer-term investment horizons, there are funds with different ranges of maturities like 57 years, 710 years, and so on, to suit your preferences.
How much of the minimal risk asset you should have in your portfolio and what maturities it should comprise depends on your circumstances and attitudes towards risk.
If youre extremely risk averse, you might put your entire portfolio into short-term minimal risk assets, but you should not expect much in terms of returns. As you add more risk mostly by adding equities your potential returns will increase, and vice versa.
Varying the amount of minimal risk asset you hold in your portfolio adjusts the risk profile.
For some investors, putting 100% of their money in the minimal risk asset is their optimal portfolio. This would be appropriate if you are unwilling to take any risk whatsoever with your investments and if you accept this means very low expected returns!
Ishares Broad Usd High Yield Corporate Bond Etf
- Average Duration: 5.50 years
- Yield to Maturity: 5.92%
- Assets Under Management: $4.45 billion
Made for long-term investors, this bond ETF offers investors cheap exposure to the US high-yield corporate bond market. Compared to HYG and JNK, it holds twice as many issues from more than twice as many issuers. It holds securities primarily from smaller issuers which increases its potential for yield.
How To Invest In Short
All Treasuries can be purchased directly online at the U.S. governments own website: www.treasurydirect.gov. They can be bought in very affordable denominations of $100.
However, to instantly gain access to a broad portfolio of Treasury securities, a short-term government bond fund is the preferred route.
Like stocks, short term government bonds are highly liquid. But they serve a different role in your portfolio. They are best used as a way to keep money liquid and secure, while getting a better rate of return than a bank or money market can offer.
So if you count yourself among those investors who need to prioritize capital preservation, short-term government bond funds may be the right answer for you.
To help in your search for short-term government bond funds, check out www.magnifi.com. You just type in a term like short-term government bond funds for retirement income and instantly get relevant, tailored results without having to run screeners or charts.
Also Check: Canadian Government Grants For Small Business
Choosing Between The Two
While short-term bond funds have low interest rate risk, they can have other types of risk depending on the securities they hold in their portfolios. Many funds invest in high-quality corporate bonds or mortgage-backed securities, but this isnt always the case. Investors learned this the hard way during the financial crisis of 2008 when many funds that had put too much money in mortgage-related securities experienced huge drops in their share prices.
Short-term doesnt necessarily mean low risk, so read the material from the issuing company very carefully to make sure the managers havent loaded up the portfolio with complicated international investments or low-quality corporate bonds. These are the types of securities that can blow up if the investment environment sours. Since the Federal Reserve hasnt raised interest rates in a while, its easy to forget that short-term bonds will typically experience share price declines during the periods when the Fed is raising rates. The declines will be modest in comparison to other types of funds, but money market funds wont experience any downside at all.
Municipal Bonds Vs Government Bonds
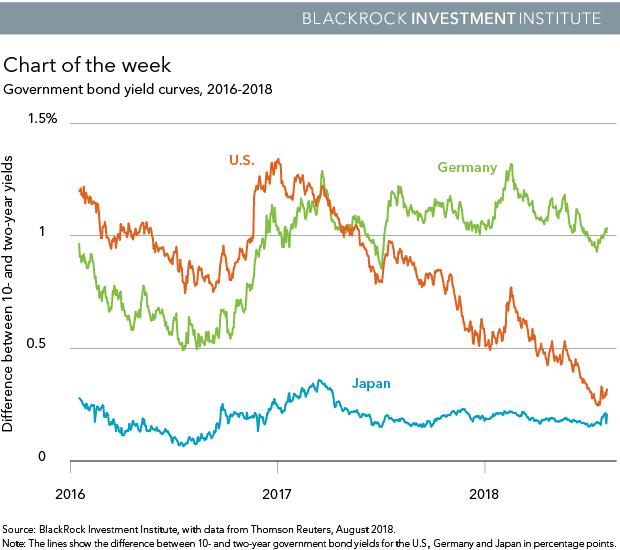
The international bond market is an attractive low-risk investment for long-term investors. In this case, the investor purchases treasury notes and earns interest on the money they loan to the government. Government bonds are popular as a safe-haven asset, among institutions, and they flock to them to avoid volatility in the stock markets and other risky investments.
However, the interest investors earn on government bonds is subject to capital gains tax. Therefore, they may not suit short-term investors that dont want to share a portion of their investment gains with the government.
Government bonds also have a relatively low yield, as they are attached to the Federal Funds Rate, which is currently a paltry 2.5-percent.
The Federal Reserve is set to reverse its current course of monetary policy, from a tightening phase to an easing environment where they cut rates. Therefore, you can expect yields on government bonds to decline over the next policy cycle, which could last 4-years or longer.
If you hold government bonds during this period, and the Fed cuts rates to zero, or negative territory, you could end up paying the government to loan them money and thats not an ideal investment strategy.
However, municipal bonds, or munis, are an attractive alternative to government bonds, and they carry a much higher interest rate.
These bonds are free of any capital gains taxes, and you get to keep all of the money you make on the investment.
Recommended Reading: Government Health Insurance Exchange Subsidy Program
How A Bond’s Maturity Impacts Its Interest Rate Sensitivity
Any change in interest rates can impact a bond’s price. When interest rates go up, bond yields rise but pond prices decline. When interest rates go down, bond yields fall and bond prices go up. However, the extent of bond price movement depends the bond’s maturity.
Over the long-term, the chances of interest rate fluctuations increase, which means bonds with longer maturities are more at risk of any price chances on that account.
Best Emerging Market Bond Etfs In Canada
An Emerging Market Bond ETF consists of fixed income debt issues from countries that have developing economies. These can include government and corporate-issued bonds in Asia, Latin America, Africa, and other countries.
The emerging market bonds usually offer higher returns as opposed to traditional bonds because they are riskier than the bonds from developed countries. The fact that developing countries tend to grow much quicker also contributes to higher potential returns.
They allow investors to diversify positions in emerging market bonds like a mutual fund, but it trades like a stock. If the underlying bonds in the ETF perform well, the ETF does as well.
Recommended Reading: Colt 45 Pistol Government Model
Costs To Manage The Fund
Investment funds, including mutual funds, charge a fee for managing the fund. The fees are called the management expense ratio .
The MER:
- may include an ongoing commission paid to advisors who sell the fund
- is paid regardless of whether the fund makes money
- is deducted before calculating the investors return
- is set at a percentage of the funds value
The percentage varies depending on the fund. This can be from less than 1% to over 3%. For example, you may have a fund with an annual return of 5%. If the funds MER was 3%, your net annual return would be 2%.
Table 1: How the management expense ratio may affect the return on your investmentRecommended Reading: Setting Up An Llc For Personal Investments
United States Government Bonds
The United States 10Y Government Bond has a 4.027% yield.
10 Years vs 2 Years bond spread is -43 bp. Yield Curve is inverted in Long-Term vs Short-Term Maturities.
Central Bank Rate is 3.25% .
The United States credit rating is AA+, according to Standard & Poor’s agency.
Current 5-Years Credit Default Swap quotation is 27.49 and implied probability of default is 0.46%.
| Residual |
|---|
You May Like: Government Grants For Black Males
Why Are Interest Rates So Low Part : Term Premiums
Longer-term interest rates are quite low around the world. Figure 1 below shows ten-year government bond yields since 1990 for the United States, Canada, Germany, the United Kingdom, and Japan. The downward trend is clear. Moreover, further sharp declines in longer-tem yields have occurred over the past year or so. For example, in the US, ten-year Treasury yields have fallen from around 3 percent at the end of 2013, to about 2.5 percent during the summer of 2014, to around 1.9 percent today. The recent renewed decline was unexpected by most observers, including me. Why are longer-term interest rates so low? And why have they fallen even further recently, despite signs of strength in the US economy?
The focus of this post, though, is on the behavior of term premiumsthe third component of bond yields. Briefly, a term premium is the extra return that lenders demand to hold a longer-term bond instead of investing in a series of short-term securities . Typically, long-term yields are higher than short-term yields, implying that term premiums are usually positive .
So what moves term premiums? The key factors are changes in the perceived riskiness of longer-term securities and changes in the demand for specific securities relative to their supply.
Treasury Bond Risks To Consider
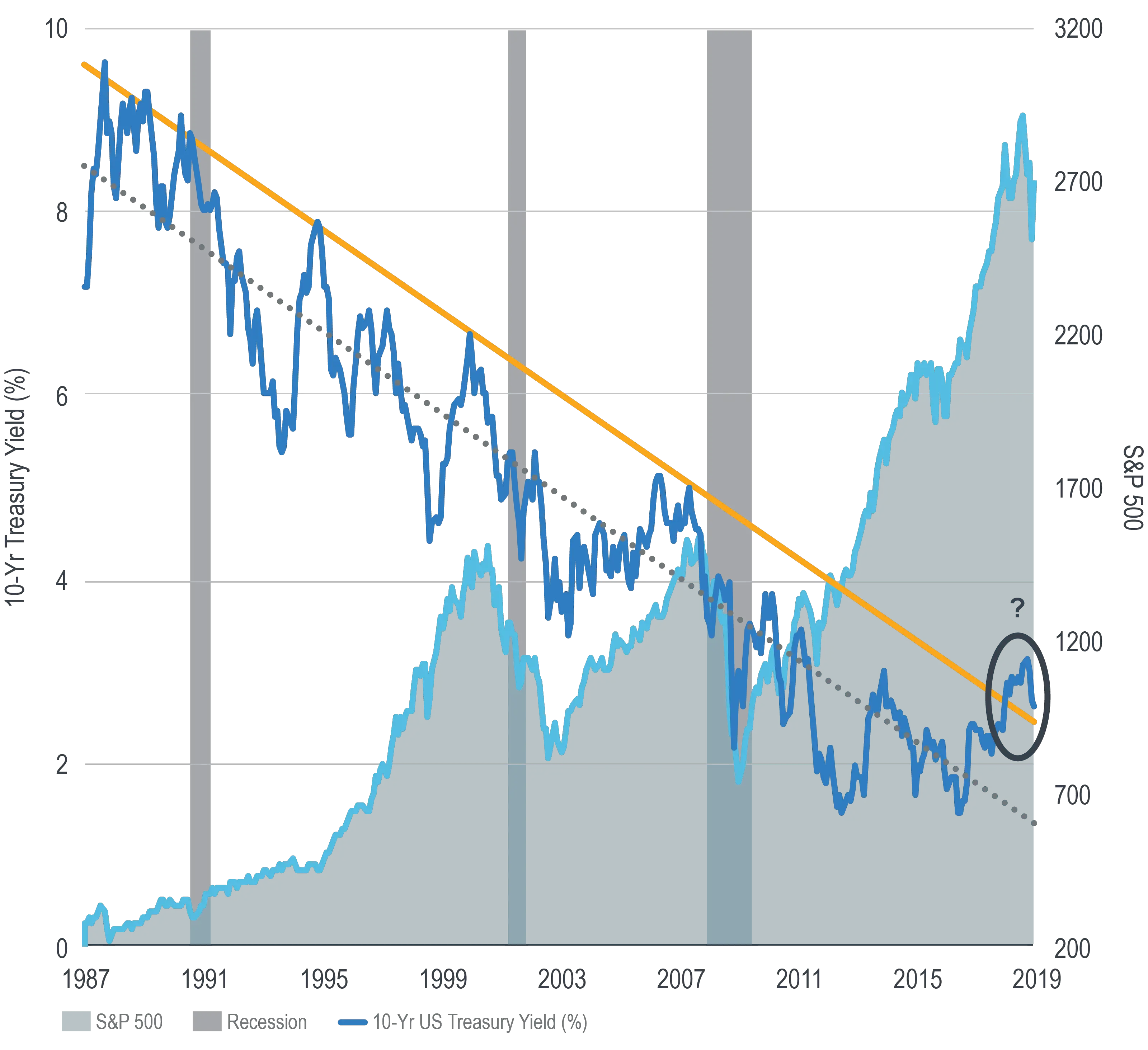
In a way, this generation of Treasury investors is the luckiest in history. Since 1981, American interest rates have been on a steady but constant march down, to the present day where they are practically zero. This has been terrific for long-time buyers of Treasuries, as over the long term the value of the bills rose as interest rates fell. However, this raises the question: Where can interest rates go from here?
We have seen negative interest rates in other countries. But for now, there is a higher probability that long term we will see interest rates rise. In a rising interest rate environment, long-term Treasury investors would be fighting an uphill battle as their bond values continually decline.
Speaking of values declining, investors in T-bills should also keep an eye on inflation. While inflation hasnât been on anyoneâs radar for over a decade, due to such low yields presently, even a moderate amount of inflation would cause investors to lose money on T-bills.
This being said, bonds and Treasury bills still have a place in a portfolio even if some of their benefits erode over time. What is most important is the safety and liquidity T-bills provide, and that investors be aware of possible future risks.
Also Check: Government Early Childhood Education Programs
Why Would Investing In Bonds Be A Bad Idea
Whether a bond investment is bad or good depends on the investorâs financial goal and market conditions. If an investor wants a steady income stream, a Treasury bond might be a good choice. However, if interest rates are rising, purchasing a bond may not be a good choice since the fixed rate of interest might underperform the market in the future. Please remember, when you purchase a Treasury bond, the fixed rate of interest for that bond never changes, regardless of where market interest rates are trading.
Also, investing in bonds and selling them in the secondary market before their maturity can lead to a loss similar to other investments such as equities. As a result, investors should be aware of the risk that they could lose money by purchasing and selling bonds before their maturities. If an investor needs the money in the next year or two, a Treasury bond, with its longer maturity date, might not be a good investment.
Dont Some Bonds Have Even Shorter Terms
Yes, there are some bonds that mature in even less than a year, such as 90-day U.S. Treasury bonds. These are known as ultra-short-term bonds, or as cash equivalents.
For investors who want to have quick access to their money, ultra-short-term bonds may be a good option. Returns for these bonds are usually higher than money market accounts but lower than conventional short-term bonds.
Also Check: State Of Texas Government Contracts
Euro Area Yield Curves
A yield curve is a representation of the relationship between market remuneration rates and the remaining time to maturity of debt securities. A yield curve can also be described as the term structure of interest rates. The ECB publishes several yield curves, as shown below.
It is updated every TARGET business day at noon . No data or other information are provided regarding any day on which the relevant trading venue from which the euro area yield curve data are sourced is not open for business.
Two Credit Risk Yield Curves
The spot, forward and par yield curves, and their corresponding time series, are calculated using two different datasets reflecting different credit default risks.
- One sample contains “AAA-rated” euro area central government bonds, i.e. debt securities with the most favourable credit risk assessment.
- The second dataset contains all euro area central government bonds.
Also Check: American Government Online Course Free
What Are Treasury Bonds
Treasury bonds are government debt securities that are issued by the U.S. Federal government and sold by the U.S. Treasury Department. T-bonds pay a fixed rate of interest to investors every six months until their maturity date, which is in 20-30 years.
However, the interest rate earned from newly-issued Treasuries tends to fluctuate with market interest rates and the overall economic conditions of the country. During times of recession or negative economic growth, the Federal Reserve typically cuts interest rates to stimulate loan growth and spending. As a result, newly-issued bonds would pay a lower rate of return in a low-rate environment. Conversely, when the economy is performing well, interest rates tend to rise as demand for credit products grows, leading to newly-issued Treasuries being auctioned at a higher rate.
How To Choose The Right Bond Funds
One of the most important aspects of investing in bond funds is understanding the differences in the types of funds and the risks and return characteristics of bonds with different maturities. There are four types of bond fundsbond mutual funds, closed-end bond funds, exchange-traded bond funds and bond unit investment trusts.
They can then be further broken down into three segments based on the bondsâ average maturities in the funds portfolios.
Learn the differences, risks and returns of each segment of bond fund based on their maturities.
Donât Miss: City Jobs In Las Vegas
Read Also: Free Government Cell Phone Washington State
What Returns Can I Expect With Short
Shorter terms translate into lower risks for investors. And that usually means lower returns. When everything else is equal, a bond with a longer term to maturity will usually pay a higher interest rate than a shorter-term bond. For example, 30-year U.S. Treasury bonds often pay one or two full percentage points higher than five-year Treasury notes.
Thats because when you buy a bond with a shorter maturity date, your money wont be tied up as long as with a longer-term bond. With a long-term bond, there is more risk that higher inflation could reduce the value of payments, as well as greater risk that higher overall interest rates could cause the bonds price to fall.
Because of those additional factors, the returns on bonds arent just dependent on the length of time until maturity. Bond returns also are influenced by current interest rates. When interest rates are rising, for instance, short-term bonds usually provide better total returns than their long-term counterparts. When interest rates are falling, longer-term bonds usually provide stronger total returns than short-term bonds.
Are Bonds A Good Investment In 2021
In 2021, the interest rates paid on bonds have been very low because the Federal Reserve cut interest rates in response to the 2020 economic crisis and the resulting recession. If investors believe that interest rates are going to rise in the next couple of years, they may opt to invest in bonds with short-term maturities.
For example, a two-year Treasury bill would pay a fixed rate of interest and return the principal invested in two years. If interest rates are higher in 2023, the investor could take that principal and invest it in a higher-rate bond at that time. However, if that same investor had purchased a 10-year Treasury note in 2021 and interest rates rose in the next couple of years, the investor would lose out on the higher interest rates because they would be stuck with the lower-rate Treasury note. Again, investors can always sell a Treasury bond before its maturity date there could be a gain or loss, meaning you might not get all of your initial investment returned to you.
Also, please consider your risk tolerance. Treasury bonds, notes, and shorter-term Treasury bills are often purchased by investors for their safety. If you believe that the overall markets are too risky and your goal is to preserve your wealth, you might opt for a Treasury security despite their low-interest rates in the current environment. We can see from the chart below that Treasury yields have declined over the last several months.
Read Also: Government Financial Aid For College
Current Benchmark Bond Yields
Selected benchmark bond yields are based on mid-market closing yields of selected Government of Canada bond issues that mature approximately in the indicated terms. The bond issues used are not necessarily the ones with the remaining time to maturity that is the closest to the indicated term and may differ from other sources. The selected 2-, 5-, 10-, or 30-year issues are generally changed when a building benchmark bond is adopted by financial markets as a benchmark, typically after the last auction for that bond. The selected 3-year issue is usually updated at approximately the same time as changes are made to the 2-year, and sometimes with the 5-year. The selected 7-year issue is typically updated at approximately the same time as the 5- or 10-year benchmarks are changed. The current benchmark bond issues and their effective dates, shown in brackets, are as follows.
- 2 year – 2024.11.01, 3.00%
- 3 year – 2025.04.01, 1.50%
- 5 year – 2027.09.01, 2.75%
- 7 year – 2029.06.01, 2.25%
- 10 year – 2032.06.01, 2.00%
- Long – 2053.12.01, 1.75%
