Supporting Indigenous Data Strategies
Recommendation 8: Recognizing that Indigenous Peoples have an inherent right to self-determination, co-develop with Indigenous partners distinctions-based strategies to advance Indigenous data governance and institutional capacity. The Government of Canada should also work with Indigenous partners, who are the custodians of their data, to co-develop indicators and data collection strategies
Goal: determine data strategies jointly with Indigenous partners, respecting the historical relationship and Canada’s commitment to honour First Nations, Inuit, and Métis rights
Looking ahead, Canada will build on existing achievements, continue to strengthen working relationships with Indigenous partners based on an approach of mutual respect and enhanced collaboration, and introduce new processes as required. This is an opportunity to advance a collaborative approach for data collection, sharing, and stewardship between Indigenous partners and Canada. It would also advance Indigenous leadership and governments’ capacity to govern their own data.
Data Governance Vs Data Privacy Vs Data Security
As our SmartData Governance service continues to gain momentum, theres often a common discussion point with customers around the difference between Data Governance, Privacy and Security/Protection.
The terminology seems to cause confusion over what each of these terms is or isnt, but the reality is theyre all critical to your overall data strategy, so I thought Id provide a short insight into each aspect and why they matter.
Data Governance The Foundation
In my opinion, Data Governance is the foundation for everything else that follows. If you dont have the right governance in place for your critical data assets then when it comes to applying privacy and security controls youre unlikely to get that right.
So what is Data Governance?
The Data Governance Institute defines it as a system of decision rights and accountabilities for information-related processes, executed according to agreed-upon models which describe who can take what actions with what information, and when, under what circumstances, using what methods.
In more simplistic terms, its a system for defining who within an organisation has authority and control over data assets and how those data assets may be used. The goal is to establish the methods, set of responsibilities, and processes to standardise, integrate, protect, and store corporate data, with the aim to:
Minimise risks
Establish internal rules for data use
Implement compliance requirements
Improve internal and external communication
Create A Data Strategy Roadmap
Once youve set goals, you need to outline plans for how you will achieve them. These plans will make up the roadmap for your data strategy.
You should have a plan for how youll accomplish every goal youve set. These plans should be specific and include who owns the goal, what process and technology they will use, how much it will cost, how long it will take and the intended outcome. These plans should also be relatively flexible so you can adjust them if you determine something isnt working as you expected or circumstances change. As your projects progress, you should regularly evaluate them to determine whats working well and what is not.
Your data strategy roadmap will outline how you plan to achieve your ultimate long-term goal and vision, as well as how you will achieve the smaller short-term goals that will help you fulfill your vision.
The Fundamentals Of Defining A Data Strategy For Your Business
Abraham Lincoln was quoted as saying Give me six hours to chop down a tree and I will spend the first four sharpening the ax.
You want to bear that quote in mind when defining your data strategy. Thats how Bernard and Philippe summarised the matter when we first discussed writing this article.
Bernard and Philippe have been working in the data field for years now. They have seen the rise and decrease of the Big Data enthusiasm, and were observing that artificial intelligence and blockchain might be following a similar path . Along the way, they have experienced the many challenges, gaps and unmet expectations that data-related technologies brought with them.
While some of those technologies are stunning and will be, arguably, more and more part of our daily lives in the next few years, a data-driven and automated world doesnt come so easily. As long as we dont have clean and quality data, sound data governance, efficient data management and a well-thought-out data strategy, pitfalls will be hard to overcome.
Years of discussion with numerous leaders addressing matters such as data strategy, data management, data architecture and digital upskilling, have helped them to identify patterns. For instance, numerous leaders have had difficulties in defining their organisations data strategy. Sometimes the basicsdetermining what a datum isisnt that obvious, and there is confusion about what data, information and digitalization are.
Greater Oversight To Better Leverage Data
Recommendation 1: Establish a senior level decision-making body for horizontal data issues by modifying the mandate and membership of DM CEPP
Recommendation 2: Strengthen and clarify roles and responsibilities around enterprise data leadership, including by establishing a Government of Canada Chief Data Steward
Recommendation 3: Develop and implement new frameworks with respect to the ethical and secure use of data
Goal: strengthen data leadership, drive change and support the strategic use of data
A deputy minister-level committee for data issues
The government has established a number of new government-wide senior official committees in recent years to support its efforts to adapt to digital and data developments. While these committees have tackled many important issues, there is a need for increased coordination of effort toward greater cohesion and coherence so that key organizations are represented and take part in the decision-making process.
- provide strategic direction
- encourage greater data and analytics use
- align and prioritize data-related investments or gaps
- drive progress on data strategies
- ensure open by default and sharing by default
- compel data decisions to be holistic.
International best practices
Roles and responsibilities around data
Champion enterprise data stewardship
Enterprise-level and organizational data stewardship can:
Next steps
Data Governance: Why Its The Key To Effective Analytics In 2021
Bad data is a real problem for your company. It can lead to extra work, a bad customer experience, and even data breaches. Fortunately, bad data can be resolved and prevented with a proper data governance strategy.
Bad data can be a real problem for your company if you allow it to sneak into your data stream. According to estimates, the side effects of bad data could cost your company as much as 30% of your yearly revenue.
Fortunately, bad data can be resolved, and even prevented, with a proper data governance strategy.
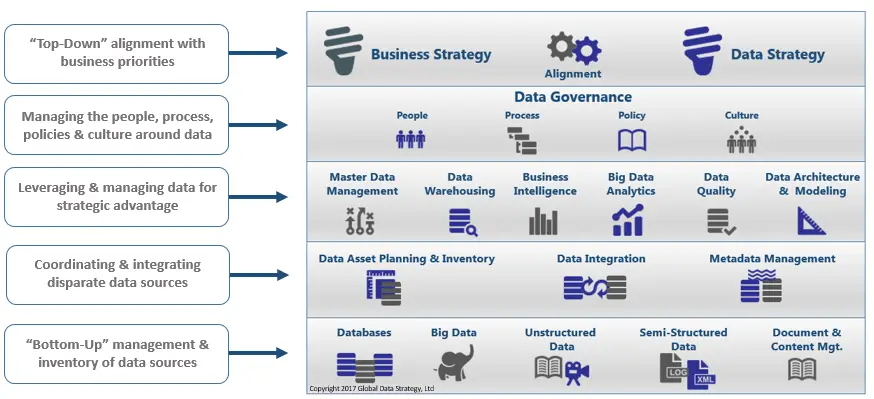
Data Governance Vs Data Management: Key Differences
Data can be one of the most valuable assets for any organization. With the rise of big data, companies can take advantage of vast stores of enterprise data to gain insights and make better decisions. However, as we create and store more data, consumer privacy concerns are growing. Companies need to comply with increasing numbers of regulations, such as GDPR. Data breaches occur with greater frequency, and they can be extremely damaging to an organizations reputation as well as expensive to clean up. The risks of poor data policies are severe, even fatal for organizations. Its essential to create data governance and data management practices to make sure that data is handled properly. Lets look at data governance vs data management.
Data Management And Data Governance: The Intersection
While the two roles are distinct, it is important to notethat data management and governance sometimes intersect. For instance, abusiness unit might have a request for more information or data from its seniormanagement. In such a case, it is the data management teams responsibility tofacilitate that access. They must ensure that users accessing the data aregiven only those privileges they require and are role-based. This way, theywill not be able to access or modify more than what they need for theirassigned job purposes. Likewise, there will be controls put in place torestrict access even further if needed.
Lastly, data management and data governance can work intandem. In this case, a business unit might want to gather more informationfrom its systems that is not readily available for analysis or reporting. Forthis, it will get involved with the data security team to ensure that onlyauthorized users have the necessary access to gather this data.
Plan For Data Storage And Organization
Your data strategy should also include policies related to data storage and organization. These aspects of data management are crucial, as they help determine how actionable and shareable your data is.
Data storage is a relatively simple technology capability, but methods for storing data can vary significantly from company to company. When creating your storage plans, you need to consider how much storage capacity you need, but you should also consider how your approach to storage will impact data sharing and usage. The way you organize your data impacts how easy it is to access, understand and use. Your storage solution also influences how easy it is for different departments to share data.
Ultimately, your goal in creating a data storage and organization plan is to make your data as accessible, shareable and actionable as possible for the parties that may need it. Different approaches may work best for different companies, but, generally, you should store your data in an easily accessible system in a consistent format.
So What Then Is Data Governance
Data governance refers to the management of data in order to improve business outcomes and fuel business growth.
So far, with the exception of asset type, data governance very similar to IT governance.
The stakeholders involved for data governance include all the individuals required for IT governance plus a few more executives: the board, executives in finance, operations, marketing, sales, HR, vendors, CIO, IT management.
However, the individual responsible for aligning data with the organizations business metrics is the chief data officer . The CDO will also enlist data scientists, programmers, and any department that generates data, which is every department within an organization.
CDOs are a recent addition to the C-suite, and they help lead companies in generating business value from data. According to Gartner, 90 percent of large organizations will have a chief data officer by 2019.
Yes, a CDO is very much a technical role, but this position also requires business and change management skillsets. After all, they have to aggregate the data, analyze the data and the most challenging of all, get the business to act on the data.
Since this data governance is a relatively new field, there arent established frameworks, such as COBIT 5.
But based on my research and speaking with pros at conferences, a companys executive suite should be asking some of the following questions:
Drivers Challenges And Goals
Drivers
The greatest driver of the SCDS is the changing requirements for data and information of Canadians, Canadian businesses and Canadian institutions. Canadians want an authoritative source of information about what is important to them â relevant information and insights which respond to the increasingly complex economy and society. The legalization of cannabis, the opioid crisis, and the effect of foreign ownership on property values are some recent examples. Statistics Canada like many other National Statistical Offices around the world is responding to this need by reshaping its business model, building new networks and expertise, and devising new ways of unlocking the value of data for public good.
Challenges
The Data Strategy Roadmap for the Federal Public Service included details on challenges faced by Government of Canada organizations:
- Absence of horizontal governance for strategic direction on data issues
- Lack of data literacy and cultural reticence to break silos
- Lack of adequate digital infrastructure and a complex rules framework
- Challenge of acquiring, governing, and managing large volumes of disparate data
Statistics Canada faces similar challenges. The agency modernization agenda is addressing these challenges through digital transformation in the form of IT modernization, the move to a broader use of administrative and alternative data sources, and fostering collaboration and partnerships with external partners including other NSOs.
Goals
What Is Master Data Management
Master data such as customer, product, asset and location data are embedded in a number of applications in a typical enterprise, only one of which is its ERP system. The field of master data management was developed in order to try to get a handle on this.
The idea behind a master data management strategy was to either copy data out from other systems into a trusted master data store that could then be used by other systems or to map where it was stored and document the differences — e.g., a product might be classified in a simple hierarchy by one department or business unit but a more detailed way by another.
For example, a marketing department might care about the brand of a product, its packaging and whether it is on special offer, but a logistics department cares about the number of products in a palette, its dimensions and weight and where to deliver it. These different needs drive different categorizations, which in turn become embedded in different computer systems.
Better Understand The Information We Hold
Recommendation 17: Establish a centralized view of government-held data, develop a government data quality framework, and develop guidance for the long-term management of digital government assets
Goal: know what data we hold and ensure their quality and maintenance
Know what data the government holds
To increase the use of and access to data and reduce duplication, we must first have a complete view of the data we hold, along with an understanding of their quality, location, and format. This exercise will create an interface or tool to view all government data assets and will support interoperability so that organizations can share, combine and make optimal use of data. The work involves attaining a common vision for governance and stewardship and the development of a data reference model, privacy protection, security protocols and a maintenance plan. This will leverage existing work, including StatCan’s Inventory of Administrative Data Providers from the Public Sector. Experience gained will inform metadata standards and inform a data reference model for a whole-of-government approach.
Next steps
Ensure the quality and maintenance of data
Next steps
- Analyze current data quality policies/practices by January 2019
- Draft proposed quality approach/framework by May 2019
Maintain digital information
Next steps
Data visualization as a tool for new insights
Supporting government decisions and accelerating change
Harnessing data visualization for internal decision-making
Peernovas Cuneiform Platform: Active Data Governance
Enterprises struggle with building effective data management and data governance strategies due to siloed systems and data quality challenges. Enterprises experience data quality issues due to their existing data governance approach and static metadata tools.
PeerNovas Cuneiform Platform is an active data governance and data quality tool that provides a strong backbone to enterprise data management strategy. The platform automatically builds, updates, monitors, and optimizes data dictionaries, glossaries, catalogs, and rule repositories. Using a dynamic approach to data quality and management, the platform creates end-to-end , integrated, and active lineages across disparate tools and systems. The Rules Engine in the platform executes all business rules in near real-time. Data Quality rules are also run as part of the Rules Engine dynamically. This means that high-quality data and metrics around data quality are always current. When there are data quality issues, the platform provides integration into third-party workflow/exception management tools to ensure that the issues are resolved quickly. Root cause analysis of the data quality issues can be performed faster using active lineages. Through a self-serve model, enterprises can create accurate regulatory and governance reports with strict audit control.
In summary, PeerNovas solution ensures enterprises can more easily implement an effective data governance framework and data management strategy.
Establishing Guidelines For Data Analysis And Application
Similarly, your data strategy should define guidelines for how employees should analyze and use data. Data governance can address this, and your business goals should inform how you interpret and apply your data. Although learning new rules may slow developers down at first, the long-term benefits will make up for this initial learning curve.
Building Block #: Launching Data Management Enabling Projects
As each Lighthouse Project gets completed, youll find yourself iteratively building deeper foundations of data management capability, albeit fully aligned to business outcomes.
Success depends on getting the business engaged and excited about the art of the possible as each slice of data capability increases in maturity following each project win.
When the business experiences the positive change resulting from data, they start to drive and take ownership of the data conversation, which is preferable to relying on IT and technical teams to guide the way.
Weve found this Agile approach delivers far more impact against strategic and tactical drivers whilst incrementally building out the key elements of a progressive Chief Data Office function.
The diagram below illustrates how, with a recent client, we iteratively rolled out layers of data maturity and function, one enabling project at a time:
The key to this approach is to assure the completion of the most critical projects, i.e. those with executive attention.
Streamlining Data Collection And Sharing
A data strategy can help you establish consistent processes for collecting and sharing data. Having established procedures means you can collect more data more efficiently, and that the data you collect will likely be higher-quality. It also keeps your information consistent and well-organized, which makes it easier to use and helps you derive value from it.
One way to make your data more shareable and usable is to establish rules for naming element data and representing data value. You also need a way to reference and access metadata. Creating a glossary of business data terminology can help with this.
Reason : Security And Compliance With Laws Concerning Data Governance
Consequences for non-compliance with data regulations can be enormous, especially where private individuals information is concerned. A case in point, the European General Data Protection Regulation for May 2018 sets non-compliance fines up to some $22 million or four percent of the offenders worldwide turnover, whichever is the higher, for data misuse or breach affecting European citizens.
Effective data governance helps an organization to avoid such issues, by defining how its data is to be acquired, stored, backed up, and secured against accidents, theft, or misuse. These definitions also include provision for audits and controls to ensure that the procedures are followed. Realistically, organizations will also conduct suitable awareness campaigns to makes sure that all employees working with confidential company, customer, or partner data understand the importance of data governance and its rules. Education and awareness campaigns will become increasingly important as user access to self-service solutions increases, as will the levels of data security already inherent in those solutions.
