The Great Federal Debt Debate
Some people worry about the countrys ability to repay its debts, or about passing on debts to the next generation. But generally, most economists agree that there is some level of debt that can be OK, and even beneficial.
Another way to see debt is as a useful tool that allows the government to respond to unforeseen crises , provide necessary services that private industry cant or wont provide, or make long-term investments for the good of the country, like in infrastructure or education. It may even save money in the long run, if we spend to prevent problems from getting more expensive. In this view, leaving some debt for future generations may well be worth it if it also means leaving a safer, stronger country and world. In the case of climate change, more spending on renewable energies now could prevent the worst-case scenarios, making the future safer and also saving money in the long run.
Deficits and debt are actually less controversial than you would think from listening to the rhetoric. Both major political parties in the U.S. tend to run deficits when they are in power. For this reason, its worth reading between the lines and asking some questions when anyone argues against a program or law on the grounds of the debt. Often, its not a question of whether or not to add to the debt. Its more a question of when politicians believe it is worth adding to the debt: from tax cuts to wars to COVID relief, all debt is not created equal.
The Debt Ceiling: An Explainer
The United States hit its debt limit on August 1st, and the Treasury Department will soon run out of cash and other resources to stay below it, risking a default on obligations. Many do not fully understand what the debt limit is and the full impact of a breach. This piece explains the basics of the debt limit, the current situation, and the differences between a debt limit default and a government shutdown.
What is the national debt?
The national debt is the total amount of outstanding borrowings by the U.S. Federal government, accumulated over our history. The Federal government needs to borrow money to pay its bills when its ongoing operations cannot be funded by Federal revenues alone. When this happens, the U.S. Treasury Department creates and sells securities. These securities are the debt owed by the Federal government. There are many different types of Treasury debt bills, notes, and bonds are the most common ones. The various types of debt differ primarily in when they matureranging from a few days to 30 yearsand in how much interest they pay. The United States has not run an annual surplus since 2001, and has thus borrowed to fund government operations every year since then.
What is the debt limit?
The debt limit is a ceiling imposed by Congress on the amount of debt that the U.S. Federal government can have outstanding. This limit has been set at $28.4 trillion since August 1st, 2021.
What happens when the U.S. government hits the debt limit?
National Debt Vs Budget Deficit
Its important to understand the difference between the federal governments annual budget deficit and the national debt. The federal government generates an annual deficit when its spending over the course of a year exceeds government revenue from sources including taxes on personal income, corporate income, and payroll earnings.
When annual congressional appropriations exceed federal revenue, the U.S. Treasury finances the deficit by issuing Treasury bills, notes, and bonds. These Treasury products may be purchased by investors including individuals and pension funds banks, insurers, and other financial institutions and the Federal Reserve as well as foreign central banks.
A countrys national debt is the sum of such annual budget deficits and any offsetting surpluses. It is the total amount of money that a country owes .
Read Also: How To Get Us Government Security Clearance
Wars And Armed Conflict
Overseas wars and military operations and military aid to foreign allies, in combination with increased domestic security spending, interest costs, and long-term veterans funding obligations, have added more than $8 trillion to the national debt since 2001, by one estimate.
Meanwhile, annual U.S. military spending exceeds that of the next nine highest spenders combined.
How Much Debt Is Too Much
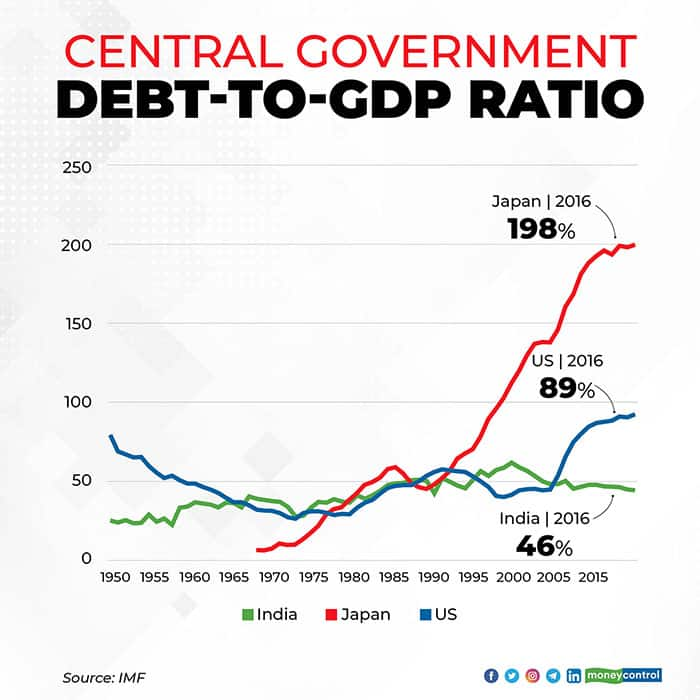
States and municipalities, most of which cannot run chronic deficits like the Federal Government due to state constitutional, statutory and charter prohibitions, must make hard choices if debt becomes burdensome.
Secretary of the Treasury Janet Yellen before the Senate Banking Committee on March 24, 2021
Senator Richard Shelby of Alabama: “Secretary Yellen, in 2017 when you were Chair of the Federal Reserve, you noted that it was concerning to you that the U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio was about 75 percent at that time. Today, the Congressional Budget Office projects debt to reach 102 percent of GDP at the end of 2021. Is the nations growing debt something to be concerned about? “
Secretary Yellen: ” In fact, interest payments on that debt relative to GDP have not gone up at all. I think thats a more meaningful metric of the burden of the debt on society and on the federal finances. I do believe that we have more fiscal space “
Below common debt metrics are listed. Each metric is described, then, for illustrative purposes, metrics are calculated with City of Detroit financial data used as inputs. Data is drawn from FY 2004FY 201310 years up to the Citys bankruptcy.
Debt per capita = debt ÷ population. This ratio measures the debt burden placed on the population supporting the debt.
So, to answer the question at hand: it depends how one measures debt.
C-Span. 2021. Treasury Secretary and Federal Reserve Chair Testimony on COVID-19 Economic Recovery.
Read Also: Government Discount Hotels Las Vegas
Why Is The National Debt So High
When the federal government spends more than it takes in, we have to borrow money to cover that annual deficit. And each years deficit adds to our growing national debt.
Historically, our largest deficits were caused by increased spending around national emergencies like major wars or the Great Depression.
What Makes The Debt Bigger
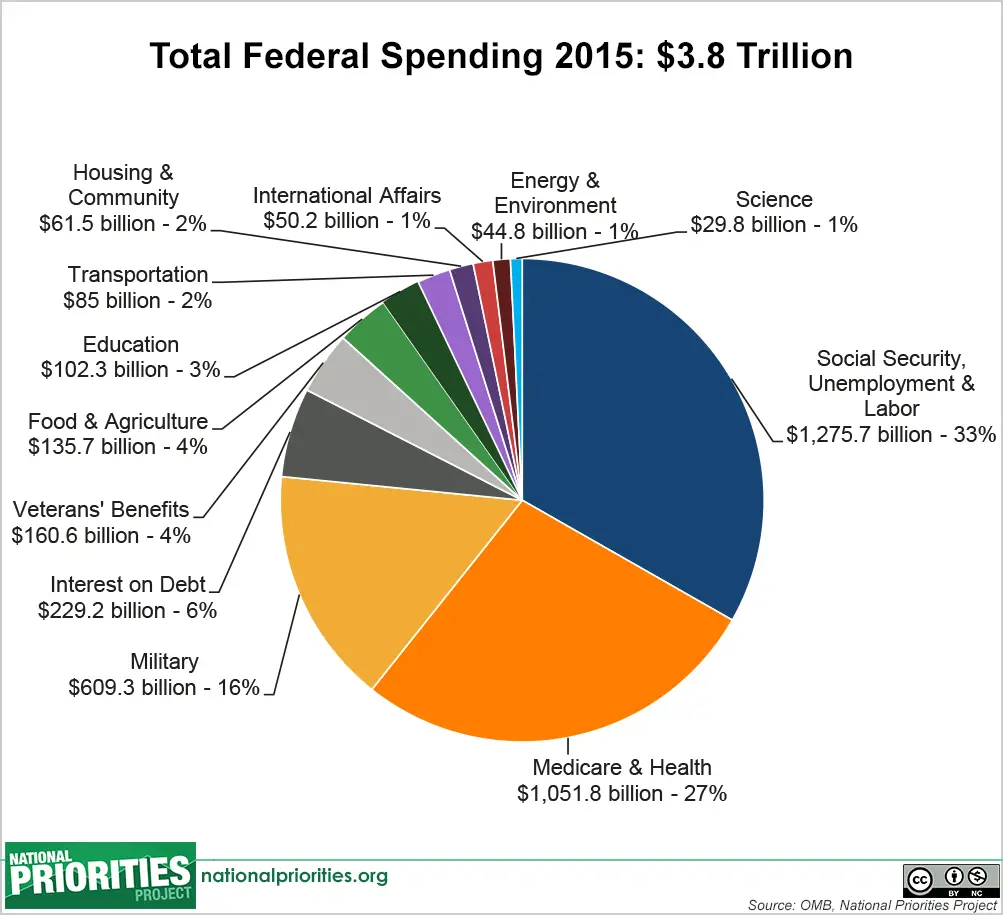
The current leading federal spending categories, which include Social Security, Medicare/Medicaid, and defense, are the same as they were in the 1990s. Thats when the U.S. national debt was much lower relative to GDP. The U.S. remains the worlds largest economy and one of the richest countries. How, then, did the debt situation deteriorate? Numerous factors are in play.
Also Check: Government Assisted Home Care For Seniors
The Us Has $235 Trillion In Debt So How Can It Still Afford A Big Coronavirus Stimulus Package
The U.S. government now owes over US $23.5 trillion in debt, or about $71,000 for every man, women and child living within its borders. It has risen $3 trillion since President Trump took office in 2017 and is almost double what it was just 10 years ago.
U.S. government officials are discussing another expensive stimulus package possibly as much as $1 trillion and bigger than the one enacted in 2009 during the midst of the financial crisis to help the U.S. economy make it through the coronavirus pandemic.
But in light of its large debt, can the federal government really afford more spending?
The national debt represents the accumulation of past deficits that the federal government has run, pretty much continuously, since 1931. Prior to that, surpluses were much more common, apart from the years following the Civil War.
But its size is not a problem. The amount of government debt simply reflects the timing of taxes. Higher spending and lower taxes today mean more borrowing that will need to be paid off by higher taxes in the future.
Not everyone will be happy about that, and the governments resources are not unlimited. But because the economy grows over time, collecting those future taxes make spending today affordable.
In addition, the $23.5 trillion figure, while large, is a bit misleading because $6 trillion of this is owed to other government agencies like Social Security. While thats real money, its a bit like owing your spouse.
Higher Tax Rates = Lower Revenue
Higher tax rates actually leads to lower tax revenue. This is contrary to what almost any politician will tell you. These numbers are adjusted for inflation as well.
In conclusion, as JFK, Reagan, and George W. Bush understood, reducing taxes has a stimulative effect on economic activity and government receipts.
You cant argue with data, economics, and history. This effect holds true for the estate tax, corporate taxes, and property taxes.
Also Check: Why We Need Data Governance
Calculating The Annual Change In Debt
Conceptually, an annual deficit should represent the change in the national debt, with a deficit adding to the national debt and a surplus reducing it. However, there is complexity in the budgetary computations that can make the deficit figure commonly reported in the media considerably different from the annual increase in the debt. The major categories of differences are the treatment of the Social Security program, Treasury borrowing, and supplemental appropriations outside the budget process.
Social Security payroll taxes and benefit payments, along with the net balance of the U.S. Postal Service, are considered “off-budget”, while most other expenditure and receipt categories are considered “on-budget”. The total federal deficit is the sum of the on-budget deficit and the off-budget deficit . Since FY1960, the federal government has run on-budget deficits except for FY1999 and FY2000, and total federal deficits except in FY1969 and FY1998FY2001.
A Brief History Of Us Debt
Debt has been a part of this country’s history from the beginning, starting with the overseas borrowing undertaken to finance the American Revolution.
Despite the effects of the Vietnam War, War on Poverty social programs, and oil price shocks, the U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio declined from 40% in 1966 to 31% by 1980. It rose to 52% by 1990 in the wake of the tax cuts and spending increases advocated by President Ronald Reagan. The debt-to-GDP ratio rose from 64% in 2008 to 100% by 2012, amid the fallout from the Great Recession. Bipartisan relief packages in response to the C0VID-19 pandemic raised the debt-to-GDP ratio from 107% in late 2019 to 135% by mid-2020 from there the ratio declined to 121% by mid-2022.
History shows the debt-to-GDP ratio tends to rise during recessions and in their aftermath, as you would expect. GDP shrinks during a recession, while government tax receipts decline and safety net spending rises. The combination of higher budget deficits with lower GDP serves to inflate the debt-to-GDP ratio. Deep recessions like those in the 1980s and in 2008-2009 can have particularly pronounced and prolonged effects on the national debt, making it less sustainable.
Read Also: Hp Federal Government Employee Discount
Why Measure Debt As A Share Of Gdp
The ratio of publicly held debt to GDP is a better measure of a country’s fiscal situation than just the nominal debt figure because it shows the burden of debt relative to the country’s total economic output and therefore its ability to finance or repay it. This measure also allows for an apples-to-apples comparison of one country’s fiscal situation over time or multiple countries’ debt burden in a meaningful way. A large nominal dollar debt is less of a problem if a country has a large economy and can easily repay it. For example, debt held by the public in 1946 was about $242 billion, or one percent of what it is today. But with a GDP of just $228 billion, debt held by the public was 106 percent of the economy, or roughly nine percentage points higher than its current level.
How Did The Us National Debt Get So Big
Kimberly Amadeo is an expert on U.S. and world economies and investing, with over 20 years of experience in economic analysis and business strategy. She is the President of the economic website World Money Watch. As a writer for The Balance, Kimberly provides insight on the state of the present-day economy, as well as past events that have had a lasting impact.
The Balance / Julie Bang
The U.S. debt is the sum of all outstanding debt owed by the federal government. On Feb. 1, 2022, it surpassed $30 trillion for the first time, and soon after it set another record on Oct. 4, 2022 by passing the $31 trillion mark. The U.S. Treasury Department tracks the current total public debt outstanding and this figure changes daily. The debt clock in New York also tracks it.
The majority of the national debt is debt held by the public. The government owes it to buyers of U.S. Treasury notes including individuals, companies, and foreign governments.
The remaining portion is intragovernmental debt. The Treasury owes this debt to its various departments that hold Government Account Series securities. The biggest owner is the Social Security Trust Fund.
These Government Account Series securities have been running surpluses for years, and the federal government uses these surpluses to pay for other departments. They will come due as people born from 1946 to 1964 retire over the next two decades.
Recommended Reading: Free Government Phones Milwaukee Wi
Debt By Year Compared To Nominal Gdp And Events
In the table below, the national debt is compared to GDP and influential events since 1929. The debt and GDP are given as of the end of the fourth quarter in each year to coincide with the end of the fiscal year. That’s the best way to accurately determine how spending in each fiscal year contributes to the debt and compare it to economic growth.
From 1947-1976, debt and GDP are given at the end of the second quarter since, during that time, the fiscal year ended on June 30. For years 1929 through 1946, debt is reported at the end of the second quarter, while GDP is reported annually, since quarterly figures are not available.
Impacts Of Government Debt
Government debt accumulation may lead to a rising interest rate, which can crowd out private investment as governments compete with private firms for limited investment funds. Some evidence suggests growth rates are lower for countries with government debt greater than around 80 percent of GDP. A World Bank Group report that analyzed debt levels of 100 developed and developing countries from 1980 to 2008 found that debt-to-GDP ratios above 77% for developed countries reduced future annual economic growth by 0.017 percentage points for each percentage point of debt above the threshold.
Excessive debt levels may make governments more vulnerable to a debt crisis, where a country is unable to make payments on its debt, and it cannot borrow more. Crises can be costly, particularly if a debt crisis is combined with a financial/banking crisis which leads to economy-wide deleveraging. As firms sell assets to pay off debt, asset prices fall which risks an even greater fall in incomes, further depressing tax revenue and requiring governments to drastically cut government services. Examples of debt crises include the Latin American debt crisis of the early 1980s, and Argentinas debt crisis in 2001. To help avoid a crisis, governments may want to maintain a fiscal breathing space. Historical experience shows that room to double the level of government debt when needed is an approximate guide.
Read Also: Bank Of America Debt Consolidation
Read Also: Is The Uso A Government Organization
What Is The History Of The National Debt
Since the founding of the United States and the American revolution, debt has been a grim reality in America. When America needed funding for the Revolutionary War in 1776, it appointed a committee, which would later become the Treasury, to borrow capital from other countries such as France and the Netherlands. Thus, after the Revolutionary War in 1783, the United States had already accumulated roughly $43 million in debt.
To cover some of this debt obligation Alexander Hamilton, the first Secretary of the Treasury, rolled out federal bonds. The bonds were seemingly profitable and helped the government create credit. This bond system established an efficient way to make interest payments when the bonds matured and secure the governments good faith state-side and internationally.
The debt load steadily grew for the next 45 years until President Andrew Jackson took office. He paid off the countrys entire $58 million debt in 1835. After his reign, however, debt began to accumulate again into the millions once again.
Flash forward to the American Civil war, which ended up costing about $5.2 billion. Because the war dragged on, the U.S. was strained to revamp the financial systems in place. To manage some of the debt at hand, the government instituted the Legal Tender Act of 1862 and the National Bank Act of 1863. Both initiatives helped lower the debt to $2.1 billion.
In 2008, quantitative easing during the Great Recession more than doubled the national debt.
The National Debt Is Now More Than $31 Trillion What Does That Mean
The gross federal debt of the United States has surpassed $31,000,000,000,000. Although the debt affects each of us, it may be difficult to put such a large number into perspective and fully understand its implications. The infographic below offers different ways of looking at the debt and its relationship to the economy, the budget, and American families.
The $31 trillion gross federal debt includes debt held by the public as well as debt held by federal trust funds and other government accounts. In very basic terms, this can be thought of as debt that the government owes to others plus debt that it owes to itself.
Americas high and rising debt matters because it threatens our economic future. The coronavirus pandemic rapidly accelerated our fiscal challenges, but we were already on an unsustainable path, with structural drivers that existed long before the pandemic. Putting our nation on a better fiscal path will help ensure a stronger and more resilient economy for the future.
Recommended Reading: Tyler Technologies County Government Records
