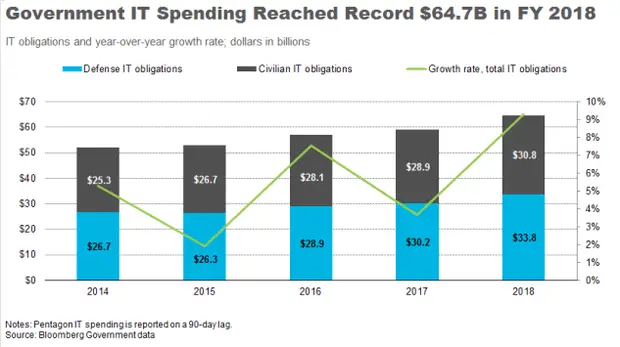
Gartner Forecasts Global Government It Spending To Grow 5% In 2021
Government Spending on Devices and Software to Record Highest Increases Year-Over-Year
Worldwide government IT spending is forecast to total $483 billion in 2021, an increase of 5.1% from 2020, according to the latest forecast by Gartner, Inc.
Government organizations continue to be challenged with the appropriate level of interventions to respond and recover from the COVID-19 pandemic, said Irma Fabular, senior research director at Gartner. Public health and safety measures, including vaccinating citizens are of paramount concern, which necessitate governments to continue to accelerate their digital transformation journey.
Three segments are on pace to exceed the overall market growth in 2021. The software segment, which includes application, infrastructure, and vertical-specific software, will experience the strongest growth in 2021. Governments are innovating at a quicker pace by adopting commercially available technology solutions for operational and mission critical needs, said Ms. Fabular. We are seeing innovative use of technology and data to control and respond to the pandemic, as well as provide financial and humanitarian assistance.
As government organizations continue to embrace remote work and hyperconnected public services, spending on devices is expected to grow 5.6% in 2021, up from 1.6% growth in 2020 .
Table 1. Government IT Spending Forecast by Segment, 2020-2021, Worldwide
|
Segment |
Receipts From Other Sources
Receipts from all other sources, which are described below, totaled $1.5 trillion in 2019, or 7.1 percent of GDP. Those receipts are projected to remain between 7.1 percent and 7.3 percent of GDP over the next decade.
Payroll Taxes. Receipts from payroll taxes, which fund social insurance programsprimarily Social Security and Medicaretotaled $1.2 trillion in 2019, or about 5.9 percent of GDP. Those receipts are projected to remain at that share throughout the next decade because workers earnings, which constitute most of the payroll tax base, remain relatively stable as a share of GDP in CBOs economic forecast.
Estate and Gift Taxes. Revenues from estate and gift taxes totaled $17 billion in 2019, or just below 0.1 percent of GDP. Revenues from that source are projected to rise to just above 0.1 percent in 2027 and subsequent years after a provision of the 2017 tax act that doubled the amount of the estate and gift tax exemption expires at the end of calendar year 2025.
In addition, an annual fee on health insurance providers was recently repealed by the Further Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2020. Because the final payment of that fee is due in September 2020, it will boost receipts this year but not in subsequent years.
What Is This Site
The IT Dashboard was launched on June 1, 2009, to provide Federal agencies and the public with the ability to view details of Federal information technology investments online and to track their progress over time. The IT Dashboard displays data received from agency IT Portfolio and Business Case reports, including general information on over 7,000 Federal IT investments and detailed data for over 700 of those investments that agencies classify as “major.”
You May Like: Government Jobs In Las Vegas Area
Total Outlays In 2020
In CBOs projections, total federal outlays in 2020 increase by $201 billion from their 2019 amounts. Most of that increase is attributable to mandatory outlays, which are anticipated to rise by $125 billion . Discretionary outlays also are expected to increase by 5 percent this year, to a total of $1.4 trillion, an increase of $69 billion. The governments net interest costs in 2020 are expected to inch up by $7 billion , to $382 billion.
Income Security And Education
Susan Yeh BeyerChild nutrition and other nutrition programs
Tia CaldwellChild Care and Development Block Grant
Meredith DeckerUnemployment insurance, training programs, Administration on Aging, Smithsonian Institution, arts and humanities
Elizabeth Cove DelisleHousing assistance
Jennifer GraySupplemental Nutrition Assistance Program and other nutrition programs, Social Services Block Grant, support programs for children and families
Justin HumphreyStudent loans, higher education
Arin KersteinRefugee assistance
Wendy KiskaPension Benefit Guaranty Corporation
Leah KoestnerElementary and secondary education, Pell grants
Justin LatusSupplemental Security Income
Susanne MehlmanTemporary Assistance for Needy Families, child support enforcement, foster care, child care programs, Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program
Noah MeyersonOld-Age and Survivors Insurance, Social Security trust funds, Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation
Emily SternDisability Insurance
Kathleen GrampEnergy, Outer Continental Shelf receipts, spectrum auction receipts, Orderly Liquidation Fund
Evan HerrnstadtSpectrum auction receipts
David HughesRecreational resources, commerce, Small Business Administration, Universal Service Fund
Wendy KiskaFederal Deposit Insurance Corporation, Orderly Liquidation Fund
Aaron KrupkinEnergy, air and water transportation
Michael McGraneFannie Mae and Freddie Mac
Erik ODonoghueAgriculture
Matthew PickfordGeneral government, legislative branch
You May Like: Government Bank Owned Foreclosed Homes In Polk County
United States Federal Budget
| This article is part of a series on the |
The United States federal budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. The government primarily spends on healthcare, retirement, and defense programs. The non-partisan Congressional Budget Office provides extensive analysis of the budget and its economic effects. It has reported that large budget deficits over the next 30 years are projected to drive federal debt held by the public to unprecedented levelsfrom 98 percent of gross domestic product in 2020 to 195 percent by 2050.
The United States has the largest external debt in the world and the 14th largest government debt as % of GDP in the world. The annual budget deficit increased from $585 billion in 2016 to $984 billion in 2019, up 68%. Relative to a CBO forecast prior to President Trump’s inauguration, the budget deficits for 2019-2021 roughly doubled, due to the Trump tax cuts and other spending legislation.
Nhe By State Of Provider 1980
- Between 2009 and 2014, U.S. personal health care spending grew, on average, 3.9 percent per year, with spending in North Dakota growing the fastest and spending in Rhode Island growing the slowest .
- In 2014, Californias personal health care spending was highest in the nation , representing 11.5 percent of total U.S. personal health care spending. Comparing historical state rankings through 2014, California consistently had the highest level of total personal health care spending, together with the highest total population in the nation. Other large states, New York, Texas, Florida, and Pennsylvania, also were among the states with the highest total personal health care spending.
- Wyomings personal health care spending was lowest in the nation , representing just 0.2 percent of total U.S. personal health care spending in 2014. Vermont, Alaska, North Dakota, and South Dakota were also among the states with the lowest personal health care spending in both 2014 and historically. All these states have smaller populations.
- Gross Domestic Product by state measures the value of goods and services produced in each state. Health spending as a share of a states GDP shows the importance of the health care sector in a states economy. As a share of GDP, Maine ranked the highest and Wyoming ranked the lowest in 2014.
For further detail, see health expenditures by state of provider in downloads below.
Also Check: Government Grants To Start Trucking Business
Mandatory Spending And Social Safety Nets
Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid expenditures are funded by more permanent Congressional appropriations and so are considered mandatory spending. Social Security and Medicare are sometimes called “entitlements”, because people meeting relevant eligibility requirements are legally entitled to benefits most pay taxes into these programs throughout their working lives. Some programs, such as Food Stamps, are appropriated entitlements. Some mandatory spending, such as Congressional salaries, is not part of any entitlement program. Mandatory spending accounted for 59.8% of total federal outlays , with net interest payments accounting for an additional 6.5%. In 2000, these were 53.2% and 12.5%, respectively.
Government Budget Balance As A Sectoral Component
Economist explained in July 2012 that government fiscal balance is one of three major financial sectoral balances in the U.S. economy, the others being the foreign financial sector and the private financial sector. The sum of the surpluses or deficits across these three sectors must be zero by definition. Since the foreign and private sectors are in surplus, the government sector must be in deficit.
Wolf argued that the sudden shift in the private sector from deficit to surplus due to the global economic conditions forced the government balance into deficit, writing: “The financial balance of the private sector shifted towards surplus by the almost unbelievable cumulative total of 11.2 per cent of gross domestic product between the third quarter of 2007 and the second quarter of 2009, which was when the financial deficit of US government reached its peak…No fiscal policy changes explain the collapse into massive fiscal deficit between 2007 and 2009, because there was none of any importance. The collapse is explained by the massive shift of the private sector from financial deficit into surplus or, in other words, from boom to bust.”
Economist Paul Krugman also explained in December 2011 the causes of the sizable shift from private sector deficit to surplus: “This huge move into surplus reflects the end of the housing bubble, a sharp rise in household saving, and a slump in business investment due to lack of customers.”
Don’t Miss: Government Grants To Start Trucking Business
Idc Government Insights: United States Federal Government It Spending Guide
The IDC Government Insights: United States Federal Government IT Spending Guide examines the federal government’s opportunity from a technology, subindustry, and agency perspective. This comprehensive database delivered via IDC’s Customer Insights query tool allows the user to easily extract meaningful information about the federal government technology market by viewing data trends and relationships and making data comparisons.
This product covers the following segments of the federal government market:
- 3 technology groups with 21 technology categories: Hardware , software , and IT services
- 2 subindustries: Federal civilian and Department of Defense
- 25+ federal civilian agencies: Department of Homeland Security, Health and Human Services, General Services Administration, and other agencies
- 4 Department of Defense agencies and services: Air Force, Army, Navy, and Marine Corps as well as other DoD agencies or DoD-wide
Data Deliverables
This spending guide is delivered on a semiannual basis via a web-based interface for online querying and downloads. For a complete delivery schedule, please contact an IDC sales representative. The deliverable for this spending guide includes:
- Annual five-year forecasts by industry, subindustry, agency, and technology delivered twice a year
About This Spending Guide
The Value of Subscribing to IDC Spending Guides
How Customers Use Spending Guides to Pinpoint Opportunities
Coverage Areas
Personal Income And Outlays October 2021
Personal income increased $93.4 billion, or 0.5 percent at a monthly rate, while consumer spending increased$214.3 billion, or 1.3 percent, in October. The increase in personal income primarily reflected an increase in compensation of employees. The personal saving rate was 7.3 percent in October, compared with 8.2 percent in September.
Read Also: City Of Las Vegas Government Jobs
Factoring In The Impacts Of Covid
Key Takeaways
- Although agency budget uncertainty remains, Congress is unlikely to enact major budgets cuts while the economy is unstable. The topline budget for FY 2021 has already been negotiated, though Congress could enact some changes to help agencies address budget shortfalls and/or address ongoing COVID-19 response issues within regular appropriations.
- Historically, federal IT budgets and spending have been somewhat insulated from Congressional efforts to reduce the federal deficit or lower federal spending. The pandemic response has underscored the role of IT as a mission enabler.
- COVID-19 operational disruptions have driven some rapid IT modernization efforts, such as scaling of remote access and telework capabilities, and emphasized the importance of cloud computing, which should drive investment in cloud capabilities and modernized network infrastructure.
The Federal IT landscape is facing unprecedented challenges. While in the midst of broad transformation and modernization efforts agencies are facing the disruptive impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. As a consequence, agencies are working to adapt to pressing needs while keeping longer-term initiatives on track.
Although the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2019 provided higher near-term funding, agencies will remain under pressure in the coming years to increase efficiency, eliminate waste and adopt emerging technologies that promise to improve service-delivery.
Forecasting the Federal IT Market in a COVID-19 Context
Cio Risk Ratings For Investments
This graph displays the latest Chief Information Officer Risk ratings for IT investments government-wide. CIOs rate each investment using a set of pre-established criteria and issue a CIO Evaluation Number that reflects the investments ability to accomplish its goals within the current fiscal year 2021. This number ranges from 1 – 5, and the higher it is, the better the investment has been rated to meet its goals. Please refer to FAQ #7 for the CIO Evaluation criteria.
% of the total number of major IT investments that scored a CIO evaluation number of 1 or 2
% of the total number of major IT investments that scored a CIO evaluation number of 3
% of the total number of major IT investments that scored a CIO evaluation number of 4 or 5
You May Like: Government Jobs In Las Vegas
Total Deficit Primary Deficit And Net Interest
Percentage of GDP
In CBOs projections, primary deficits fluctuate between 2.3 percent and 2.9 percent of GDP over the next decade, but total deficits grow because of rising interest costs.
Primary deficits or surpluses exclude net outlays for interest.
When October 1 falls on a weekend, certain payments that would have ordinarily been made on that day are instead made at the end of September and thus are shifted into the previous fiscal year. All projections presented here have been adjusted to exclude the effects of those timing shifts. Historical amounts have been adjusted as far back as the available data will allow.
GDP = gross domestic product.
The deficits projected in CBOs baseline would boost federal debt held by the public, which consists mostly of the securities that the Treasury issues to raise cash to fund the federal governments activities and pay off its maturing liabilities. The net amount that the Treasury borrows by issuing those securities is influenced primarily by the annual budget deficit.
In CBOs baseline, after accounting for all of the governments borrowing needs, debt held by the public rises from $17.9 trillion at the end of 2020 to $31.4 trillion at the end of 2030 . As a percentage of GDP, that debt would increase from 81 percent at the end of 2020 to 98 percent by the end of the projection period. At that point, such debt would be the largest since 1946 and more than twice the average over the past 50 years.
Quantifying The Uncertainty In Cbos Projections
To quantify the uncertainty surrounding its projections for the next five years, CBO analyzed its past forecasts of several key macroeconomic variables . On the basis of that analysis, CBO estimates thatif the errors in the agencys current economic forecast are similar to those in its previous forecaststhere is approximately a two-thirds chance that the average annual rate of real GDP growth will be between 0.5 percent and 3.1 percent over the next five years . That range encompasses cumulative growth over the five-year period ranging between 2.4 percent and 16.5 percent.17 Similarly, errors in CBOs past forecasts of inflation suggest that there is roughly a two-thirds chance that the average annual rate of inflation will fall between 1.9 percent and 3.0 percent over the next five years.
You May Like: Las Vegas Rtc Jobs
Personal Income By County And Metropolitan Area 2020
In 2020, personal income increased in 3,040 counties, decreased in 69, and was unchanged in 3. Personal income increased 6.4 percent in the metropolitan portion of the United States and increased 7.6 percent in the nonmetropolitan portion. Personal income estimates were impacted by the response to the spread of COVID-19, as governments issued and lifted stay-at-home orders. The full economic effects of the COVID-19 pandemic cannot be
Explanation Of The Expenditure Authorities Table
Expenditure authority from Parliament is provided in two ways: annual Appropriation Acts, or Supply Bills, that specify the amounts and broad purposes for which funds can be spent and other specific statutes that authorize payments and set out the amounts and time periods for those payments. The amounts approved in appropriation acts are referred to as voted amounts, and the expenditure authorities provided through other statutes are called statutory authorities. Estimates documents are prepared to support Appropriation Acts however, forecasts of statutory amounts are presented to give a more complete picture of total parliamentary authorities to be used during the fiscal year.
This table provides forecasts of statutory expenditures and the in-year available expenditure authorities for voted authorities by Department, Agency, and Crown Corporation for which a financial requirement has been identified, whether in Main Estimates, or Supplementary Estimates. Budgetary expenditures encompass the cost of servicing the public debt, operating and capital expenditures, transfer payments and subsidies to other levels of government, organizations and individuals and payments to Crown corporations and separate legal entities. This table also presents expenditure authority provided through allocations from Treasury Board Central votes . Central votes are used to supplement other appropriations for such purposes as:
You May Like: City Of Las Vegas Government Jobs
Consequences Of Rising Federal Debt
If federal debt as a percentage of GDP continued to rise at the pace that CBO projects it would under current law, the economy would be affected in two significant ways:
- That growing debt would dampen economic output over time, and
- Rising interest costs associated with that debt would increase interest payments to foreign debt holders and thus reduce the income of U.S. households by increasing amounts.
The increases in debt that CBO projects would also pose significant risks to the fiscal and economic outlook, although those risks are not currently apparent in financial markets. In addition, high debt might cause policymakers to feel constrained from implementing deficit-financed fiscal policy to respond to unforeseen events or for other purposes, such as to promote economic activity or strengthen national defense. Negative economic and financial effects that were less abrupt but still significantsuch as expectations of higher inflation or an increased burden of financing public and private activitywould also have a greater chance of occurring. Those effects would worsen the consequences associated with high and rising federal debt.
To put debt on a sustainable path, lawmakers will have to make significant changes to tax and spending policiesincreasing revenues more than they would under current law, reducing spending below projected amounts, or adopting some combination of those approaches.
