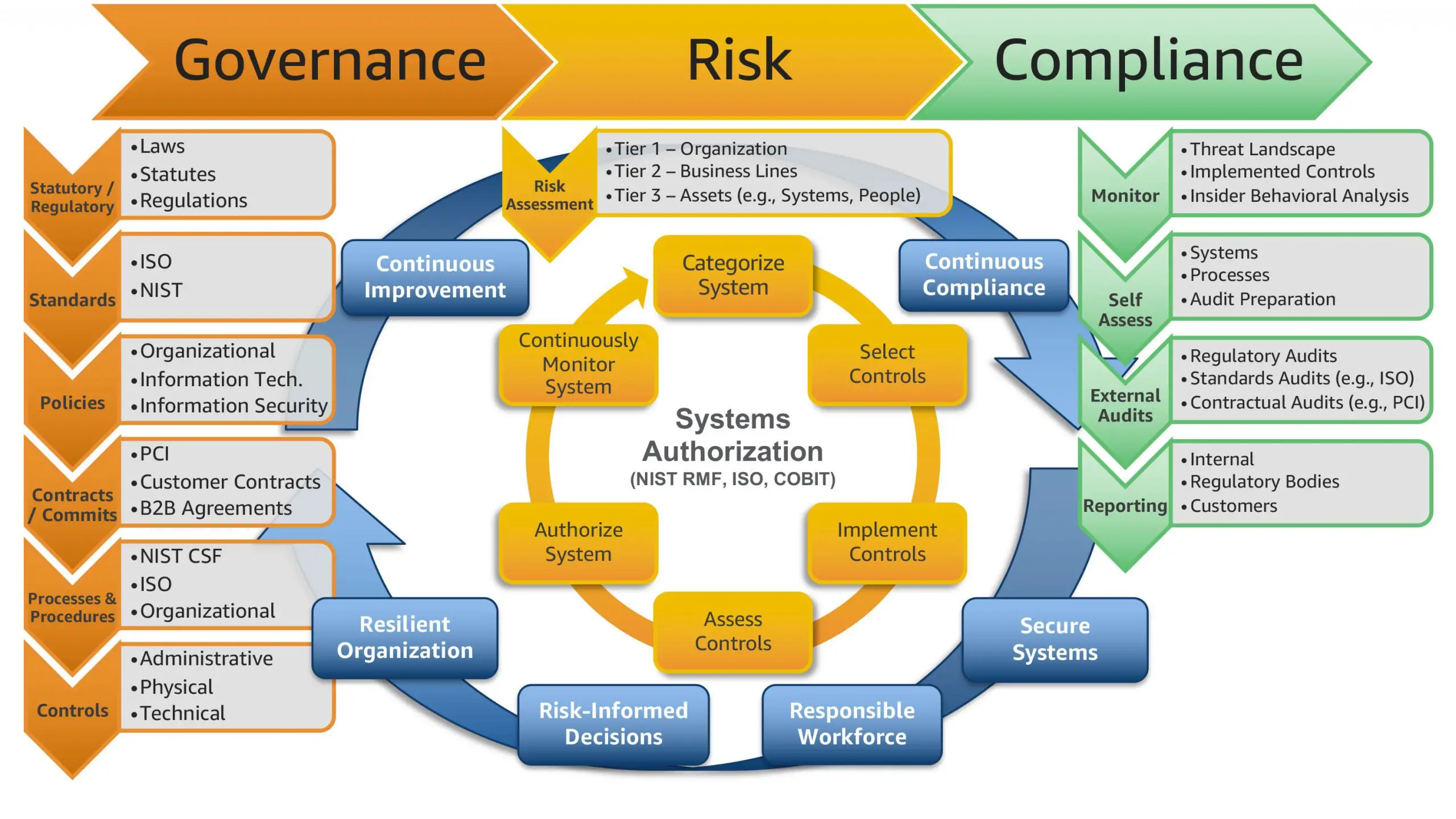
Data Lake And Sandboxes
BigData Architecture Proposal, Review and Recommendations and Solution Engineering, Without a systematic and automated way to manage and govern data, you wont know what data you have, be able to trust your data quality, provide access to data for multiple users, or comply with security and privacy regulations.
Overcome Business Compliance Challenges With Better Data Quality And Data Governance
Looking ahead, its safe to say regulatory compliance will only bring more changes and widen its reach. See how the intersection of data quality and data governance can help you overcome compliance challenges.
As new, stringent regulations emerge with greater frequency than ever before, assessing data quality on an ongoing basis is necessary for keeping up with the evolving regulatory compliance landscape. Otherwise youll be reacting to the regulation at hand rather than proactively addressing compliance.
Compliance with regulatory initiatives is prompting many organizations to closely examine their data quality and data governance efforts. But as organizations address these requirements, they find that the intersection of data quality and data governance offers significant business benefits beyond the compliance focus.
Data governance and data quality tools, along with outputs like data relationship maps and data lineage graphs, are highly complementary for regulatory compliance use cases. Data governance tools provide a broad set of essential capabilities to identify and manage data assets, including enabling non-technical business users to define data policies and associated rules using natural language. However, data governance tools do not:
- support the technical application of rules to your data
- express those rules in a valid technical syntax
- test your data to verify compliance with rules on an ongoing basis
Protect Customer Privacy While Enriching Data Analytics
Learn more about Dataguise and AWS »
Effectively complying with global privacy lawslike the General Data Protection Regulation requires an automated technology solution that discovers and protects sensitive data across a variety of repositoriesand, ideally, preserves the business value and availability of that data.
DgSecure, an automated, no-coding, policy-based data privacy solution from Dataguise, helps simplify compliance with numerous privacy regulations, including GDPR. DgSecure immediately identifies and masks sensitive data, and protects and monitors that data on an ongoing basis.
Watch this webinar to learn how Trv Insurance Solutions, an insurance agency licensed to sell on-demand property and casualty insurance products, adopted DgSecure on Amazon Web Services to anonymize production data to help comply with GDPR and other data privacy regulations. The solution helps Trv meet privacy standards while enabling its analytics teams to use data to better serve its clients.
Webinar Topic:AWS Presenter:Partner Presenter:
Recommended Reading: Congress Mortgage Stimulus Middle Class
What Are Evolving Trends In Data Governance
Recent events such as the COVID-19 pandemic and the passage of GDPR and other data privacy legislation have hastened the need for strong data governance. The following are some of the broader data governance trends that are emerging.
- Unstructured data is on the rise: The explosion of unstructured data information held in random documents, images and videos across the enterprise is one of the biggest challenges facing businesses today. And content sprawl is expected to get worse, increasing risk and expenses.
- Remote work is creating islands of sensitive data: Legions of employees suddenly working from home are creating more security issues, largely attributed to employees using personal devices on home networks.
- Artificial intelligence is coming to data management: Emerging AI and machine learning tools can be used to identify documents that contain sensitive data often where it is not supposed to be. These tools can then use automation technologies to redact or encrypt the information in those documents, helping to secure enterprise data without manual oversight, often in real time.
- Data quality is increasingly considered at the source: Why clean up data after you receive it when instead you can be sure that its high in quality from the start? Numerous recent strategies aim to let businesses work more closely with their partners to keep customer data accurate and synchronized across various channels.
Build A Trusted Data Sharing Capability With Data Republic
Learn more about Data Republic »
Innovative companies know they need to quickly analyze data, increase its capacity to be shared, and move faster than competitors to make business decisions based upon data insights. At the same time, they face stringent benchmarks for data security and control, regulatory requirements, and data governance.
Learn how ANZ, a large Australian bank, uses Data Republics Senate Platformdeployed on Amazon Web Services to confidently and quickly analyze and share internal and external datasets. The Senate Platform applies robust legal, governance, and licensing workflows and enables ANZ to leverage its data while remaining confident that customer privacy and PII is protected.
Webinar Topic:AWS Presenter:Partner Presenter:
You May Like: Rtc Bus Driver Salary Las Vegas
Data Governance Challenges Are Not The Same For Everyone
Diverse governance’s use-cases based on industry needs and organizations size
There are two main drivers for data governance programs:
- Level of regulation needed in the industry
Data regulation push the minimum bar of data governance processes higher. It requires business to add controls, security, reporting and documentation. Organizations set up a governance program to ensure transparency over sometimes unclear processes.
- Level of complexity of the data assets
Having a strong governance become increasingly important with the exponential growth of data resources, tools and people in a company.
The level of complexity increases with the scope of business operations , the velocity of data creation or the level of automation based on data.
Data Governance For Regulatory Compliance And Data Protection
In the past couple of months, I’ve been approached by a number of clients asking about the role of the chief data officer in instituting appropriate data governance processes and procedures to address regulatory compliance. This is motivated in part by the the European Unions General Data Protection Regulation that went into effect in May 2018, demanding some level of data management accountability for protecting personal data. But my impression is that we’re at a tipping point in terms of awareness of the connections between external pressures for data protection and effective, internally defined data protection policies.
Consider that the GDPR is only the tip of the iceberg the full impact of compliance won’t be determined until we begin to see which organizations are alerted to their noncompliance, and penalties are assessed. A number of US states are developing legislation and passing laws about data privacy that are similar in tone to GDPR. In particular, California has passed the California Consumer Privacy Act mandating protection of personal data .
Read Also: Local Government Federal Credit Union Member Connect
Three Key Points For Chief Data Officers
All things considered, I believe there are three key points for the CDO to consider when looking at data governance for regulatory compliance and data protection:
- Regulatory compliance implies the need for data protection.
- The scope of regulatory compliance covers more than just protecting data.
- The scope of data protection extends beyond regulatory compliance.
Lets break these points apart by doing a close reading of an example regulation, CCPA. First, I think it’s interesting that the text of the assembly bill I found online has the phrase personal information in it 204 times. But the phrase is used 142 times before it’s defined. That being said, their definition of personal information is:
Personal information means information that identifies, relates to, describes, is capable of being associated with, or could reasonably be linked, directly or indirectly, with a particular consumer or household. Personal information includes, but is not limited to, the following:
Identifiers such as a real name, alias, postal address, unique personal identifier, online identifier Internet Protocol address, email address, account name, social security number, drivers license number, passport number, or other similar identifiers.
Any categories of personal information described in subdivision of Section 1798.80.
Characteristics of protected classifications under California or federal law.
Biometric information.
Geolocation data.
Hitachi Content Platform S Series
Cost-optimized exabyte scale deep data storage and protection for Hitachi Content Platform with among the worlds greatest density.
Thank you. We will contact you shortly.
Note: Since you opted to receive updates about solutions and news from us, you will receive an email shortly where you need to confirm your data via clicking on the link. Only after positive confirmation you are registered with us.
If you are already subscribed with us you will not receive any email from us where you need to confirm your data.
Explore more about us:
Don’t Miss: Government Benefits For Legally Blind
What Is Data Governance And Gdpr
Data governance refers to the policies and processes that define the appropriate use of data as it flows into and out of an organization. Data governance is not implemented through a single technology but rather is a wide-ranging discipline that comprises people, processes, strategies, guidelines and tools in order to achieve its goals.
Specifically, data governance and data governance initiatives are concerned with ensuring that organizations maintain high standards throughout the data life cycle from creation to long-term storage, archiving and disposal for the purposes of internal policies as well as external regulations. This is important because successful data governance leads to the right decision-making based on the right data armed with accurate, consistent and up-to-date information about customers, markets and assets, an organization is able to act properly in response to new data-changing business conditions. Conversely, companies with poor data governance systems often find themselves floundering in fast-paced market conditions, paralyzed due to a lack of information or misled into making the wrong choices.
Data governance has become especially critical for global regulatory mandates such as the European Unions General Data Protection Regulation , which among other things, protects a consumers right to be forgotten, while imposing steep financial penalties of more than $20 million or up to 4% of annual worldwide turnover for violations.
Benefits Of Data Governance
Most companies already have some form of governance for individual applications, business units, or functions, even if the processes and responsibilities are informal. As a practice, it is about establishing systematic, formal control over these processes and responsibilities. Doing so can help companies remain responsive, especially as they grow to a size in which it is no longer efficient for individuals to perform cross-functional tasks. Several of the overall benefits of data management can only be realized after the enterprise has established systematic data governance. Some of these benefits include:
- Better, more comprehensive decision support stemming from consistent, uniform data across the organization
- Clear rules for changing processes and data that help the business and IT become more agile and scalable
- Reduced costs in other areas of data management through the provision of central control mechanisms
- Increased efficiency through the ability to reuse processes and data
- Improved confidence in data quality and documentation of data processes
- Improved compliance with data regulations
Don’t Miss: Hiro Mortgage Program Legit
Why Do I Need A Data Governance Framework
A data governance framework enables the business to define and document standards and norms, accountability, and ownership. In addition to setting out roles and responsibilities, this involves establishing key quality indicators , key data elements , key performance indicators , data risk and privacy metrics, policies and processes, a shared business vocabulary and semantics, and data quality rules.
A data governance framework includes discovery of data to create a unified view across the enterprise. This includes not only the data itself, but data relationships and lineage, technical and enterprise metadata, data profiling, data certification, data classification, data engineering, and collaboration.
A data governance framework supports the execution of data governance by defining the essential process components of a data governance program, including implementing process changes to improve and manage data quality, managing data issues, identifying data owners, building a data catalog, creating reference data and master data, protecting data privacy, enforcing and monitoring data policies, driving data literacy, and provisioning and delivering data.
How Do You Set Up A Good Data Governance And Privacy Strategy
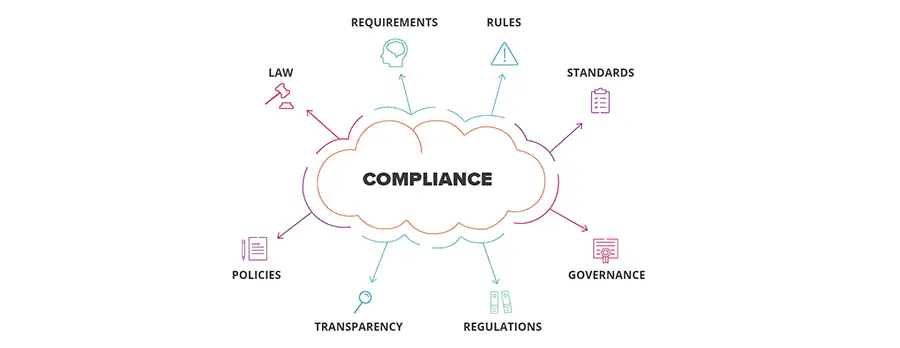
Several bricks are needed to enforce data management
- Data Architecture
Before even talking about data governance framework, a company needs the basis: a good infrastructure to begin with. Based on business needs and the company’s data maturity, the nature of the data architecture framework can change a lot. Regarding storage, do you go for: on-premise or cloud? data warehouse or data lake? Regarding modeling: Spark or DBT? in data warehouse or in BI tool? real-time or batch? Regarding visualization: do you allow anyone to build dashboards or data teams only? etc.
- Search and Discovery
The first level of any data governance strategy is making sure relevant people can find the relevant datasets to do their analysis or build their AI model. If you don’t implement this step, companies end up with a lot of questions on Slack and useless meetings with the engineering teams. The company ends up with a lot of duplicate tables, analyses and dashboards. It takes valuable time to engineering resources that are needed to perform the next steps.
- Metadata and Documentation
- Data Quality
- Security and Access Rights
- Compliance and Regulation
Also Check: Where To Buy Gold Bars In Las Vegas
Data Governance Goals And Benefits
A key goal of data governance is to break down data silos in an organization. Such silos commonly build up when individual business units deploy separate transaction processing systems without centralized coordination or an enterprise data architecture. Data governance aims to harmonize the data in those systems through a collaborative process, with stakeholders from the various business units participating.
Another data governance goal is to ensure that data is used properly, both to avoid introducing data errors into systems and to block potential misuse of personal data about customers and other sensitive information. That can be accomplished by creating uniform policies on the use of data, along with procedures to monitor usage and enforce the policies on an ongoing basis. In addition, data governance can help to strike a balance between data collection practices and privacy mandates.
Foundation For Data Governance Readiness
To get a more in-depth look at the methods and best practices you can use to implement a successful data governance initiative at your organization, read the Definitive Guide to Data Governance.
Youll learn more details about the various data governance strategies discussed above. You’ll also explore new areas including:
- Multiple ways that data governance initiatives can save you time, money, and resources
- How to choose the best data governance strategies and models for your needs
- Three steps to delivering high quality data you can trust, at any scale
- Tips for building a data team and a data-driven culture
Read Also: Grant For Dental Implants For Seniors
Pitfalls With Data Governance
Data governance, as with any other major data practice, is not without its own pitfalls. A few of the most common ones include:
Hyper-focusing on IT: Though often those in technology disciplines are the first to recognize the need for governance, they are neither the creators nor the users of the data.
SOLUTION: Keep the majority of data governance efforts on the business side and integrate IT as an active partner
Assuming the value of data is understood: Not everyone within an organization is aware of the value of data and subsequently of the value of ensuring its quality. This generally occurs not because people are willfully ignorant, but rather because they have had the benefit of only receiving the clean data instead of having to work with the resources necessary to achieve it.
SOLUTION: Communicate the value of clean data and how important it is to becoming a better business from within.
Choosing the wrong metrics: Its tempting to pick an easy and straightforward metric that may ultimately sound great, but not actually mean anything . Instead, choose metrics that demonstrate how improvements to data and governance are helping people to achieve their goals.
SOLUTION: Connect different metrics that demonstrate both progress and impact across an entire company.
SOLUTION: Make data governance a change in culture and mindset and include all departments in the planning and creation of data governance strategies.
Why Data Governance Matters
Without effective data governance, data inconsistencies in different systems across an organization might not get resolved. For example, customer names may be listed differently in sales, logistics and customer service systems. That could complicate data integration efforts and create data integrity issues that affect the accuracy of business intelligence , enterprise reporting and analytics applications. In addition, data errors might not be identified and fixed, further affecting BI and analytics accuracy.
Poor data governance can also hamper regulatory compliance initiatives, which could cause problems for companies that need to comply with new data privacy and protection laws, such as the European Union’s GDPR and the California Consumer Privacy Act . An enterprise data governance program typically results in the development of common data definitions and standard data formats that are applied in all business systems, boosting data consistency for both business and compliance uses.
Also Check: Nevada Federal Jobs
Organizations That Already Have A Data Governance Capability In Place Have A Solid Head Start And Can Leverage It To Facilitate Many Aspects Of Data Privacy Compliance
Agile Innovations in Data Management
GDPR. CCPA. Whats next? Data privacy regulations are just starting to take hold. As of the end of 2018, were over 6 months past the GDPR deadline, and barely a year away from the California Consumer Privacy Act. Many companies are still analyzing and formulating their approaches to these new regulations. A recent survey by the International Association of Privacy Professionals notes that more than 50 percent of companies estimate that they are not yet compliant with the GDPR.
However, these regulations are part of a growing desire by consumers to ensure that organizations take more care with their data. Their impact is global and real, and there will be more enacted, in the form of additional states , or even at the federal level.
The first major GDPR fine was Googles $57 million fine from the French data authority, which Google plans to appeal. The regulator laid out two areas in which Google was failing to meet GDPR standards: