Grow Up Kid: The Maturity Model
Measuring your organization up against a data governance maturity model can be a very useful element in making the roadmap and communicating the as-is and to-be part of the data governance initiative and the context for deploying a data governance framework.
One example of such a maturity model is the Enterprise Information Management maturity model from Gartner, the analyst firm:
Figure 2.
Most organizations will before embarking on a data governance program find themselves in the lower phases of such a model.
Phase 0 Unaware: This might be in the unaware phase, which often will mean that you may be more or less alone in your organization with your ideas about how data governance can enable better business outcomes. In that phase you might have a vision for what is required but need to focus on much humbler things as convincing the right people in the business and IT on smaller goals around awareness and small wins.
Phase 1 Aware: In the aware phase where lack of ownership and sponsorship is recognized and the need for policies and standards is acknowledged there is room for launching a tailored data governance framework addressing obvious pain points within your organization.
Phases 4 and 5 Managed & Effective: By reaching the managed and effective phases your data governance framework will be an integrated part of doing business.
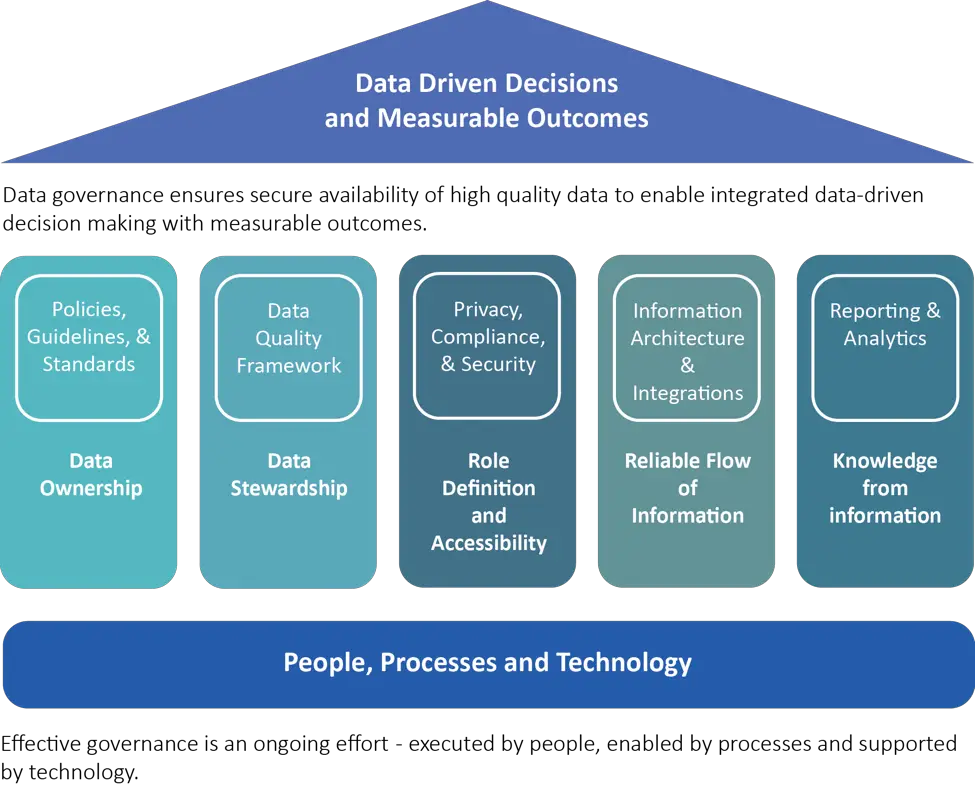
Collaborative Data Governance Framework Template A Modern Approach
A collaborative data governance framework is all about balancing the concerns of the top-down and bottom-up philosophies. This framework recognizes that working with data as a team is essential for success otherwise, the amount of work needed to validate that the data is trustworthy will be overwhelming.
The collaborative framework is scalable, allowing for an increasing number of data sources to be introduced by an increasing number of people across the organization. Well-defined principles for collaborative content curation must be established to maintain this scalability. This can involve selecting subject matter experts in each business unit to serve as data stewards who help maintain high data quality for the datasets they know best.
Of course, some business processes rely on heavily regulated data elements that require specific attention. Risk data aggregation in financial services, for example, or data like consumer credit card information may not be the best candidates for this approach. In these cases, the collaborative framework can complement, rather than replace, a more controlled top-down approach. The organizations data governance team should define which data governance model applies in these types of situations.
Data Governance Framework Best Practices Definitions And Examples
Inside Out Security Blog » Compliance & Regulation » Data Governance Framework Best Practices, Definitions and Examples
Its 2020, do you know where your data is? If you answered yes to that rhetorical question, you have a decent grasp of data governance. If not, its time to start to figure that out. Either way, read on to learn more about data governance and how Varonis can help automate you out of a big hole.
If you need more convincing about why you need data governance, check out the Varonis 2019 Data Risk Report. Its an eye-opener.
You May Like: Safelink Free Replacement Phone
Why You Need A Data Governance Policy
Data is an asset, just like cash, buildings, and people. Just like other assets, data requires strong, consistent management.
When we neglect data, the results arent pretty you get data quality issues, conflicting information, and confused staff who dont know how to get answers. The result is lower quality data that causes mistrust and frustration. Staff turn to other means intuition, politics, and tradition when its not easy to make data-guided decisions and that can cost your organization.
Data governance is a cross-functional management activity that, at its core, recognizes data as an enterprise asset. A data governance policy will ensure that your association is treating data as an asset.
Data Governance Manager And Team
Data governance managers may be covered by the chief data officer role or may be separate staff. This role is responsible for managing your data governance team and having a more direct role in the distribution and management of tasks. This person helps coordinate governance processes, leads training sessions and meetings, evaluates performance metrics, and manages internal communications.
Recommended Reading: Government Suburban 2500 For Sale
How Are Gdpr And Data Governance Readiness Related
In 2016, the European Union adopted GDPR. This powerful privacy regulation expanded the definition of personal data as any data that can directly or indirectly be used to identify an individual. Suddenly, organizations had to classify a wider range of data assets as sensitive data in need of extra protection. GDPR also stipulates that any personal data belongs to the data subject, rather than the organizations that may collect or use that data.
With GDPR in place, any business with customers in the EU must be able to answer key questions about how it handles data ownership. Those questions include:
- Where does all personal data exist across the organization?
- How is data ownership assigned within the organization?
- Should the ownership of data be single-point or collaborative?
Since data owners within an organization have a vested interest in the integrity of their data, they can focus on defining policies and standards that keep their data compliant. For example, data owners can implement deletion and retention policies that ensure that the sensitive data they are responsible for aligns to regulatory requirements.
Check out our Definitive Guide to Data Governance today
Data Governance In Healthcare
Healthcare may be at the top of the list of industries that require a comprehensive data governance policy. Consider the enormous amount of healthcare data available to any individual, the sensitive nature of that data, and the life-or-death situations that rely on accurate data. It is indeed understandable why data governance is critical in healthcare.
Patient records, blood test results, EKGs, MRIs, billing records, drug prescriptions, and other sensitive medical information are all examples of data in the healthcare profession. Medical professionals require healthcare data to make educated decisions about patient treatment. Data governance gives healthcare organizations a regulated and structured way to share medical data so that each patient receives the best possible treatment.
Recommended Reading: Los Lunas Gov
Data Protection And Data Privacy
The increasing awareness around data protection and data privacy as for example manifested by the European Union General Data Protection Regulation has a strong impact on data governance.
Terms as data protection by default and data privacy by default must be baked into our data policies and data standards not at least when dealing with data domains as employee data, customer data, vendor data and other party master data.
As a data controller you must have the full oversight over where your data is stored, who is updating the data and who is accessing the data for what purposes. You must know when you handle personal identifiable information and do that for the legitimate purposes in the given geography both in production environments and in test and development environments.
Having well enforced rules for deletion of data is a must too in the compliance era.
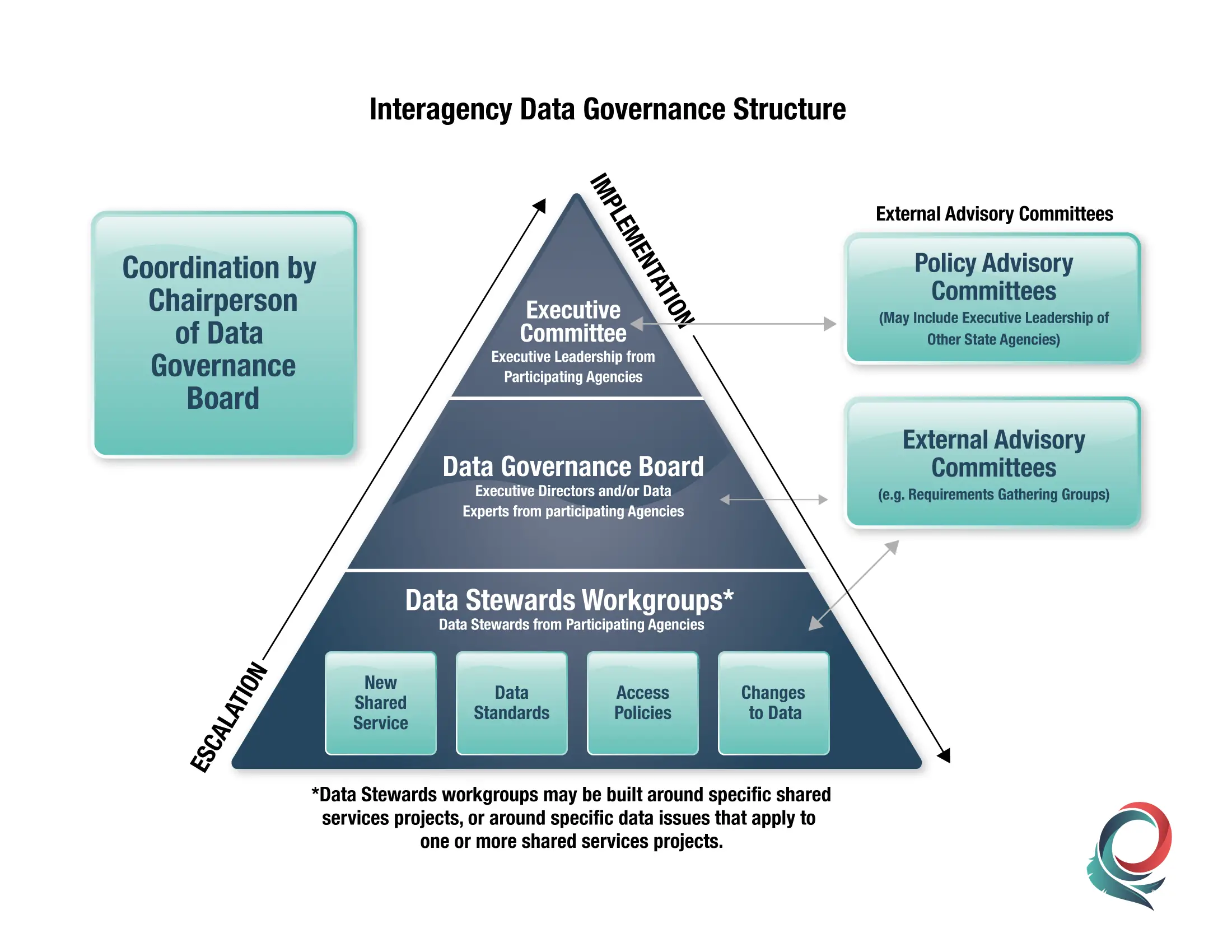
Data Governance Structure Policy
Data governance involves making strategic, effective decisions about a company’s data and information assets. It defines laws, policies and restrictions that affect all members of the business communityincluding employees, subcontractors, and external partnersdirecting them how to use and manage data correctly.
A structure policy defines how data governance will be practiced at the organization. The organization should adopt formal guidelines to manage company data and information resources and require employees to follow them. It also defines who should manage data governance at the organizationprimarily a data governance leader position, and the enterprise data management team, assisted by senior managers, administrators, data stewards who help to organize and maintain datasetdss, and end-users of the data.
Don’t Miss: Government Dental Grants
The 10 Components Of Data Governance
All data management programs get built on the foundation of data governance. It is a necessary practice that underpins all other aspects of data management expertise. It also features components for each knowledge area that fulfill the companys data management requirements. These 10 components include:
What Businesses Need Data Governance
Most businesses benefit from strong data governance, but industries with heavy regulatory burdens such as banking, finance, and health care have a greater need for formalized governance initiatives and are particularly focused on activities that put them at regulatory risk. Adherence to the regulatory challenges directly impact how they manage, report, and protect their sensitive information. Noncompliance can lead to fines, brand damage, or even jail time.
However, it should be noted that any organization that collects sensitive data, such as financial information, Social Security numbers, or medical records, is also subject to regulatory compliance mandates. Strong data governance first validates and promotes quality data, and then puts in place policies, controls, and management to meet internal and external expectations.
And although banking, finance, and healthcare are some of the most highly regulated industries, their governance structures can provide advantages that go beyond information security. In health care, for example, knowledge acquisition can open up opportunities for better patient outcomes.
Also Check: City Of Hot Springs Jobs
Policy Vs Standard Vs Control Vs Procedure
|
When it comes to cybersecurity compliance, words have specific meaning and it is important to get those terms correct. In reality, these cybersecurity documentation terms have quite different implications and those differences should be kept in mind since the use of improper terminology has cascading effects that can negatively impact the internal controls of an organization. Cybersecurity, IT professionals, privacy and legal professionals routinely abuse the terms policy and standard as if these words were synonymous, when they are not! ComplianceForge compiled the information on this page to help get everyone on the same sheet of music, since documentation terminology is important as these words have specific meanings as they pertain to cybersecurity and privacy requirements. Cybersecurity & data protection documentation needs to usable it cannot just exist in isolation. This means the documentation needs to be written clearly, concisely and in a business-context language that users can understand. By doing so, users will be able to find the information they are looking for and that will lead to cybersecurity and privacy “best practices” being implemented throughout your organization. Additionally, having clearly-written and concise documentation can be half the battle when preparing for an audit, since it shows that effort went into the program and key requirements can be easily found. |
Click here for a free guide |
What Right Looks Like
In the context of good cybersecurity documentation, these components are hierarchical and build on each other to build a strong governance structure that utilizes an integrated approach to managing requirements.
Well-designed documentation is comprised of five core components:
- Policies are established by an organizations corporate leadership establishes managements intent for cybersecurity and data protection requirements that are necessary to support the organizations overall strategy and mission.
- Control Objectives identify the technical, administrative and physical protections that are generally tied to a law, regulation, industry framework or contractual obligation.
- Standards provide organization-specific, quantifiable requirements for cybersecurity and data protection.
- Guidelines are additional guidance that is recommended, but not mandatory.
- Procedures establish the defined practices or steps that are performed to meet to implement standards and satisfy controls / control objectives.
You May Like: Assurance Wireless Las Vegas Nv
How To Implement A Data Governance Initiative
A goal of a data governance initiative is to identify the principles for the team and to establish targets and direction. This template will aid you in capturing the meaning of data governance for your organization before you begin your initiative. It will help you gain sponsorship and educate the organization about your mission, vision, and goals.
What Wrong Looks Like
All too often, documentation is not scoped properly, and this leads to the governance function being more of an obstacle as compared to an asset. A multiple-page policy document that blends high-level security concepts , configuration requirements , and work assignments is an example of poor governance documentation that leads to confusion and inefficiencies across technology, cybersecurity, and privacy operations. Several reasons why this form of documentation is considered poorly-architected documentation include:
- Human nature is always the mortal enemy of unclear documentation, as people will not take the time to read it. An ignorant or ill-informed workforce entirely defeats the premise of having the documentation in the first place.
- If the goal is to be audit ready with documentation, having excessively-wordy documentation is misguided. Excessive prose that explains concepts ad nauseum in paragraph after paragraph makes it very hard to understand the exact requirements, and that can lead to gaps in compliance.
Read Also: Where To Buy Gold Bars In Las Vegas
Why Is Data Governance Important
Data is, without a doubt, an organizations most valuable asset. Data governance ensures that information is useful, available, and secure. Data governance translates to improved data analytics, which leads to better decision-making and operations management. It also aids in the prevention of data inconsistencies or errors, which can result in data integrity concerns, poor decision-making, and many organizational issues.
Moreover, data governance is also critical for compliance issues, ensuring that firms meet all levels of regulatory obligations consistently. This feature is essential for decreasing operational expenses and eliminating vulnerabilities. At its most basic level, data governance leads to greater data quality, lower data management costs, and greater data access for all users. As a result, you make better decisions, which leads to better business outcomes.
The Difference Between Data Governance And Data Management
The Dictionary of Data Management defines data governance as the exercise of authority, control, and shared decision making over the management of data assets. Data governance initiatives provide the foundation to develop appropriate data management protocols and procedures.
Data management, on the other hand, is the process that puts governance policies into action. Governance provides a framework thereafter, you can define areas for management and infrastructure or architecture management. The governance establishes the why and who for data accessibility and control, while management sets the where and how.
In a similar vein, it should be noted that data governance and data quality are not synonymous, but are closely related. Data quality is the measurement of data accuracy, completeness, availability, and effectiveness. Data governance policies apply guidelines to this vetted data.
Don’t Miss: Grants To Start A Trucking Company
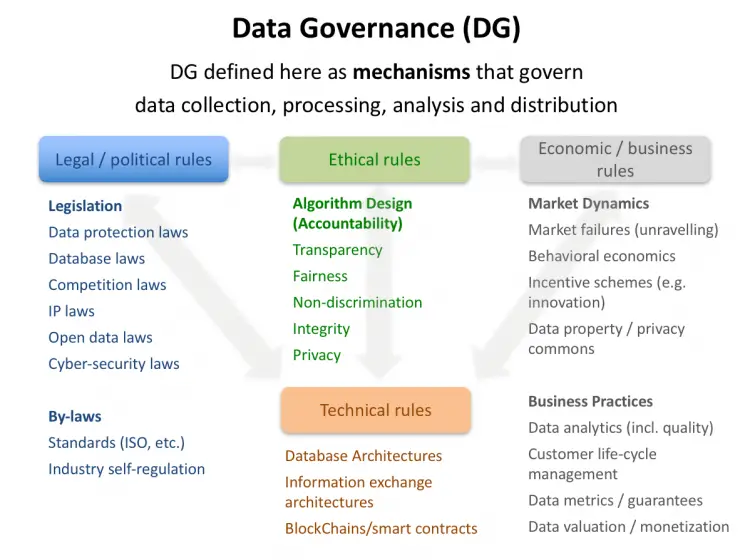
What Is Data Governance
Data Governance is the process, and procedure organizations use to manage, utilize, and protect their data. In this context, data can mean either all or a subset of a companys digital and/or hard copy assets. In fact, defining what data means to an organization is one of the data governance best practices. Once you have defined data, you can brainstorm all the ways you could use your data to advance your business.
Think of data governance as the who, what, when, where, and why about your organizations data.
Another aspect of data governance is protecting the company and customer private data, which should be a high priority task for organizations in this day and age. Data breaches are near-daily occurrences in 2019 and governments are enacting laws HIPAA, GDPR, CCPA, and more to protect the private data of citizens. A data governance program builds controls to protect data and help organizations adhere to compliance regulations.
S To Creating A Data Governance Policy
Building a data governance policy doesnt take place in a vacuum. This process should be part of a bigger effort to implement a data governance plan or to create a data governance framework. Organizations typically have some of the components in place for a solid policy, such as an identified mission and purpose.
If your data governance policy creation is a standalone exercise, here are the recommended steps:
You May Like: Replacement Government Phone
Normative Laws And Regulations
Every successful data governance process will need to develop and follow uniform rules and regulations to secure the data and guarantee it gets handled according to all relevant external laws. These standardized rules and regulations, which will be developed at the data governance council level and implemented by the data steward, will provide criteria for all aspects of data usage.
What Is A Data Governance Policy And Why Is It Important
Data governance policies are guidelines that you can use to ensure your data and assets are used properly and managed consistently. These guidelines typically include policies related to privacy, security, access, and quality. Guidelines also cover the roles and responsibilities of those implementing policies and compliance measures.
The purpose of these policies are to ensure that organizations are able to maintain and secure high-quality data. Governance policies form the base of your larger governance strategy and enable you to clearly define how governance is carried out.
Recommended Reading: Huntsville Al Government Jobs
Why Do Organizations Need Data Governance
More and more, in-house information is finding a new life as a valued asset across the entire organization rather than simply as the property of individual departments. In fact, many data governance initiatives originate as attempts to improve data as it becomes actionable across the organization. Data is now used to develop organizational efficiencies, identify profit opportunities, enhance customer experiences, and improve or develop new products.
However, two of the primary reasons for data governance are regulatory mandates and risk assessments that rely on high-quality data. In particular, many regulations focus on an organizations data to show proof of compliance, especially in the area of data security. According to the 2013 Rand Secure Archive Data Governance Survey, 82 percent of respondents know they face external regulatory requirements, but 44 percent of those respondents still dont have a defined data governance policy.
Areas that benefit from data governance include those that require regulatory reporting data to meet guidelines for Sarbanes-Oxley Basel I, II, and III COBIT Dodd-Frank cGMP ISO/IEC 38500 and elements of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act .
