Business Licensing And Banking
Governments have also been exploring applications of blockchain to improve the efficiency of business licensing and banking. Besides property registration, an important aspect of the legal framework of business is providing easy opportunities for businesses to secure a license . Blockchain is used to bring together private and public sectors in an expedited and secure manner. Dubaiâs Smart City initiative seeks to use technology, including blockchain and AI, to increase government efficiency and reduce costs of doing business. Some of its accomplishments include using blockchain to issue business licenses more quickly and to make all business and government transactions entirely paperless, thereby increasing the efficiency of transactions in both the public and private sectors .
Central Bank Digital Currencies
CBDCs offer a way for central banks to improve management of the money supply by, for example, quickly and efficiently getting money into the hands of citizens and businesses in the event of a liquidity crisis. CBDCs also make it possible for governments to offer a higher level of transparency into the money supply, even potentially introducing hard limits on money issuance and government spending.
Companies Trying To Solve This Problem
- General Services Administration U.S. Agency using blockchain to improve services for agencies and citizens.
About Sam Mire
Sam is a Market Research Analyst at Disruptor Daily. He’s a trained journalist with experience in the field of disruptive technology. Hes versed in the impact that blockchain technology is having on industries of today, from healthcare to cannabis. Hes written extensively on the individuals and companies shaping the future of tech, working directly with many of them to advance their vision. Sam is known for writing work that brings value to industry professionals and the generally curious as well as an occasional smile to the face.
Recommended Reading: Government Grants For Furnace Replacement
Trustless Interactions And Transactions
Blockchain for government services offers direct peer-to-peer interactions within private channels along with trustless transactions with proper verification. Furthermore, its an important feature because it gets rid of the trust issues and doesnt fully rely on the paper-based system.
Moreover, if blockchain for government services use the technology to register citizens, then theyll get a blockchain based I.D. Thus, they can finally use it to support their real-time fraud-free government to citizen transactions.
Furthermore, when the citizens give access to their documents on the blockchain for government platform, every single document will get stored securely. In reality, it would also harness personal privacy schemes along with making all interactions trustless and bureaucratic. So, in the end, every service would become much more affordable.
Application Of Blockchain Technology In The Government Sector Part I
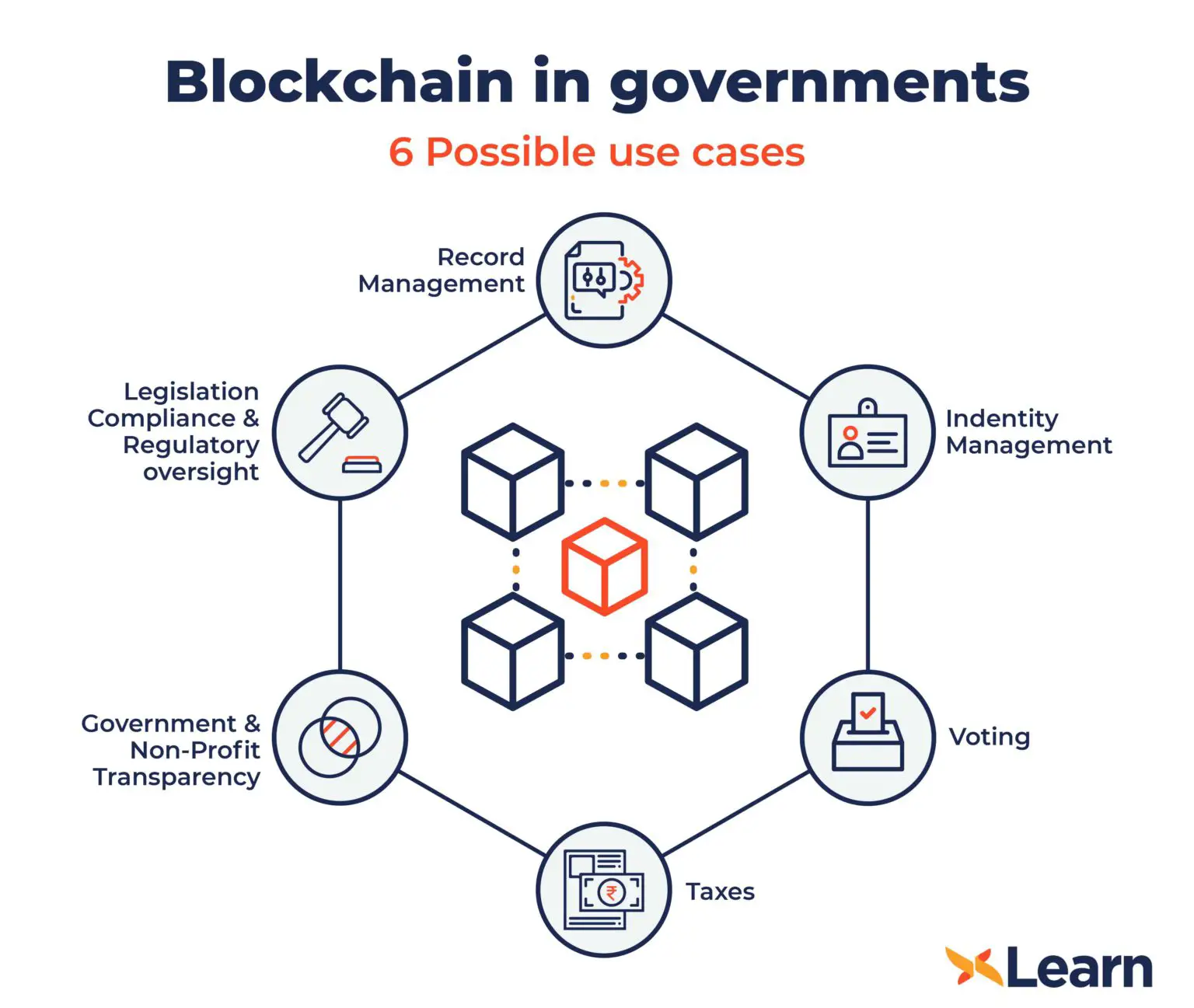
The development of blockchain technology is global. The main reason why this technology is ahead of previous breakthrough technologies and is gaining critical mass so quickly is that it emerged in an era of digital transformation that affected most sectors of the economy.
At a first glance, blockchain and government processes are not the most compatible things. There is a general perception that technology and governments are competing with each other. This is likely because cryptocurrencies are reducing or even eliminating the need for centralized institutions. In fact, we are beginning to see that many nations are pushing for more widespread use of blockchain technology for many reasons.
Blockchain provides governments with a fast, secure, efficient, and transparent way to deliver government services and communicate with their populations. Areas, where governments could apply blockchain, include supply chain, medical records, transportation, voting, energy, taxation, land ownership, tokenization of social benefits, citizen engagement, and the use of digital currencies.
Here are the most used use cases for blockchain technology in government applications.
Also Check: How To Get Government Insurance
Future Of Blockchain And Conclusion
Blockchains have evolved beyond cryptocurrencies to general purpose and can be used across an array of applications, particularly those that need high service availability and data integrity. If their adoption increases, then blockchain-based solutions may reintroduce a trusted broker: the data center, whether in the cloud or on premise. A cloud-based blockchain system makes the cloud provider into a new type of trusted broker. If instead nodes are on premise but are used by the public, then whatever entity is hosting them becomes the trusted broker, and the system becomes vulnerable to any failures that may render the entire system unreliable. Therefore, replacing a fallible human or bureaucracy with a blockchain may shift risk rather than eliminate it .
Blockchain In The Public Sector
- 23 December, 2021
The public sector faces great challenges, among others because it must provide public services, in quantity and quality, efficiently and transparently, and often with fewer available resources.
For this reason, modern technology such as Blockchain is used in many countries, in order to improve the quality of their public services and processes, making them more efficient, transparent, dependable and traceable in order to improve.
Through the present article, I comment on some benefits of applying BC in the public sector, as well as in which cases its application should be analyzed, and next I present some concrete cases of use in order to formulate some final thoughts.
BC is a digital mechanism for creating a distributed digital ledger, in which two or more participants in a peer-to-peer network can exchange information and assets directly, without intermediaries.BC authenticates the participants, validates that they have the assets they want to trade, and records the trades in this digital ledger, of which all participants have an updated copy and whose entries or records, which are not modifiable, are chronologically organized and packaged in blocks, encrypted, and linked to each other.
Its essential elements are distribution, asymmetric encryption and pseudonymity, immutability, tokenization , and decentralization.
Also Check: Annual Credit Report Government Sponsored
Why Is Blockchain Important And Why Does It Matter For Government
HyFi Blockchain | Tokenization of Asset | LEARN Token
Blockchain technology is a decentralized database that allows you to store information securely. This type of technology is used in cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin. You can use it to keep track of contracts, agreements, financial records, voting, etc.
The blockchain consists of blocks which contain a record of transactions. Each block includes a cryptographic hash of the previous block. The data stored in a block cannot be changed without changing the entire chain of hashes.
Improving Shared Services Models
Last year, the complexity of shared services the consolidation of operations across a business divisions for efficiency and cost savings was once again on the rise, as the number of shared services centers with more than three functions rose to 53%, compared with 20% in 2013. And theyre getting better, with 73% of respondents reporting productivity increases of 5% or greater. The adoption of more sophisticated, knowledge-based shared services systems has doubled and even tripled, in some cases since 2013.
Considering some estimates show $27.9 billion in potential savings from the incorporation of shared services systems, these upward trends can be reasonably expected to continue. Many businesses consolidate facets of IT, HR, accounting, payroll, security, and compliance though other facets of an organization can also be included because there is some measure of overlap between these divisions. Fittingly, the blockchain has viable uses in each of these fields, and so it serves as a logical basis for integrating and elevating shared services models going forward.
Read Also: Us Government Medicare Sign Up
Registries Of Beneficial Corporate Ownership
Concerns over opaque or undeclared beneficial company ownership have risen in the wake of recent corruption scandals worldwide. As it stands right now, anyone with the right connections and enough money can use gray-area firms for laundering money, bribing individuals, or lobbying government officials in an illegal way.
To better track conflicts of interest and illegal conduct, many governments are beginning to build a central registry for beneficial business ownership. Blockchain-based registries that are tamper-proof and widely accessible could provide much-needed transparency and disclosure.
Blockchain Iot Use Cases
One of the most unique and promising applications of blockchain technology to the Internet of Things is being spearheaded by IOTA. The IOTA platform was specifically designed for IoT and its backed by the IOTA Foundation.
IOTA offers several blockchain IoT use cases, most significantly regarding the transportation industry, in line with its partnership with Volkswagen. The German car manufacturer had been working with the IOTA Foundation in order to develop their autonomous cars. IOTA-enabled Digital Car Passes will be able to collect and communicate car data, and can also be used to pay parking tickets.
Interestingly, IOTA differs from the traditional blockchains. It has its own distributed ledger technology Tangle which has no miners and no transaction fees. All users in the network approve the transactions, which allows more transactions per second to be approved compared to other blockchains.
IOTA has been criticized for not being completely decentralized since its consensus mechanism depended on a consensus-coordinator node operated by the IOTA foundation. The node constituted a single point of failure for the IOTA network. The good news is that IOTA listened to its critics and no longer uses a consensus coordinator and is thoroughly .
In any case, IOTA promises efficiency coupled with transparency that the car industry and consumers need in order to move into the future.
You May Like: How Do You Qualify For A Free Government Cell Phone
Blockchain Supply Chain Use Cases
One of the most celebrated blockchain supply chain use cases has been IBMs Food Trust, which global food chain giants such as Walmart, Nestle, Unilever, and Carrefour have all signed up for. IBM has its own blockchain platform, a public cloud service that can be used to build different blockchain networks. It is based on Hyperledger Fabric, an open-source collaborative blockchain project hosted by the Linux Foundation.
In 2018, 210 people in 36 different states were infected with E.coli from a bad batch of romaine lettuce. The FDA investigation lasted over two months and the Centers for Disease Control advised people to throw out the lettuce that was grown in Yuma, Arizona. Walmart cited the outbreak to explain the decision to take part in Food Trust, claiming that blockchain technology can be used to trace each batch of goods from farms to the markets.
Blockchain technology offers an alternative to traditional supply chain management systems that benefits both the producers and the consumers. The transparency and immutability of the supply chain records on the blockchain make it possible to prevent any middlemen from adding unjustified costs to their services, and at the same time, it provides traceability for defective goods, thus easing recall efforts.
What Blockchain Can Do In The Government
Blockchain technology ensures that every copy of data is always accessible, verifiable, and trustworthy. In terms of data dispersion, it works similarly to an old photocopying machine in that it can make copies of any object available to everyone who uses it. Moreover, it functions more like a notary public in terms of the trust, ensuring that any copy of data is genuine and that the copies cannot be forgotten or counterfeited. Finally, it works like a general ledger in transaction processing, requiring transactions to get recorded in the same order.
A set of replicated servers known as nodes gets used in handling data exchange, transaction processing, and validation. Each node uses a consensus mechanism to reach an agreement with all other nodes regarding a particular transaction without the need for human intervention.
The primary purpose of such a system is to leverage replication to offer security, notably availability and integrity, while also allowing distributed servers to act as a centralized decision-maker.
You May Like: Working For Us Government Overseas
How Blockchain Contributes To The Transformation Of Government Processes
6 July, 2021
Blockchain and government may seem like an incompatible combination at first glance. However, together they can address key issues such as lack of digitalization and transparency, privacy concerns, inefficiencies, and many more. But how?
Blockchain has come a long way, evolving from a new experimental technology into a vital tool for improving business performance, increasing workflow efficiency, and boosting revenue.
In 2021, Deloitte conducted the Global Blockchain Survey that explored overall attitudes and investments in blockchain and digital assets. The company surveyed 1,280 senior executives and practitioners in 10 countries.
The survey found that 81% of global respondents believe that blockchain technology is broadly scalable and has achieved mainstream adoption and 73% of them shared that their organizations would lose their competitive advantage if they didnt introduce digital assets and blockchain-based solutions.
Governments and public sector organizations are also among those who either already use blockchain or have big plans for this tech. They mainly leverage it to replace inefficient centralized systems that can be unsafe and quite expensive. Blockchain, on the other hand, allows for the creation of more secure, flexible, and cost-effective platforms.
Lets find out more about why governments adopt blockchain, understand what benefits this technology brings, and explore real-life blockchain government use cases.
The National Government As A Blockchain Use Case
The government is simply a group of people shepherding an organized community, or nation. Through Government, organizational policies are enforced and mechanisms for setting these policies are determined. The government system in one state or country differs from another. But they all have their pre-documented book of rules and regulation , governing principles and philosophy This constitution is what sits as the hindrance to absolute lawlessness or deviance of citizens or total oppression of citizens with government personal interests. The word government is commonly affixed in reference to about 200 existing independent national governments on Earth, including subsidiary organizations even though all types of organizations have governance.
Blockchain can be described as a highly secure and decentralized ledger system on which information can be stored but cannot be altered. The population of people that may have knowledge of Blockchain may not be as many as those who dont but Blockchain can still be referred to as a worldwide craze not just for the tech lovers/fanatics or experts but just anyone. The highest tier of regulatory bodies in a state or country which is the government is slowly becoming a part of the blockchain space in one way or another. If the government is involved, it is only a matter of time for the citizens or any layman to be led to Blockchain adoption.
National Cryptos
No Budget Padding
Paper Work, be gone.
You May Like: Government Contracts For Disabled Veterans
Building Trust In Government
Blockchain technology could help government agencies streamline processes and cut costs while improving efficiency and accountability. But there are some challenges associated with adopting blockchain solutions in government. Some experts say governments must consider blockchain technologies’ benefits before implementing them.
Blockchain Use Cases For The Government
CNBCTV18.com
Governments worldwide can benefit immensely from blockchain technology especially as the public roar for blockchain and cryptocurrency adoption grows louder every day. Read on to know more.
The benefits of blockchain to governmentsAlso Read:Five blockchain government use casesDigital identity managementOverhauling the voting systemAlso Read:HealthcarePatent managementCentral Bank Digital Currency
Don’t Miss: Government Mortgage Stimulus Program 2020
Cryptocurrencies And Macroeconomic Policy
Much of the discourse on cryptocurrencies focuses on whether these currencies compete with government. Central banking is considered a core function of public sector governance. Blockchain promises what has been called polycentric banking, which has as one of its manifestations allowing the choice of currency besides those controlled by central banks . Despite the concern of losing control, central banks are issuing their own digital currencies. These central bank digital currencies would serve as a bank for anyone and provide services to people, much like a regular bank. Under any agreement, central banks would have to ensure the interface between people and their currencies is transparent and open. Relatedly, central banks in several countries are exploring open banking, where the central bank shares information with other banks provided the customer allows such sharing of information .
Where Could Blockchain Be Adopted In Government
Federal, state, and local governments are awash in data. The emergence of electronic databases, as opposed to file folders and filing cabinets, dramatically improved the efficiency and cost of managing all that information. But it took the Internet to unlock the greater value by making the data more accessible and transparent. The creation and exchange of that ocean of information take place via a tsunami of transactions each year: collections, disbursements, transfers, procurements, sales, fees, fines, certifications, approvals, and many more. Wherever those transactions involve, or could involve, a digitization of assets and decentralized exchange, there exists a potential blockchain opportunity.
The map in figure 1 displayed many of the announced areas in which public sector leaders are considering using blockchainincluding, in particular, digital currencies and the payments industry. The government must wrestle with these applications simply to continue to keep pace and interact with the commercial sector, as evidenced in the SEC guidance on securities published June 2017.13 Since the general press on blockchain covers these applications comprehensively, well focus more on three areas in which governments current active interest in blockchain potentially leverages the use case characteristics and business values shown in figures 4 and 6: identity management, land registration, and voting.
Existing pain points:
Blockchain value proposition:
Read Also: Free Government Phone Q Link
Though Far From A Mature Technology Blockchain Is Gaining Prominence As A Sound And Highly Secure Method Of Conducting Myriad Transactions In Multiple Applications And Industries
Blockchain technology is a shared database that keeps track of a given collection of transactions. Groups of transactions comprise a block, the contents of which can never be changed. Each block is timestamped and joined to the filled block before it with another block joined behind it when it becomes filled with data, forming what is known as a blockchain. Its most common use is as a distributed ledger wherein all participants agree on each transaction’s “truth” and verify the legitimacy of the transaction before it becomes a permanent record in a block.
There are some private blockchains with few or no other participants in the accounting of transactions. Even so, a block and the blockchain retain the same characteristics.
According to a 2019 Forrester Consulting blockchain survey commissioned by EY, formerly known as Ernst & Young, “preservation of data integrity was the number one driver and most common use case for blockchain adoption,” said Chen Zur, EY U.S. blockchain practice leader. “About half of all the respondents said they prioritize use cases that would improve efficiencies and enable new revenue models like supply chain track and trace, payment support processes and digitization of document flows.”
Blockchain came into prominence with the advent of cryptocurrencies like bitcoin, a peer-to-peer electronic money system. Blockchain use cases and industry applications have since expanded a great deal.
This article is part of
