What Are The Differences Between Data Privacy And Data Security
Despite their differences, data privacy and data security are interlinked. IT leaders generally view data privacy as a sub-component of data security. And more recently, data governance leaders are making data security a central focus of their responsibilities.
To illustrate the subtle differences between data privacy and data security, consider a bank vault. A bank vault has both security and privacy measures in place to protect the contents within.
Security features thwarts external threats. Guards, an alarm system, and the vaults lock represent security features.
Privacy measures prevent internal threats. Those may include protocols that limit employees access to the vault or knowledge of its contents. Privacy measures can also mitigate external threats, so if personal information is stolen, its value is restricted by anonymization.
Taking a wider view, the primary differences between data privacy and data security are:
Transforms Reference Data Management
IBM InfoSphere® Master Data Management Reference Data Management Hub is an advanced solution for centrally managing and distributing reference data across the enterprise. It extends the InfoSphere Master Data Management portfolio with a hub and stewardship application engineered for superior management of trusted enterprise reference information.
Failing To Anticipate The Flood Of Data And Breadth Of Complexity
Data governance is getting evermore complex with the devolution of company tech borders, data flowing to and from a breadth of devices, which are more often mobile and across a wider range of operating systems and platforms, says Ian Moyse, Sales Director at Axios Systems.
Rob Steele, Consulting Systems Engineer at RoundTower Technologies, adds, Most businesses already have a big data problem as they are constantly trying to keep up with the influx of new data, including the rapid growth of the IoT.
Also Check: Cio Sp3 Fbo
Data Privacy And Why It Matters
Failing to protect sensitive information can put a lot of people at risk of being exploited by cybercriminals, and can make a company face enormous legal penalties.The way information is shared and stored can put the information at risk. It is risky to store personal information on portable devices, which are easily lost or stolen. In addition, the consequences of a data breach can be devastating. Identity theft could lead to financial losses, and a company could face lawsuits and legal penalties. This presentation covers what kinds of personal information must be protected & guidelines for keeping this info safe.
A Building Privacy Values Into Cyber Security Policy Directions

We know that certain degrees of monitoring, logging, data mining or surveillance will create tensions or conflicting requirements between privacy and cyber security efforts. As Canada’s Interim Privacy Commissioner stated in 2011, “violating people’s privacy in the interest of ensuring cyber security would defeat the very purpose of cyber security.”Footnote 73 While cyber security activities may require some degree of monitoring in order to be able to detect anomalies and protect cyber infrastructure and information, cyber security strategies and activities should not be an excuse for building massive surveillance regimes for unfettered monitoring and analysis of the personal information of individuals. Privacy regulators and advocates have a role to play to ensure that cyber security strategies, principles, action plans and implementation activities promote privacy protection both as a guiding principle and an enduring standard.
There are clear advantages to building cyber security into programs and activities from the start rather than retroactively mitigating cyber risks after the fact. Undertaking preventative measures to ensure security and informing consumers of the potential risks and how they have been mitigated can foster trust in individuals using the internet.
Recommended Reading: Los Lunas Government
Data Governance Is Finding The Right Balance Between Data Monetization And Risk Reduction
CDOs are primarily charged with three things: boosting the top line, improving the bottom line, and reducing risk. Data governance is how you go about accomplishing them. Within that, theres a whole slew of activities related to meeting complex and regionally specific regulatory requirements. Still, I tell my peers that if you keep those top three things in mind, data governance begins to make sense.
A good data governance framework enables you to move forward while at the same time managing risk at an acceptable level. The goal is to keep the flow going so that the data can be used to drive value. Whether it be innovation for new products, insights around processes, or reducing cycle time, its all about being able to keep that flow going sufficiently so you attain your targets while minimizing risk.
A Complexity Of The Connected Environment
The continuing evolution of cyberspace, as a fully electronic world created by interconnected networks in parallel with our physical environment, is characterized by an enormous amount of data. The modern economy increasingly depends on vast quantities of digital data that are generated through financial transactions, communications, entertainment, travel, shopping, online browsing, and hundreds of other routine activities.Footnote 19 Data elements are continually being combined, connected, compared and linked to other information as organizations try to capitalize on its value and to offer new and improved services to their users. The electronic systems and digital networks that facilitate these transactions and communications also capture our preferences and other personal details, and track our online and, increasingly, physical movements. The volume of data generated in cyberspace can only increase exponentially once the “Internet of things” becomes a reality, and sensors within devices autonomously report on location, status, surrounding environment, provide real-time updates or help monitor and control devices remotely.Footnote 20
Read Also: Sacramento Federal Jobs
The Push Towards Self
As any other privacy or security issue, you must balance big data privacy issues against your business goals. Why do you collect and manage data in the first place? Youre typically using it to fuel an operational effort or an analytical effort .
For e-commerce or online customer experiences, that data is more visible to the customer throughout their journey. As a result, the data can have a more direct impact on the bottom line. After all, without a good e-commerce experience, customers may choose to go elsewhere. Similarly, a poor online support program may lead to increased churn.
This transparency comes with some risk. More self-service interactions with customers means you are collecting and packaging more information about customers about their accounts, their purchases and their preferences. More data can lead to a better customer experience, but it can also put you at risk. There is simply a greater risk of exposure of personal or confidential information.
As a result, data and IT governance efforts are finding a new push as organizations begin to collect data for more public consumption. And now business and IT, once mortal enemies , are now realizing that data is everyones responsibility.
Preparing For Privacy In A Big Data World
When planning big data privacy efforts, a starting point is to understand the sources of data and how this data is used. As we all know, that conversation rapidly goes in the direction of how to use or exploit data.
However, there is tendency to avoid the delicate subject of how to support privacy of the individual and how to protect data in an increasingly digital world. The complicating factor is how to keep a balance between:
- The value to end users.
- The level of privacy and protection is necessary for both you and your customer.
This issue has to be addressed if you want your digital business practices to be seen as credible to your customers as providers of big data content.
You May Like: Government Jobs In San Antonio
C Facilitating Broader Dialogue On Cyber Security That Acknowledges Its Importance For Privacy Trust And Responsible Data Stewardship
The complexities of cyberspace and the mounting sophistication of threats necessitate that organizations do more about privacy protection, particularly with respect to cyber security efforts. Security safeguards are a key element of the ability to protect personal information and preserve privacy in cyberspace, with technical safeguards being only one aspect of an overall risk management approach to cyber security and personal information protection. It is no longer enough to simply be compliant with privacy requirements or technical safeguards to the minimum extent possible. Protection of personal information requires giving effect to all privacy principles, and practicing privacy compliance throughout the lifespan of the information, including: demonstrating accountability, being transparent, practicing data minimization, ensuring appropriate use and disclosure, implementing effective access controls, and abiding by reasonable retention periods and safe destruction methods.
Adobe Experience Platform Data Governance
As a Platform service, Adobe Experience Platform Data Governance allows you to manage customer data and ensure compliance with regulations, restrictions, and policies applicable to data use. It plays a key role within Experience Platform at various levels, including data usage labeling, data usage policies, policy enforcement, and data lineage.
See the Data Governance overview for more information.
You May Like: Government Grants For Home Repairs
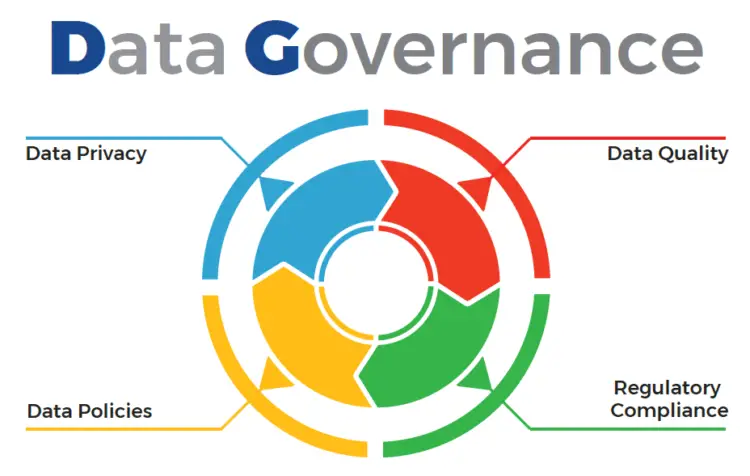
What Is Data Governance
Data governance is the capability within an organization to help provide for and protect for high quality data throughout the lifecycle of that data. This includes data integrity, data security, availability, and consistency. Data governance includes people, processes, and technology that help enable appropriate handling of the data across the organization. Data governance program policies include:
- Delineating accountability for those responsible for data and data assets
- Assigning responsibility to appropriate levels in the organization for managing and protecting the data
- Determining who can take what actions, with what data, under what circumstances, using what methods
- Identifying safeguards to protect data
- Providing integrity controls to provide for the quality and accuracy of data
Understanding Personal Data Privacy Management And Data Governance
The concept of personal information has become more broadly understood since the European Union implemented the General Data Protection Regulations in 2016 however, geographical and cultural differences still exist in how personal information is defined. For our purposes, personal information is any digital or hard copy data that can be directly or indirectly related to a natural person. It is important to understand that we mean more than just personally identifiable information . The scope of privacy management can include transactional information that does not contain PII. If the transactions could be combined with other information that connects the data to a specific individual, we must protect it. For example, if I share personal information with you including that a person has six fingers on their right hand, you probably will not be able to identify that person however, if you discover through alternate sources that the person I mentioned lives in Watch Hill, Rhode Island, with a population of 154, you would be able to identify that person with minimal effort.
The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology released its data privacy framework in 2020. The framework breaks down the key activities necessary to support privacy management.
Ultimately, data governance can be leveraged to enable privacy management and facilitate the goal of privacy by design.
Read Also: Government Jobs Las Vegas No Experience
Data Governance Vendors And Tools
Data governance tools are available from various vendors. That includes major IT vendors, such as IBM, Informatica, Information Builders, Oracle, SAP and SAS Institute, as well as data management specialists like Adaptive, ASG Technologies, Ataccama, Collibra, Erwin, Infogix and Talend. In most cases, the governance tools are offered as part of larger suites that also incorporate metadata management features and data lineage functionality.
Data catalog software is included in many of the data governance and metadata management platforms, too. It’s also available as a stand-alone product from vendors such as Alation, Alteryx, Boomi, Cambridge Semantics and Data.world. Learn more about the features that data catalog software offers, including its governance-related capabilities.
Continue Reading About What is data governance and why does it matter?
Can You Trust Your Data
You need trusted data to get the insights that drive better strategic decisions. The Talend Trust Assessor evaluates the reliability of your data, and gives you quantified feedback on three critical aspects of your data:
- Validity: Is your data correctly formatted and stored in the right way?
- Completeness: Does your dataset include values for all the fields required by your system?
- Uniqueness: Is your data free from duplicates and dummy entries?
When you know that you can trust your data, you can make informed strategic business decisions with confidence. Assess your data now.
Don’t Miss: Entry Level Government Jobs For College Graduates
And Why Governance Is The Gordian Knot To All Your Problems
“Data governance is a measure of a company’s control over its data”
Data governance is a data management concept. It is a measure of the control an organization has over its data. This control can be achieved through high-quality data, visibility on data pipelines, actionable rights management, and clear accountability. Data governance encompasses the people, processes, and tools required to create consistent and proper handling of a company’s data. By consistent and proper handling of data, I mean ensure availability, usability, consistency, understandability, data integrity, and data security.
The most comprehensive governance modelâ say, for a global bankâwill have a robust data-governance council to drive it a high degree of automation with metadata recorded in an enterprise dictionary or data catalog data lineage traced back to the source for many data elements and a broader domain scope with ongoing prioritization as enterprise needs shift.
A good data governance and privacy model is a mix of people, process and software.
Hybrid Cloud Adds Flexibility
The other key technical aspect that were prioritizing at IBM is our hybrid cloud framework.
A hybrid cloud environment is giving us increased flexibility with regard to regulatory compliance through a mix of pre-defined policies and run-time automation, coupled with AI.
Traditionally, regulatory compliance has been handled by looking at ten different regulations, taking the one thats most restrictive, and standardizing for that. With our AI-infused hybrid cloud approach, we are able to configure aspects of data processing to appropriately access and process data in compliance with all these different regulations simultaneously.
For example, access control can be determined not only by the role of the user but also by policies implemented at run time that align to regulations. Consider a data scientist who logs in from the U.S. and accesses certain sets of data. Later, if that same person with the same role logs in from a different country, they may not have the same access. These types of real-time decisions are critical to privacy regulation compliance.
Recommended Reading: Local Government Employee Credit Union
The Latest Report Reinforces The Correlation Between Data Culture And Revenue Explains The First Steps To Building A Data Culture And Reveals That The C
The Q1 2022 Alation State of Data Culture Report brings a touch of pessimism but a beacon of hope for companies looking to become more data-driven.
There was a drop in the Data Culture Index , a metric of an organization’s fitness to enable data-driven decision-making. Only 15% of companies qualified as a top-tier data culture this year meaning widespread adoption across the three pillars of data culture versus 29% from Q3 2021.
The good news? The report notes that 87% of data leaders cite data catalogs as very important or essential to establishing a data culture, up from 68% from Q3 2021.
The latest report now includes respondents from North America, EMEA, and APAC, confirming that data culture and maintaining a competitive edge are worldwide concerns.
- The link between organizations with top-tier data cultures and exceeding the revenue goal
- How the need for additional investment in data and analytics remains one of the greatest challenges for data leaders
- The C-level strategy gap that occurs when organizations dont have alignment between leadership and data priorities
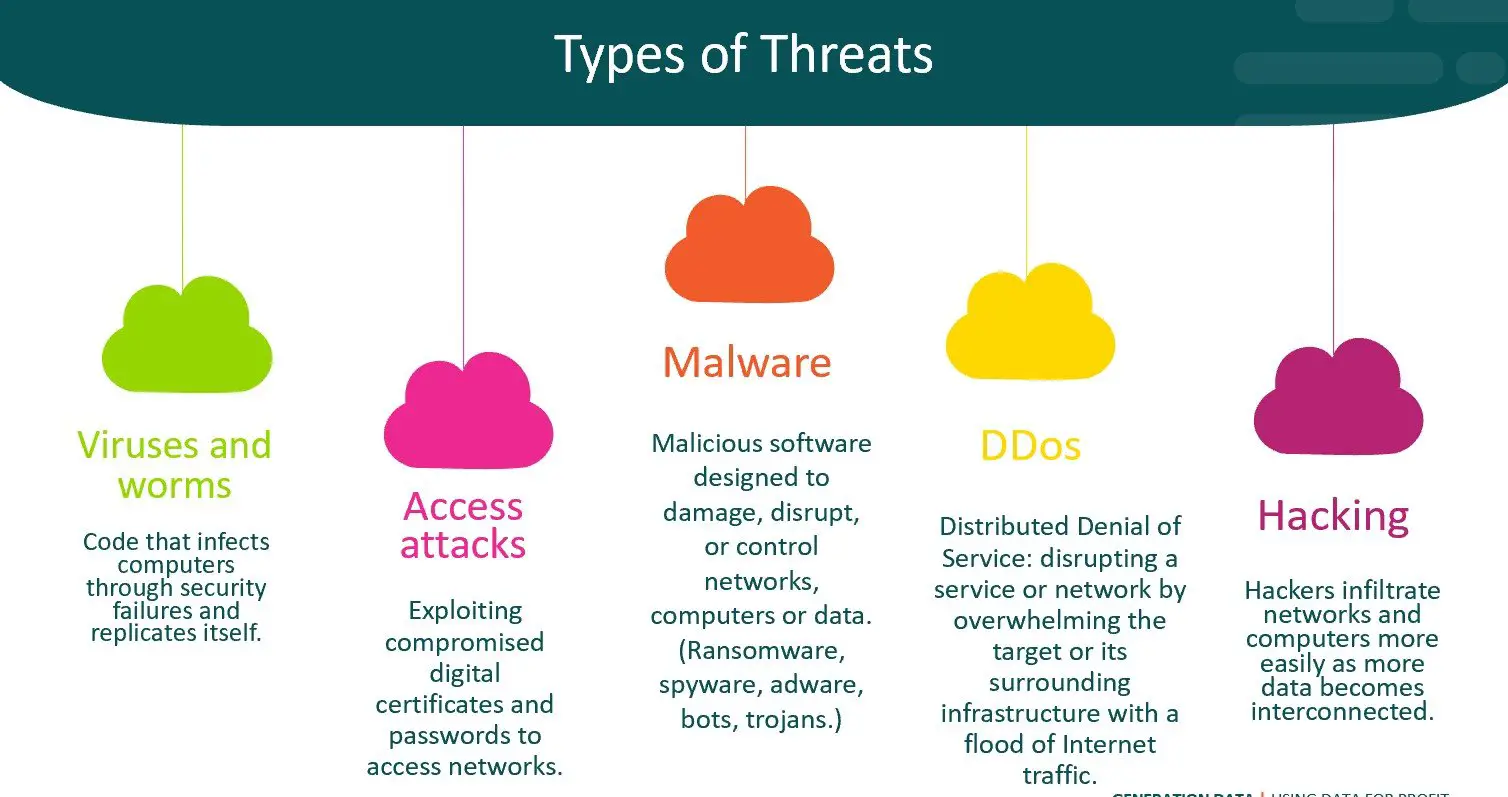
What Is Data Security
Data security refers to the processes and procedures that protect data from unauthorized access, use, or alteration. At their core, data security measures keep data from falling into the hands of those with malicious intent.
Some of the most common data security mechanisms include:
- Firewalls
- Network access control
- Multi-factor authentication
There is no one-size-fits-all data security solution. As every organization is different, so are the frameworks that keep their data safe. Data security processes vary by organization and are largely rooted in:
- Industry
- Database size
- Regulatory guidelines
Regardless of what an organizations data security program looks like, next to maintaining a framework is having documentation of the implemented controls. Should an infiltration occur, an organization has written proof of its efforts to keep its data protected.
Read Also: Grants For Dental Implants
Common Mistakes Spotlight Pitfalls And Lessons Learned
Tyrone Grandison, Deputy Chief Data Officer at the US Department of Commerce, says agility and nimbleness are key to capitalizing on emerging trends like the internet of things .
But he warns that waterfall demands on the data management life cycle will force firms to increase their focus on more complex and detailed data governance. These intensified demands, in turn, lower the probability of organizational success in this space.
When industry experts were asked to weigh in on the topic, several key themes emerged. The result is a list of 10 common mistakes organizations have made in their efforts to seize the momentum around IoT.
With the IoT, big data has become even bigger and more dynamic, amplifying both the opportunities and the challenges.
Video: 4 Steps Towards Data Intelligence: Step 2 Govern Your Data
The second installment of the 4 Steps Towards Data Intelligence video series we explore the need for properly governing your data by balancing an ever-expanding list of privacy and security lawsand a growing need for datademocratization.
Watch the video: 4 Steps Towards Data Intelligence: Step 2 Govern Your Data
Also Check: Best Careers For History Majors
Not Asking The Right Questions
Kirk Borne, Principal Data Scientist at Booz Allen Hamilton, reminds us that the promise of IoT is greater visibility and actionability. Further, he contends that this promise can go unfulfilled if we dont ask the right questions, such as:
- Who owns the data?
- How do we ensure data quality, discovery, usability and security for the many different teams and business units that create, use and manage the data?
- What are the key business questions and goals that are driving what data we collect and use?
- How do we manage ad hoc data analytics? Do we restrict it or encourage it?
